2-deoxy-2-((18)F)fluoro-D-glucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography imaging in paediatric oncology
- PMID: 25349660
- PMCID: PMC4209422
- DOI: 10.4329/wjr.v6.i10.741
2-deoxy-2-((18)F)fluoro-D-glucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography imaging in paediatric oncology
Abstract
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a minimally invasive technique which has been well validated for the diagnosis, staging, monitoring of response to therapy, and disease surveillance of adult oncology patients. Traditionally the value of PET and PET/computed tomography (CT) hybrid imaging has been less clearly defined for paediatric oncology. However recent evidence has emerged regarding the diagnostic utility of these modalities, and they are becoming increasingly important tools in the evaluation and monitoring of children with known or suspected malignant disease. Important indications for 2-deoxy-2-((18)F)fluoro-D-glucose (FDG) PET in paediatric oncology include lymphoma, brain tumours, sarcoma, neuroblastoma, Langerhans cell histiocytosis, urogenital tumours and neurofibromatosis type I. This article aims to review current evidence for the use of FDG PET and PET/CT in these indications. Attention will also be given to technical and logistical issues, the description of common imaging pitfalls, and dosimetric concerns as they relate to paediatric oncology.
Keywords: Computed tomography; Dosimetry; Fluorodeoxyglucose F18; Oncology; Paediatrics; Positron emission tomography; Technical issues.
Figures
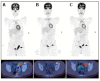


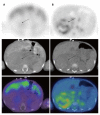
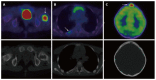
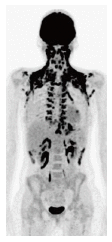
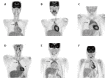
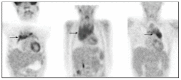

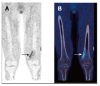
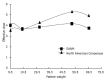
References
-
- Gatta G, Zigon G, Capocaccia R, Coebergh JW, Desandes E, Kaatsch P, Pastore G, Peris-Bonet R, Stiller CA; EUROCARE Working Group. Survival of European children and young adults with cancer diagnosed 1995-2002. Eur J Cancer. 2009;45:992–1005. - PubMed
-
- Juweid ME, Cheson BD. Positron-emission tomography and assessment of cancer therapy. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:496–507. - PubMed
-
- Storto G, Nicolai E, Salvatore M. [18F]FDG-PET-CT for early monitoring of tumor response: when and why. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2009;53:167–180. - PubMed
-
- Wegner EA, Barrington SF, Kingston JE, Robinson RO, Ferner RE, Taj M, Smith MA, O’Doherty MJ. The impact of PET scanning on management of paediatric oncology patients. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2005;32:23–30. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

