Pharmacokinetics, safety, and tolerability of faldaprevir in patients with renal impairment
- PMID: 25348520
- PMCID: PMC4291359
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.03359-14
Pharmacokinetics, safety, and tolerability of faldaprevir in patients with renal impairment
Abstract
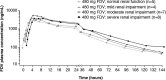
Faldaprevir is a potent hepatitis C virus (HCV) NS3/4A protease inhibitor with negligible urinary excretion. We assessed the pharmacokinetics and safety of a single oral dose of faldaprevir (480 mg) in 32 HCV-negative subjects with renal impairment or normal renal function. Compared with subjects with normal renal function, the adjusted geometric mean ratios (90% confidence intervals in parentheses) for overall exposure area under the concentration-time curve from zero to infinity (AUC0-∞) were 113.6% (41.6 to 310.2%), 178.3% (85.2 to 373.0%), and 169.2% (73.2 to 391.2%) for subjects with mild, moderate, and severe renal impairment, respectively. Overall, 5/8 (63%) subjects with normal renal function and 20/24 (83%) subjects with renal impairment reported adverse events, with gastrointestinal events being the most common. No severe or serious adverse events or deaths were reported. These results suggest that moderate or severe renal impairment can result in a modest increase in faldaprevir exposure. The increase in exposure may be related to decrease in the activity of the liver uptake transporter OATP1B1 as a result of renal impairment. Given this relatively slight increase in exposure, a dose adjustment in HCV patients with renal impairment is not warranted. (This study has been registered at ClinicalTrials.gov under registration number NCT01957657.).
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of the hepatitis C virus protease inhibitor faldaprevir on the pharmacokinetics of an oral contraceptive containing ethinylestradiol and levonorgestrel in healthy female volunteers.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015 Jan;59(1):514-9. doi: 10.1128/AAC.03589-14. Epub 2014 Nov 10. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015. PMID: 25385099 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Safety and efficacy of faldaprevir with pegylated interferon alfa-2a and ribavirin in Japanese patients with chronic genotype-1 hepatitis C infection.Liver Int. 2014 Jan;34(1):78-88. doi: 10.1111/liv.12254. Epub 2013 Aug 15. Liver Int. 2014. PMID: 23944720 Clinical Trial.
-
Mechanisms underlying benign and reversible unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia observed with faldaprevir administration in hepatitis C virus patients.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2014 Nov;351(2):403-12. doi: 10.1124/jpet.114.218081. Epub 2014 Sep 9. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2014. PMID: 25204339 Clinical Trial.
-
Faldaprevir for the treatment of hepatitis C.Drugs Today (Barc). 2015 May;51(5):289-301. doi: 10.1358/dot.2015.51.5.2321008. Drugs Today (Barc). 2015. PMID: 26097902 Review.
-
Faldaprevir for the treatment of hepatitis C.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Mar 4;16(3):4985-96. doi: 10.3390/ijms16034985. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25749475 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
In Silico Evaluation of the Effectivity of Approved Protease Inhibitors against the Main Protease of the Novel SARS-CoV-2 Virus.Molecules. 2020 May 29;25(11):2529. doi: 10.3390/molecules25112529. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32485894 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical