Stretch-activated ion channel Piezo1 directs lineage choice in human neural stem cells
- PMID: 25349416
- PMCID: PMC4234578
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1409802111
Stretch-activated ion channel Piezo1 directs lineage choice in human neural stem cells
Abstract
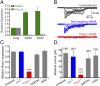
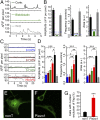
Neural stem cells are multipotent cells with the ability to differentiate into neurons, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes. Lineage specification is strongly sensitive to the mechanical properties of the cellular environment. However, molecular pathways transducing matrix mechanical cues to intracellular signaling pathways linked to lineage specification remain unclear. We found that the mechanically gated ion channel Piezo1 is expressed by brain-derived human neural stem/progenitor cells and is responsible for a mechanically induced ionic current. Piezo1 activity triggered by traction forces elicited influx of Ca(2+), a known modulator of differentiation, in a substrate-stiffness-dependent manner. Inhibition of channel activity by the pharmacological inhibitor GsMTx-4 or by siRNA-mediated Piezo1 knockdown suppressed neurogenesis and enhanced astrogenesis. Piezo1 knockdown also reduced the nuclear localization of the mechanoreactive transcriptional coactivator Yes-associated protein. We propose that the mechanically gated ion channel Piezo1 is an important determinant of mechanosensitive lineage choice in neural stem cells and may play similar roles in other multipotent stem cells.
Keywords: Yap/Taz; blebbistatin; calcium signaling; matrix mechanics; myosin II.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Watt FM, Huck WT. Role of the extracellular matrix in regulating stem cell fate. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013;14(8):467–473. - PubMed
-
- Jones DL, Wagers AJ. No place like home: Anatomy and function of the stem cell niche. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008;9(1):11–21. - PubMed
-
- Tyler WJ. The mechanobiology of brain function. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2012;13(12):867–878. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

