Clinicopathological characteristics of colon cancer diagnosed at primary health care institutions
- PMID: 25349580
- PMCID: PMC4204700
- DOI: 10.5217/ir.2014.12.2.131
Clinicopathological characteristics of colon cancer diagnosed at primary health care institutions
Abstract
Background/aims: The purpose of this study was to evaluate the clinicopathologic characteristics of colon cancers detected at the SOK Sokpeynhan Internal Medical Network, a nationwide system of primary health care institutions.
Methods: We analyzed 579 colon cancer patients diagnosed using colonoscopy at the SOK network from January 2011 through December 2012. Cancers from the rectum to the splenic flexure were classified as left colon cancer. Patients over 65 were classified as senior.
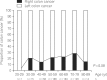
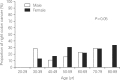
Results: The mean age (±SD) of subjects was 60.9±10.5 years and 61.1% were men. More than one quarter (28.2%) of patients were asymptomatic. The prevalence of left colon cancer was higher (77.9%) than that for right colon cancer. The most frequent macroscopic and histologic types were depressed (58.9%) and moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma (52.2%), respectively. Asymptomatic subjects displayed protruding or well differentiated adenocarcinoma, while symptomatic patients were more likely to display depressed or moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma (P<0.05). The mean age of the right colon cancer group was higher than that for the left colon cancer group (P<0.05). Among symptomatic patients, the most frequent symptoms were bloody stool for patients with left colon cancer and abdominal discomfort for patients with right colon cancer (P<0.05). The prevalence of depressed cancer was higher in older subjects as compared to younger subjects (P<0.05). The prevalence of right colon cancer tended to increase with age, although this difference did not achieve statistical significance (P>0.05).
Conclusions: Study results indicated an increase of colon cancer amongst younger demographics in recent years. The effectiveness of colonoscopy screening was also evident, as asymptomatic patients demonstrated frequent findings of well differentiated adenocarcinomas. Study results also suggested a need for closer examination of older patients, as right colon cancer tended to increase with age.
Keywords: Colonic neoplasms; Population characteristics; Primary health care.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: None.
Figures
References
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:74–108. - PubMed
-
- Cancer Statistics in 2009. Cancer incidence [homepage on the Internet] Goyang: National Cancer Institute; 2012. [cited 2012 Apr 11]. Available from: http://www.cancer.go.kr/
-
- Cho YK, Pyun YJ, Sung KC, et al. A study for The changing subsite distribution of colorectal cancer with age and sex. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 1997;17:771–777.
-
- Lee HL, Han DS, Jun DW, et al. Relationship between age and site of colorectal cancer based on colonoscopic findings. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 2004;29:181–184.
-
- Lee HS, Lee S, Seo JH, et al. Characteristics of colorectal cancer in elderly patients in comparision with younger patients. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 2007;34:76–82.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources