Phosphorylation status of human RNA-binding protein 8A in cells and its inhibitory regulation by Magoh
- PMID: 25349214
- PMCID: PMC4935374
- DOI: 10.1177/1535370214556945
Phosphorylation status of human RNA-binding protein 8A in cells and its inhibitory regulation by Magoh
Abstract
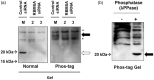
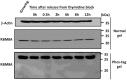
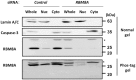
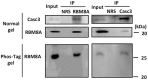
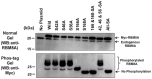
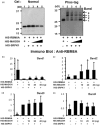
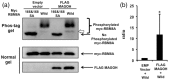
The RNA-binding protein 8A (RBM8A)-mago-nashi homolog, proliferation-associated (Magoh) complex is a component of the exon junction complex (EJC) required for mRNA metabolism involving nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD). RBM8A is a phosphorylated protein that plays some roles in NMD. However, the detailed status and mechanism of the phosphorylation of RBM8A is not completely understood. Therefore, in this study, we analyzed in detail RBM8A phosphorylation in human cells. Accordingly, analysis of the phosphorylation status of RBM8A protein in whole-cell lysates by using Phos-tag gels revealed that the majority of endogenous RBM8A was phosphorylated throughout the cell-cycle progression. Nuclear and cytoplasmic RBM8A and RBM8A in the EJC were also found to be mostly phosphorylated. We also screened the phosphorylated serine by mutational analysis using Phos-tag gels to reveal modifications of serine residues 166 and 168. A single substitution at position 168 that concomitantly abolished the phosphorylation of serine 166 suggested the priority of kinase reaction between these sites. Furthermore, analysis of the role of the binding protein Magoh in RBM8A phosphorylation revealed its inhibitory effect in vitro and in vivo. Thus, we conclude that almost all synthesized RBM8A proteins are rapidly phosphorylated in cells and that phosphorylation occurs before the complex formation with Magoh.
Keywords: Magoh; Phos-tag gel; RBM8A(Y14); mRNA; phosphorylation.
© 2014 by the Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Depletion of RNA-binding protein RBM8A (Y14) causes cell cycle deficiency and apoptosis in human cells.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2013 Aug 1;238(8):889-97. doi: 10.1177/1535370213494646. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2013. PMID: 23970407
-
RNA-binding protein RBM8A (Y14) and MAGOH localize to centrosome in human A549 cells.Histochem Cell Biol. 2014 Jan;141(1):101-9. doi: 10.1007/s00418-013-1135-4. Epub 2013 Aug 15. Histochem Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 23949737
-
Two mammalian MAGOH genes contribute to exon junction complex composition and nonsense-mediated decay.RNA Biol. 2013 Aug;10(8):1291-8. doi: 10.4161/rna.25827. Epub 2013 Jul 23. RNA Biol. 2013. PMID: 23917022 Free PMC article.
-
Multifaceted roles of MAGOH Proteins.Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Feb;50(2):1931-1941. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07904-1. Epub 2022 Nov 17. Mol Biol Rep. 2023. PMID: 36396768 Review.
-
The Physiological Roles of the Exon Junction Complex in Development and Diseases.Cells. 2022 Apr 1;11(7):1192. doi: 10.3390/cells11071192. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35406756 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 and alternative splicing.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2018 Nov;9(6):e1501. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1501. Epub 2018 Aug 17. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2018. PMID: 30118183 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiple Phosphorylations of SR Protein SRSF3 and Its Binding to m6A Reader YTHDC1 in Human Cells.Cells. 2022 Apr 26;11(9):1461. doi: 10.3390/cells11091461. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35563766 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphoproteomics reveals that glycogen synthase kinase-3 phosphorylates multiple splicing factors and is associated with alternative splicing.J Biol Chem. 2017 Nov 3;292(44):18240-18255. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.813527. Epub 2017 Sep 15. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28916722 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic approach to understand the molecular physiology of symbiotic interaction between Piriformospora indica and Brassica napus.Sci Rep. 2018 Apr 10;8(1):5773. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-23994-z. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29636503 Free PMC article.
-
Function and pathological implications of exon junction complex factor Y14.Biomolecules. 2015 Apr 10;5(2):343-55. doi: 10.3390/biom5020343. Biomolecules. 2015. PMID: 25866920 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

