Comparison of select analytes in exhaled aerosol from e-cigarettes with exhaled smoke from a conventional cigarette and exhaled breaths
- PMID: 25350011
- PMCID: PMC4245607
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph111111177
Comparison of select analytes in exhaled aerosol from e-cigarettes with exhaled smoke from a conventional cigarette and exhaled breaths
Abstract
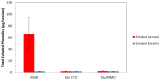
Exhaled aerosols were collected following the use of two leading U.S. commercial electronic cigarettes (e-cigarettes) and a conventional cigarette by human subjects and analyzed for phenolics, carbonyls, water, glycerin and nicotine using a vacuum-assisted filter pad capture system. Exhaled breath blanks were determined for each subject prior to each product use and aerosol collection session. Distribution and mass balance of exhaled e-cigarette aerosol composition was greater than 99.9% water and glycerin, and a small amount (<0.06%) of nicotine. Total phenolic content in exhaled e-cigarette aerosol was not distinguishable from exhaled breath blanks, while total phenolics in exhaled cigarette smoke were significantly greater than in exhaled e-cigarette aerosol and exhaled breaths, averaging 66 µg/session (range 36 to 117 µg/session). The total carbonyls in exhaled e-cigarette aerosols were also not distinguishable from exhaled breaths or room air blanks. Total carbonyls in exhaled cigarette smoke was significantly greater than in exhaled e-cigarette aerosols, exhaled breath and room air blanks, averaging 242 µg/session (range 136 to 352 µg/session). These results indicate that exhaled e-cigarette aerosol does not increase bystander exposure for phenolics and carbonyls above the levels observed in exhaled breaths of air.
Figures



References
-
- Laugesen M. Safety Report on the Ruyan® E-cigarette Cartridge and Inhaled Aerosol. Public Health Medicine Registrar, Auckland District Health Board; Auckland, New Zealand: 2008.
-
- Laugesen M. Poster 5–11. Society for Research on Nicotine and Tobacco (SRNT); Dublin, Ireland: 2009.
-
- Pellegrino R.M., Tinghino B., Mangiaracina G., Marani A., Vitali M., Protano C., Osborn J.F., Cattaruzza M.S. Electronic cigarettes: An evaluation of exposure to chemicals and fine particulate matter (PM) Ann. Ig. 2012;24:279–288. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

