Relationships between pazopanib exposure and clinical safety and efficacy in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 25349968
- PMCID: PMC4229638
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2014.503
Relationships between pazopanib exposure and clinical safety and efficacy in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma
Erratum in
- Br J Cancer. 2014 Dec 9;111(12):2383
Abstract
Background: Pazopanib, an oral angiogenesis inhibitor targeting vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR)/platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR)/c-Kit, is approved in locally advanced/metastatic renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
Methods: Data from trials in advanced solid tumours and advanced/metastatic RCC were used to explore the relationships between plasma pazopanib concentrations and biomarker changes, safety, and efficacy. Initially, the relationships between pharmacokinetic parameters and increased blood pressure were investigated, followed by analysis of steady-state trough concentration (Cτ) and sVEGFR2, safety, progression-free survival (PFS), response rate, and tumour shrinkage. Efficacy/safety end points were compared at Cτ decile boundaries.
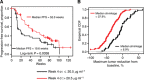
Results: Strong correlation between increased blood pressure and Cτ was observed (r(2)=0.91), whereas weak correlation was observed between Cτ and decline from baseline in sVEGFR2 (r(2)=0.27). Cτ threshold of >20.5 μg ml(-1) was associated with improved efficacy (PFS, P<0.004; tumour shrinkage, P<0.001), but there was no appreciable benefit in absolute PFS or tumour shrinkage from Cτ >20.5 μg ml(-1). However, the association of Cτ with certain adverse events, particularly hand-foot syndrome, was continuous over the entire Cτ range.
Conclusions: The threshold concentration for efficacy overlaps with concentrations at which toxicity occurs, although some toxicities increase over the entire Cτ range. Monitoring Cτ may optimise systemic exposure to improve clinical benefit and decrease the risk of certain adverse events.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00334282.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Pazopanib in locally advanced or metastatic renal cell carcinoma: results of a randomized phase III trial.J Clin Oncol. 2010 Feb 20;28(6):1061-8. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.23.9764. Epub 2010 Jan 25. J Clin Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20100962 Clinical Trial.
-
Prognostic or predictive plasma cytokines and angiogenic factors for patients treated with pazopanib for metastatic renal-cell cancer: a retrospective analysis of phase 2 and phase 3 trials.Lancet Oncol. 2012 Aug;13(8):827-37. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(12)70241-3. Epub 2012 Jul 2. Lancet Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22759480
-
Pazopanib for the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma.Clin Ther. 2012 Mar;34(3):511-20. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2012.01.014. Epub 2012 Feb 16. Clin Ther. 2012. PMID: 22341567 Review.
-
Pazopanib for the treatment of renal cancer.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2011 May;12(7):1171-89. doi: 10.1517/14656566.2011.571206. Epub 2011 Apr 7. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2011. PMID: 21470066 Review.
-
Phase II study of pazopanib as second-line treatment after sunitinib in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a Southern China Urology Cancer Consortium Trial.Eur J Cancer. 2015 Mar;51(5):595-603. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2015.01.005. Epub 2015 Jan 21. Eur J Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25618828 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Effect of Concomitant Proton Pump Inhibitors with Pazopanib on Cancer Patients: A Retrospective Analysis.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Sep 28;14(19):4721. doi: 10.3390/cancers14194721. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36230642 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of unbound fraction of pazopanib in vitro and in cancer patients reveals albumin as the main binding site.Invest New Drugs. 2016 Feb;34(1):41-8. doi: 10.1007/s10637-015-0304-9. Epub 2015 Nov 16. Invest New Drugs. 2016. PMID: 26572909 Clinical Trial.
-
Exposure-response analyses of cabozantinib in patients with metastatic renal cell cancer.BMC Cancer. 2022 Mar 2;22(1):228. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09338-1. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35236333 Free PMC article.
-
Relation between Plasma Trough Concentration of Pazopanib and Progression-Free Survival in Metastatic Soft Tissue Sarcoma Patients.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Jun 9;14(6):1224. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14061224. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35745797 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Kinase Inhibitors in Oncology.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2023 Oct;62(10):1333-1364. doi: 10.1007/s40262-023-01293-9. Epub 2023 Aug 16. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2023. PMID: 37584840 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Australian Government Department of Health and Ageing 2010. Drugs designated as orphan drugs: Pazopanib (PATORMA) http://www.tga.gov.au/industry/pm-orphan-drugs.htm .
-
- Burstein HJ, Elias AD, Rugo HS, Cobleigh MA, Wolff AC, Eisenberg PD, Lehman M, Adams BJ, Bello CL, DePrimo SE, Baum CM, Miller KD. Phase II study of sunitinib malate, an oral multitargeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in patients with metastatic breast cancer previously treated with an anthracycline and a taxane. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26 (11:1810–1816. - PubMed
-
- Cacheux W, Boisserie T, Staudacher L, Vignaux O, Dousset B, Soubrane O, Terris B, Mateus C, Chaussade S, Goldwasser F. Reversible tumor growth acceleration following bevacizumab interruption in metastatic colorectal cancer patients scheduled for surgery. Ann Oncol. 2008;19 (9:1659–1661. - PubMed
-
- Deng Y, Sychterz C, Suttle AB, Dar MM, Bershas D, Negash K, Qian Y, Chen EP, Gorycki PD, Ho MY. Bioavailability, metabolism and disposition of oral pazopanib in patients with advanced cancer. Xenobiotica. 2013;43 (5:443–453. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

