A fatal case of multidrug resistant acinetobacter necrotizing fasciitis: the changing scary face of nosocomial infection
- PMID: 25349748
- PMCID: PMC4202280
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/705279
A fatal case of multidrug resistant acinetobacter necrotizing fasciitis: the changing scary face of nosocomial infection
Abstract
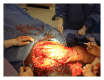
Necrotizing fasciitis is an uncommon soft-tissue infection, associated with high morbidity and mortality. Early recognition and treatment are crucial for survival. Acinetobacter baumannii is rarely associated with necrotizing fasciitis. Wound infections due to A. baumannii have been described in association with severe trauma in soldiers. There are only sporadic reports of monomicrobial A. baumannii necrotizing fasciitis. We report a unique case of monomicrobial necrotizing fasciitis caused by multidrug resistant (MDR) A. baumannii, in absence of any preceding trauma, surgery, or any obvious breech in the continuity of skin or mucosa. A 48-year-old woman with history of HIV, asthma, hypertension, and tobacco and excocaine use presented with acute respiratory failure requiring mechanical ventilation. She was treated for pneumonia for 7 days and was successfully extubated. All septic work-up was negative. Two days later, she developed rapidly spreading nonblanching edema with bleb formation at the lateral aspect of right thigh. Emergent extensive debridement and fasciotomy were performed. Operative findings and histopathology were consistent with necrotizing fasciitis. Despite extensive debridement, she succumbed to septic shock in the next few hours. Blood, wound, and tissue cultures grew A. baumannii, sensitive only to amikacin and polymyxin. Histopathology was consistent with necrotizing fasciitis.
Figures


References
-
- Quirk WF, Jr., Sternbach G. Joseph Jones: infection with flesh eating bacteria. The Journal of Emergency Medicine. 1996;14(6):747–753. - PubMed
-
- Smith GL, Bunker CB, Dinneen MD. Fournier's gangrene. British Journal of Urology. 1998;81(3):347–355. - PubMed
-
- Fournier A. Gangrène foudroyante de la verge. La Semaine Médicale. 1883;3:p. 345.
-
- Meleney FL. Hemolytic streptococcus gangrene. Archives of Surgery. 1924;9:317–364.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

