Preservation of memory with conformal avoidance of the hippocampal neural stem-cell compartment during whole-brain radiotherapy for brain metastases (RTOG 0933): a phase II multi-institutional trial
- PMID: 25349290
- PMCID: PMC4239303
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2014.57.2909
Preservation of memory with conformal avoidance of the hippocampal neural stem-cell compartment during whole-brain radiotherapy for brain metastases (RTOG 0933): a phase II multi-institutional trial
Abstract
Purpose: Hippocampal neural stem-cell injury during whole-brain radiotherapy (WBRT) may play a role in memory decline. Intensity-modulated radiotherapy can be used to avoid conformally the hippocampal neural stem-cell compartment during WBRT (HA-WBRT). RTOG 0933 was a single-arm phase II study of HA-WBRT for brain metastases with prespecified comparison with a historical control of patients treated with WBRT without hippocampal avoidance.
Patients and methods: Eligible adult patients with brain metastases received HA-WBRT to 30 Gy in 10 fractions. Standardized cognitive function and quality-of-life (QOL) assessments were performed at baseline and 2, 4, and 6 months. The primary end point was the Hopkins Verbal Learning Test-Revised Delayed Recall (HVLT-R DR) at 4 months. The historical control demonstrated a 30% mean relative decline in HVLT-R DR from baseline to 4 months. To detect a mean relative decline ≤ 15% in HVLT-R DR after HA-WBRT, 51 analyzable patients were required to ensure 80% statistical power with α = 0.05.
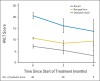
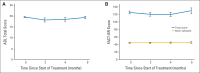
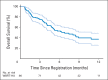
Results: Of 113 patients accrued from March 2011 through November 2012, 42 patients were analyzable at 4 months. Mean relative decline in HVLT-R DR from baseline to 4 months was 7.0% (95% CI, -4.7% to 18.7%), significantly lower in comparison with the historical control (P < .001). No decline in QOL scores was observed. Two grade 3 toxicities and no grade 4 to 5 toxicities were reported. Median survival was 6.8 months.
Conclusion: Conformal avoidance of the hippocampus during WBRT is associated with preservation of memory and QOL as compared with historical series.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01227954.
© 2014 by American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest are found in the article online at
Figures

Comment in
-
Hippocampal-avoidance whole-brain radiation therapy: a new standard for patients with brain metastases?J Clin Oncol. 2014 Dec 1;32(34):3789-91. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2014.58.4367. Epub 2014 Oct 27. J Clin Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25349293 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Does Hippocampal-Avoidance Whole-Brain Radiotherapy for Brain Metastases Meaningfully Change Current Practice?J Clin Oncol. 2015 Jun 10;33(17):1985. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2014.60.4769. Epub 2015 Apr 20. J Clin Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25897152 No abstract available.
-
Reply to M.C. Chamberlain.J Clin Oncol. 2015 Jun 10;33(17):1986. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2015.60.9297. Epub 2015 Apr 20. J Clin Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25897163 No abstract available.
-
[Memory protection with conformal avoidance of the hippocampal neural stem-cell compartment during whole-brain radiotherapy for brain metastases?].Strahlenther Onkol. 2015 Jun;191(6):534-5. doi: 10.1007/s00066-015-0834-2. Strahlenther Onkol. 2015. PMID: 26221646 German. No abstract available.
References
-
- Eriksson PS, Perfilieva E, Björk-Eriksson T, et al. Neurogenesis in the adult human hippocampus. Nat Med. 1998;4:1313–1317. - PubMed
-
- Monje ML, Mizumatsu S, Fike JR. Irradiation induces neural precursor-cell dysfunction. Nat Med. 2002;8:955–962. - PubMed
-
- Gondi V, Hermann BP, Mehta MP, et al. Hippocampal dosimetry predicts neurocognitive function impairment after fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for benign or low-grade adult brain tumors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2013;85:348–354. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

