ComPPI: a cellular compartment-specific database for protein-protein interaction network analysis
- PMID: 25348397
- PMCID: PMC4383876
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gku1007
ComPPI: a cellular compartment-specific database for protein-protein interaction network analysis
Abstract
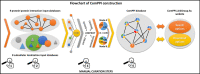
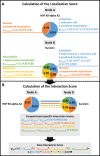
Here we present ComPPI, a cellular compartment-specific database of proteins and their interactions enabling an extensive, compartmentalized protein-protein interaction network analysis (URL: http://ComPPI.LinkGroup.hu). ComPPI enables the user to filter biologically unlikely interactions, where the two interacting proteins have no common subcellular localizations and to predict novel properties, such as compartment-specific biological functions. ComPPI is an integrated database covering four species (S. cerevisiae, C. elegans, D. melanogaster and H. sapiens). The compilation of nine protein-protein interaction and eight subcellular localization data sets had four curation steps including a manually built, comprehensive hierarchical structure of >1600 subcellular localizations. ComPPI provides confidence scores for protein subcellular localizations and protein-protein interactions. ComPPI has user-friendly search options for individual proteins giving their subcellular localization, their interactions and the likelihood of their interactions considering the subcellular localization of their interacting partners. Download options of search results, whole-proteomes, organelle-specific interactomes and subcellular localization data are available on its website. Due to its novel features, ComPPI is useful for the analysis of experimental results in biochemistry and molecular biology, as well as for proteome-wide studies in bioinformatics and network science helping cellular biology, medicine and drug design.
© The Author(s) 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures


References
-
- Firth S.M., Baxter R.C. Cellular actions of the insulin-like growth factor binding proteins. Endocr. Rev. 2002;23:824–854. - PubMed
-
- Azar W.J., Zivkovic S., Werther G.A., Russo V.C. IGFBP-2 nuclear translocation is mediated by a functional NLS sequence and is essential for its pro-tumorigenic actions in cancer cells. Oncogene. 2014;33:578–588. - PubMed
-
- Semenza G.L. Regulation of oxygen homeostasis by hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Physiology (Bethesda) 2009;24:97–106. - PubMed
-
- Koh G.C.K.W., Porras P., Aranda B., Hermjakob H., Orchard S.E. Analyzing protein-protein interaction networks. J. Proteome Res. 2012;11:2014–2031. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

