Aquatic exercise training for fibromyalgia
- PMID: 25350761
- PMCID: PMC10638613
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011336
Aquatic exercise training for fibromyalgia
Abstract
Background: Exercise training is commonly recommended for individuals with fibromyalgia. This review examined the effects of supervised group aquatic training programs (led by an instructor). We defined aquatic training as exercising in a pool while standing at waist, chest, or shoulder depth. This review is part of the update of the 'Exercise for treating fibromyalgia syndrome' review first published in 2002, and previously updated in 2007.
Objectives: The objective of this systematic review was to evaluate the benefits and harms of aquatic exercise training in adults with fibromyalgia.
Search methods: We searched The Cochrane Library 2013, Issue 2 (Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, Health Technology Assessment Database, NHS Economic Evaluation Database), MEDLINE, EMBASE, CINAHL, PEDro, Dissertation Abstracts, WHO international Clinical Trials Registry Platform, and AMED, as well as other sources (i.e., reference lists from key journals, identified articles, meta-analyses, and reviews of all types of treatment for fibromyalgia) from inception to October 2013. Using Cochrane methods, we screened citations, abstracts, and full-text articles. Subsequently, we identified aquatic exercise training studies.
Selection criteria: Selection criteria were: a) full-text publication of a randomized controlled trial (RCT) in adults diagnosed with fibromyalgia based on published criteria, and b) between-group data for an aquatic intervention and a control or other intervention. We excluded studies if exercise in water was less than 50% of the full intervention.
Data collection and analysis: We independently assessed risk of bias and extracted data (24 outcomes), of which we designated seven as major outcomes: multidimensional function, self reported physical function, pain, stiffness, muscle strength, submaximal cardiorespiratory function, withdrawal rates and adverse effects. We resolved discordance through discussion. We evaluated interventions using mean differences (MD) or standardized mean differences (SMD) and 95% confidence intervals (95% CI). Where two or more studies provided data for an outcome, we carried out meta-analysis. In addition, we set and used a 15% threshold for calculation of clinically relevant differences.
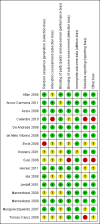
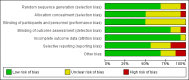
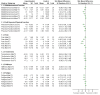
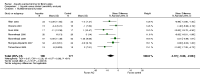
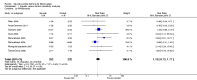
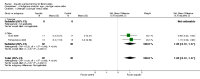
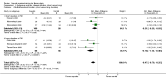
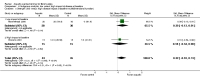
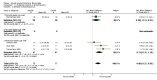
Main results: We included 16 aquatic exercise training studies (N = 881; 866 women and 15 men). Nine studies compared aquatic exercise to control, five studies compared aquatic to land-based exercise, and two compared aquatic exercise to a different aquatic exercise program.We rated the risk of bias related to random sequence generation (selection bias), incomplete outcome data (attrition bias), selective reporting (reporting bias), blinding of outcome assessors (detection bias), and other bias as low. We rated blinding of participants and personnel (selection and performance bias) and allocation concealment (selection bias) as low risk and unclear. The assessment of the evidence showed limitations related to imprecision, high statistical heterogeneity, and wide confidence intervals. Aquatic versus controlWe found statistically significant improvements (P value < 0.05) in all of the major outcomes. Based on a 100-point scale, multidimensional function improved by six units (MD -5.97, 95% CI -9.06 to -2.88; number needed to treat (NNT) 5, 95% CI 3 to 9), self reported physical function by four units (MD -4.35, 95% CI -7.77 to -0.94; NNT 6, 95% CI 3 to 22), pain by seven units (MD -6.59, 95% CI -10.71 to -2.48; NNT 5, 95% CI 3 to 8), and stiffness by 18 units (MD -18.34, 95% CI -35.75 to -0.93; NNT 3, 95% CI 2 to 24) more in the aquatic than the control groups. The SMD for muscle strength as measured by knee extension and hand grip was 0.63 standard deviations higher compared to the control group (SMD 0.63, 95% CI 0.20 to 1.05; NNT 4, 95% CI 3 to 12) and cardiovascular submaximal function improved by 37 meters on six-minute walk test (95% CI 4.14 to 69.92). Only two major outcomes, stiffness and muscle strength, met the 15% threshold for clinical relevance (improved by 27% and 37% respectively). Withdrawals were similar in the aquatic and control groups and adverse effects were poorly reported, with no serious adverse effects reported. Aquatic versus land-basedThere were no statistically significant differences between interventions for multidimensional function, self reported physical function, pain or stiffness: 0.91 units (95% CI -4.01 to 5.83), -5.85 units (95% CI -12.33 to 0.63), -0.75 units (95% CI -10.72 to 9.23), and two units (95% CI -8.88 to 1.28) respectively (all based on a 100-point scale), or in submaximal cardiorespiratory function (three seconds on a 100-meter walk test, 95% CI -1.77 to 7.77). We found a statistically significant difference between interventions for strength, favoring land-based training (2.40 kilo pascals grip strength, 95% CI 4.52 to 0.28). None of the outcomes in the aquatic versus land comparison reached clinically relevant differences of 15%. Withdrawals were similar in the aquatic and land groups and adverse effects were poorly reported, with no serious adverse effects in either group. Aquatic versus aquatic (Ai Chi versus stretching in the water, exercise in pool water versus exercise in sea water)Among the major outcomes the only statistically significant difference between interventions was for stiffness, favoring Ai Chi (1.00 on a 100-point scale, 95% CI 0.31 to 1.69).
Authors' conclusions: Low to moderate quality evidence relative to control suggests that aquatic training is beneficial for improving wellness, symptoms, and fitness in adults with fibromyalgia. Very low to low quality evidence suggests that there are benefits of aquatic and land-based exercise, except in muscle strength (very low quality evidence favoring land). No serious adverse effects were reported.
Conflict of interest statement
We confirm that any present or past affiliations or other involvement in any organization or entity with an interest in the review, which might lead me/us to have a real or perceived conflict of interest, are listed below.
Julia Bidonde: none known
Angela J Busch: none known
Sandra C Webber: none known
Candice L Schachter: none known
Adrienne Danyliw: none known
Tom J Overend: none known
Rachel S Richards: none known
Tamara Rader: none known
Figures
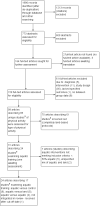







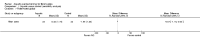






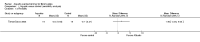










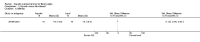








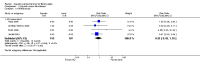

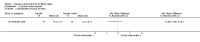







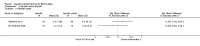





















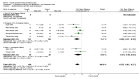

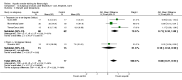
References
References to studies included in this review
Altan 2004 {published data only}
-
- Altan L, Bingol U, Aykac M, Koc Z, Yurtkuran M. Investigation of the effects of pool‐based exercise on fibromyalgia syndrome. Rheumatology International 2004;24(5):272‐7. - PubMed
Arcos‐Carmona 2011 {published data only}
-
- Arcos‐Carmona IM, Castro‐Sanchez AM, Mataran‐Penarrocha GA, Gutierrez‐Rubio AB, Ramos‐Gonzalez E, Moreno‐Lorenzo C. Effects of aerobic exercise program and relaxation techniques on anxiety, quality of sleep, depression, and quality of life in patients with fibromyalgia: a randomized controlled trial [Effectos de un programa de ejercicios aerobicos y tecnicas de relajacion sobre el estado de ansiedad, calidad del sueno, depresion y calidad de vida en pacientes con fibromialgia: ensayo clinico aleatorizado]. Medicina Clinica 2011;137(9):398‐401. - PubMed
Assis 2006 {published data only}
-
- Assis MR, Duardo Silva L, Martins Barros Alves A, Pessanha AP, Valim V, Feldman D, et al. A randomized controlled trial of deep water running: clinical effectiveness of aquatic exercise to treat fibromyalgia. Arthritis & Rheumatism 2006;55(1):57‐65. - PubMed
Calandre 2010 {published data only}
-
- Calandre EP, Rodriguez‐Claro ML, Rico‐Villademoros F, Vilchez JS, Hidalgo J, Delgado‐Rodriguez A. Effects of pool‐based exercise in fibromyalgia symptomatology and sleep quality: a prospective randomized comparison between stretching and Tai Chi. Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology 2009;27(5 Suppl 56):S21‐8. - PubMed
De Andrade 2008 {published data only}
de Melo Vitorino 2006 {published data only}
Evcik 2008 {published data only}
Gowans 2001 {published data only}
-
- Gowans SE, deHueck A, Abbey SE. Measuring exercise‐induced mood changes in fibromyalgia: a comparison of several measures. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2002;47(6):603‐9. - PubMed
-
- Gowans SE, deHueck A, Voss S, Silaj A, Abbey SE, Reynolds WJ. Effect of a randomized, controlled trial of exercise on mood and physical function in individuals with fibromyalgia. Arthritis Care and Research 2001;45:519‐29. - PubMed
Gusi 2006 {published data only}
-
- Gusi N, Tomas‐Carus P, Hakkinen A, Hakkinen K, Ortega‐Alonso A. Exercise in waist‐high warm water decreases pain and improves health‐related quality of life and strength in the lower extremities in women with fibromyalgia. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2006;55(1):66‐73. - PubMed
-
- Tomas‐Carus P. Aquatic training and detraining on fitness and quality of life in FM. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 2007;39(7):1044‐50. - PubMed
-
- Tomas‐Carus P. Effects of aquatic training and subsequent detraining on the perception and intensity of pain and number of sensitive points in women with fibromyalgia [Efectos del entrenamiento acuatico y posterior desentrenamiento sobre la percepcion e intensidad del dolor y numero de puntos sensibles de mujeres con fibromialgia]. Apunts.Medicina de l'Esport 2007;154:76‐81.
-
- Tomas‐Carus P. The fibromyalgia treatment with physical exercise in warm water reduces the impact of disease [El tratamiento para la fibromialgia con ejercicio fisico en agua caliente reduce el impacto de la enfermedad en la salud fisica y mental de mujeres afectadas]. Reumatologia Clinica 2007;3(1):33‐7. - PubMed
Hecker 2011 {published data only}
-
- Hecker CD, Melo C, Silva Tomazoni S, Brandao Lopes Martins RA, Pinto Leal EC. Analysis of effects of kinesiotherapy and hydrokinesiotherapy on the quality of life of patients with fibromyalgia ‐ a randomized clinical trial [Analise dos efeitos da cinesioterapia e da hidrocinesioterapia sobre a qualidade de vida de pacientes com fibromialgia ‐ um ensaio clinico randomizado]. Fisioterapia em Movimento 2011;24(1):57‐64.
Ide 2008 {published data only}
-
- Ide MR, Laurindo LMM, Rodrigues‐Junior AL, Tanaka C. Effect of aquatic respiratory exercise‐based program in patients with fibromyalgia. APLAR Journal of Rheumatology 2008;11(2):131‐40.
Jentoft 2001 {published data only}
-
- Jentoft ES, Kvalvik AG, Mengshoel AM. Effects of pool‐based and land‐based aerobic exercise on women with fibromyalgia/chronic widespread muscle pain. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2001;45:42‐7. - PubMed
Mannerkorpi 2000 {published data only}
-
- Mannerkorpi K, Ahlmen M, Ekdahl C. Six‐ and 24‐month follow‐up of pool exercise therapy and education for patients with fibromyalgia. Scandinavian Journal of Rheumatology 2002;31(5):306‐10. - PubMed
-
- Mannerkorpi K, Nyberg B, Ahlmen M, Ekdahl C. Pool exercise combined with an education program for patients with fibromyalgia syndrome. A prospective, randomized study. Journal of Rheumatology 2000;27(10):2473‐81. - PubMed
Mannerkorpi 2009 {published data only}
-
- Mannerkorpi K, Nodeman L, Eericsson A, Arndorw M, and the GAU Study Group. Pool exercise for patients with fibromyalgia or chronic widespread pain: a randomized controlled trial and subgroup analysis. Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine 2009;41:751‐60. - PubMed
Munguia‐Izquierdo 2007 {published data only}
-
- Munguia‐Izquierdo D, Legaz‐Arrese A. Assessment of the effects of aquatic therapy on global symptomatology in patients with fibromyalgia syndrome: a randomized controlled trial. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2008;89:2250‐7. - PubMed
-
- Munguia‐Izquierdo D, Legaz‐Arrese A. Exercise in warm water decreases pain and improves cognitive function in middle‐aged women with fibromyalgia. Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology 2007;25(6):823‐30. - PubMed
Tomas‐Carus 2008 {published data only}
-
- Tomas‐Carus P, Gusi N, Hakkinen A, Hakkinen K, Leal A, Ortega‐Alonso A. Eight months of physical training in warm water improves physical and mental health in women with fibromyalgia: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine 2008;40(4):248‐52. - PubMed
-
- Tomas‐Carus P, Gusi N, Hakkinen A, Hakkinen K, Raimundo A, Ortega‐Alonso A. Improvements of muscle strength predicted benefits in HRQOL and postural balance in women in fibromyalgia: an 8‐month randomized controlled trial. Rheumatology 2009;48:1147‐51. - PubMed
-
- Tomas‐Carus P, Raimundo A, Timon R, Gusi N. Exercise in warm water decreases pain but not the number of tender points in women with fibromyalgia: a randomized controlled trial [El ejercicio fisico en agua caliente reduce el dolor pero no el numero de puntos sensibles de mujeres con fibromialgia: un ensayo clinico randomizado]. Seleccion 2007;16(2):98‐102.
References to studies excluded from this review
Ahlgren 2001 {published data only}
-
- Ahlgren C, Waling K, Kadi F, Djupsjobacka M, Thornell L, Sundelin G. Effects on physical performance and pain from three dynamic training programs for women with work‐related trapezius myalgia. Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine 2001;33(4):162‐9. - PubMed
Alentorn‐Geli 2009 {published data only}
-
- Alentorn‐Geli E, Moras G, Padilla J, Fernandez‐Sola J, Bennett RM, Lazaro‐Haro C, et al. Effect of acute and chronic whole‐body vibration exercise on serum insulin‐like growth factor‐1 levels in women with fibromyalgia. Journal of Alternative & Complementary Medicine 2009;15(5):573‐8. - PubMed
Astin 2003 {published data only}
-
- Astin JA, Berman BM, Bausel B, Lee WL, Hochberg M, Forys KL. The efficacy of mindfulness meditation plus Qigong movement therapy in the treatment of fibromyalgia: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Rheumatology 2003;30(10):2257‐62. - PubMed
Bailey 1999 {published data only}
-
- Bailey A, Starr L, Alderson M, Moreland J. A comparative evaluation of a fibromyalgia rehabilitation program. Arthritis Care and Research 1999;12(5):336‐40. - PubMed
Bakker 1995 {published data only}
-
- Bakker C, Rutten M, Santen‐Hoeufft M, Bolwijn P, Doorslaer E, Linden S. Patient utilities in fibromyalgia and the association with other outcome measures. Journal of Rheumatology 1995;22:1536‐43. - PubMed
Carbonell‐Baeza 2011 {published data only}
-
- Carbonell‐Baeza A, Aparicio VA, Ortega FB, Cuevas AM, Alvarez IC, Ruiz JR, et al. Does a 3‐month multidisciplinary intervention improve pain, body composition and physical fitness in women with fibromyalgia?. British Journal of Sports Medicine 2011;45(15):1189‐95. - PubMed
Carbonell‐Baeza 2012 {published data only}
Casanueva‐Fernandez 2012 {published data only}
-
- Casanueva‐Fernandez B, Llorca J, Rubio JBI, Rodero‐Fernandez B, Gonzalez‐Gay MA. Efficacy of a multidisciplinary treatment program in patients with severe fibromyalgia. Rheumatology International 2012;32(8):2497‐502. - PubMed
Castro‐Sanchez 2011 {published data only}
-
- Castro‐Sanchez AM, Mataran‐Penarrocha GA, Arroyo‐Morales M, Saavedra‐Hernandez M, Fernandez‐Sola C, Moreno‐Lorenzo C. Effects of myofascial release techniques on pain, physical function, and postural stability in patients with fibromyalgia: a randomized controlled trial. Clinical Rehabilitation 2011;25(9):800‐13. - PubMed
Dal 2011 {published data only}
-
- Dal U, Cimen OB, Incel NA, Adim M, Dag F, Erdogan AT, et al. Fibromyalgia syndrome patients optimize the oxygen cost of walking by preferring a lower walking speed. Journal of Musculoskeletal Pain 2011;19(4):212‐7.
daSilva 2007 {published data only}
-
- Silva GD, Lorenzi‐Filho G, Lage LV. Effects of yoga and the addition of Tui Na in patients with fibromyalgia. Journal of Alternative & Complementary Medicine 2007;13(10):1107‐13. - PubMed
Dawson 2003 {published data only}
-
- Dawson KA, Tiidus PM, Pierrynowski M, Crawford JP, Trotter J. Evaluation of a community‐based exercise program for diminishing symptoms of fibromyalgia. Physiotherapy Canada 2003;55:17‐22.
Finset 2004 {published data only}
-
- Finset A, Wigers SH, Gotestam KG. Depressed mood impedes pain treatment response in patients with fibromyalgia. Journal of Rheumatology 2004;31(5):976‐80. - PubMed
Gandhi 2000 {published data only}
-
- Gandhi N. Effect of an exercise program on quality of life of women with fibromyalgia. Microform Publications, University of Oregon, Eugene, Or 2000.
Geel 2002 {published data only}
-
- Geel SE, Robergs RA. The effect of graded resistance exercise on fibromyalgia symptoms and muscle bioenergetics: a pilot study. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2002;47:82‐6. - PubMed
Gowans 2002 {published data only}
-
- Gowans SE, deHueck A, Abbey SE. Measuring exercise‐induced mood changes in fibromyalgia: a comparison of several measures. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2002;47(6):603‐9. - PubMed
Gowans 2004 {published data only}
-
- Gowans SE, deHueck A, Voss S, Silaj A, Abbey SE. Six‐month and one‐year followup of 23 weeks of aerobic exercise for individuals with fibromyalgia. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2004;51(6):890‐8. - PubMed
Guarino 2001 {published data only}
-
- Guarino P, Peduzzi P, Donta ST, Engel CC, Clauw DJ, Williams DA, et al. A multicenter two by two factorial trial of cognitive behavioral therapy and aerobic exercise for Gulf War veterans' illnesses: design of a Veterans Affairs cooperative study (CSP #470). Controlled Clinical Trials 2001;22:310‐32. - PubMed
Han 1998 {published data only}
-
- Han SS. Effects of a self‐help program including stretching exercise on symptom reduction in patients with fibromyalgia. Taehan Kanho 1998;37:78‐80. - PubMed
Hoeger 2011 {published data only}
-
- Hoeger Bement MK, Weyer A, Hartley S, Drewek B, Harkins AL, Hunter SK. Pain perception after isometric exercise in women with fibromyalgia. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2011;92(1):89‐95. - PubMed
Huyser 1997 {published data only}
-
- Huyser B, Buckelew SP, Hewett JE, Johnson JC. Factors affecting adherence to rehabilitation interventions for individuals with fibromyalgia. Rehabilitation Psychology 1997;42:75‐91.
Jones 2011 {published data only}
Kadetoff 2010 {published data only}
-
- Kadetoff D, Kosek E. Evidence of reduced sympatho‐adrenal and hypothalamic‐pituitary activity during static muscular work in patients with fibromyalgia. Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine 2010;42(8):765‐72. - PubMed
Karper 2001 {published data only}
-
- Karper WB, Hopewell R, Hodge M. Exercise program effects on women with fibromyalgia syndrome. Clinical Nurse Specialist 2001;15:67‐75. - PubMed
Kendall 2000 {published data only}
-
- Kendall SA, Brolin MK, Soren B, Gerdle B, Henriksson KG. A pilot study of body awareness programs in the treatment of fibromyalgia syndrome. Arthritis Care and Research 2000;13:304‐11. - PubMed
Kesiktas 2011 {published data only}
-
- Kesiktas N, Karagülle Z, Erdogan N, Yazıcıoglu K, Yılmaz H, Paker N. The efficacy of balneotherapy and physical modalities on the pulmonary system of patients with fibromyalgia. Journal of Back and Musculoskeletal Rehabilitation 2011;24(1):57. - PubMed
Khalsa 2009 {published data only}
-
- Khalsa KPS. Bodywork for fibromyalgia: alternative therapies soothe the pain. Massage & Bodywork 2009;May/June:80‐9.
Kingsley 2005 {published data only}
-
- Kingsley JD, Panton LB, Toole T, Sirithienthad P, Mathis R, McMillan V. The effects of a 12‐week strength‐training program on strength and functionality in women with fibromyalgia. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2005;86(9):1713‐21. - PubMed
Kingsley 2010 {published data only}
-
- Kingsley JD, McMillan V, Figueroa A. The effects of 12 weeks of resistance exercise training on disease severity and autonomic modulation at rest and after acute leg resistance exercise in women with fibromyalgia. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2010;91(10):1551‐7. - PubMed
Klug 1989 {published data only}
-
- Klug GA, McAuley E, Clark S. Factors influencing the development and maintenance of aerobic fitness: lessons applicable to the fibrositis syndrome. Journal of Rheumatology. Supplement 1989;19:30‐9. - PubMed
Lange 2011 {published data only}
-
- Lange M, Krohn‐Grimberghe B, Petermann F. Medium‐term effects of a multimodal therapy on patients with fibromyalgia. Results of a controlled efficacy study. Schmerz (Berlin, Germany) 2011; Vol. 25, issue 1:55‐61. - PubMed
Lorig 2008 {published data only}
-
- Lorig KR, Ritter PL, Laurent DD, Plant K, Lorig KR, Ritter PL. The internet‐based arthritis self‐management program: a one‐year randomized trial for patients with arthritis or fibromyalgia. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2008;59(7):1009‐17. - PubMed
Mannerkorpi 2002 {published data only}
-
- Mannerkorpi K, Ahlmen M, Ekdahl C. Six‐ and 24‐month follow‐up of pool exercise therapy and education for patients with fibromyalgia. Scandinavian Journal of Rheumatology 2002;31(5):306‐10. - PubMed
Mason 1998 {published data only}
Matsumoto 2011 {published data only}
-
- Matsumoto S, Shimodozono M, Etoh S, Miyata R, Kawahira K. Effects of thermal therapy combining sauna therapy and underwater exercise in patients with fibromyalgia. Complementary Therapies in Clinical Practice 2011;17(3):162‐6. - PubMed
McCain 1986 {published data only}
-
- McCain GA. Role of physical fitness training in the fibrositis/fibromyalgia syndrome. American Journal of Medicine 1986;81(3A):73‐7. - PubMed
Meiworm 2000 {published data only}
-
- Meiworm L, Jakob E, Walker UA, Peter HH, Keul J. Patients with fibromyalgia benefit from aerobic endurance exercise. Clinical Rheumatology 2000;19(4):253‐7. - PubMed
Meyer 2000 {published data only}
-
- Meyer BB, Lemley KJ. Utilizing exercise to affect the symptomology of fibromyalgia: a pilot study. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 2000;32(10):1691‐7. - PubMed
Mobily 2001 {published data only}
-
- Mobily KE, Verburg MD. Aquatic therapy in community‐based therapeutic recreation: pain management in a case of fibromyalgia. Therapeutic Recreation Journal 2001;35:57‐69.
Mutlu 2013 {published data only}
-
- Mutlu B, Paker N, Bugdayci D, Tekdos D, Kesiktas N. Efficacy of supervised exercise combined with transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation in women with fibromyalgia: a prospective controlled study. Rheumatology International 2013;33(3):649‐55. - PubMed
Newcomb 2011 {published data only}
Nielens 2000 {published data only}
-
- Nielens H, Boisset V, Masquelier E. Fitness and perceived exertion in patients with fibromyalgia syndrome. Clinical Journal of Pain 2000;16:209‐13. - PubMed
Nijs 2004 {published data only}
-
- Nijs J, Parijs M. Long‐term effectiveness of pool exercise therapy and education in patients with fibromyalgia. Journal of Chronic Fatigue Syndrome 2004;12(3):73‐9.
Offenbacher 2000 {published data only}
-
- Offenbacher M, Stucki G. Physical therapy in the treatment of fibromyalgia. Scandinavian Journal of Rheumatology 2000;Suppl 29:78. - PubMed
Oncel 1994 {published data only}
-
- Oncel A, Eskiyurt N, Leylabadi M. The results obtained by different therapeutic measures in the treatment of generalized fibromyalgia syndrome. Tip Fakultesi Mecmuasi 1994;57(4):45‐9.
Peters 2002 {published data only}
-
- Peters S, Stanley I, Rose M, Kaney S, Salmon P. A randomized controlled trial of group aerobic exercise in primary care patients with persistent, unexplained physical symptoms. Family Practice 2002;19:665‐74. - PubMed
Pfeiffer 2003 {published data only}
-
- Pfeiffer AT, Thompson JM, Nelson A, Tucker S, Luedtke C, Finnie S, et al. Effects of a 1.5‐day multidisciplinary outpatient treatment program for fibromyalgia: a pilot study. American Journal of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation 2003;82:186‐91. - PubMed
Piso 2001 {published data only}
-
- Piso U, Kuther G, Gutenbrunner C, Gehrke A. Analgesic effects of sauna in fibromyalgia [German]. Physikalische Medizin Rehabilitationsmedizin Kurortmedizin 2001;11(3):94‐9.
Rooks 2002 {published data only}
-
- Rooks DS, Silverman CB, Kantrowitz FG. The effects of progressive strength training and aerobic exercise on muscle strength and cardiovascular fitness in women with fibromyalgia: a pilot study. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2002;47:22‐8. - PubMed
Salek 2005 {published data only}
-
- Salek AK, Khan MM, Ahmed SM, Rashid MI, Emran MA, Mamun MA. Effect of aerobic exercise on patients with primary fibromyalgia syndrome. Mymensingh Medical Journal 2005;14(2):141‐4. - PubMed
Santana 2010 {published data only}
-
- Soares de Santana J, Goncalves de Almeida AP, Martins Carvalho Brandao P. The effect of Ai Chi method in fybromyalgic patients [Os efeitos do metodo Ai Chi em pacientes portadores da sindrome fibromialgica]. Ciencia & Saude Coletiva 2010;15 Suppl 1:1433‐8. - PubMed
Sigl‐Erkel 2011 {published data only}
-
- Sigl‐Erkel T. A randomized trial of tai chi for fibromyalgia [Studienbesprechung zu tai chi (taiji) bei fibromyalgie]. Chinesische Medizin 2011;26(2):112‐6.
Suman 2009 {published data only}
-
- Suman AL, Biagi B, Biasi G, Carli G, Gradi M, Prati E, et al. One‐year efficacy of a 3‐week intensive multidisciplinary non‐pharmacological treatment program for fibromyalgia patients. Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology 2009;27(1):7‐14. - PubMed
Thieme 2003 {published data only}
-
- Thieme K, Gronica‐Ihle E, Flor H. Operant behavioral treatment of fibromyalgia: a controlled study. Arthritis Care and Research 2003;49:314‐20. - PubMed
Thijssen 1992 {published data only}
-
- Thijssen Ej, Klerk E. Evaluatie van een zwemprogramma voor patienten met fibromyalgie. Nederlands Tijdschrift voor Fysiotherapie 1992;102(3):71‐5.
Tiidus 1997 {published data only}
-
- Tiidus PM. Manual massage and recovery of muscle function following exercise: a literature review. Journal of Orthopaedic and Sports Physical Therapy 1997;25:107‐12. - PubMed
Uhlemann 2007 {published data only}
-
- Uhlemann C, Strobel I, Muller‐Ladner U, Lange U. Prospective clinical trial about physical activity in fibromyalgia [German]. Aktuelle Rheumatologie 2007;32(1):27‐33.
Vlaeyen 1996 {published data only}
-
- Vlaeyen JW, Teeken‐Gruben NJ, Goossens ME, Rutten‐van Molken MP, Pelt RA, Eek H, et al. Cognitive‐educational treatment of fibromyalgia: a randomized clinical trial. I Clinical effects. Journal of Rheumatology 1996;23(7):1237‐45. - PubMed
Williams 2010 {published data only}
Worrel 2001 {published data only}
-
- Worrel LM, Krahn LE, Sletten CD, Pond GR. Treating fibromyalgia with a brief interdisciplinary program: initial outcomes and predictors of response. Mayo Clinic Proceedings 2001;76:384‐90. - PubMed
Zijlstra 2005 {published data only}
-
- Zijlstra TR, Laar MA, Bernelot Moens HJ, Taal E, Zakraoui L, Rasker JJ. Spa treatment for primary fibromyalgia syndrome: a combination of thalassotherapy, exercise and patient education improves symptoms and quality of life. Rheumatology 2005;44:539‐46. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Amanollahi 2013 {published data only}
-
- Amanollahi A, Naghizadeh J, Khatibi A, Hollisaz MT, Shamseddini AR, Saburi A. Comparison of impacts of friction massage, stretching exercises and analgesics on pain relief in primary fibromyalgia syndrome: a randomized clinical trial. Tehran University Medical Journal 2013;70(10):616‐22.
Aslan 2001 {published data only}
-
- Aslan UB, Yuksel I, Yazici M. A comparison of classical massage and mobilization techniques treatment in primary fibromyalgia [Turkish]. Fizyoterapi Rehabilitasyon 2001;12(2):50‐4.
Ekici 2008 {published data only}
-
- Ekici G, Yakut E, Akbayrak T. Effects of pilates exercises and connective tissue manipulation on pain and depression in females with fibromyalgia: a randomized controlled trial [Turkish]. Fizyoterapi Rehabilitasyon 2008;19(2):47‐54.
Gomes da Silva 2008 {published data only}
-
- Gomes da Silva T, Suda EY, Marçulo CA, Silva Paes FH, Pinheiro GT. Comparison of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation and hydrotherapy effects on pain, flexibility and quality of life in patients with fibromyalgia [Comparação dos efeitos da estimulação elétrica nervosa transcutânea e da hidroterapia na dor, flexibilidade e qualidade de vida de pacientes com fibromialgia]. Fisioterapia e Pesquisa 2008;15(2):118‐24.
López‐Rodríguez 2012 {published data only}
Additional references
Ablin 2013
-
- Ablin JN, Buskila D, Amital H, Fitzcharles M, Shir Y, Henningsen P. A paradigm change for treatment strategies for fibromyalgia syndrome reflected by recommendations of recent evidence‐based interdisciplinary guidelines developed independently in three countries. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2013;65(Suppl 10):839.
ACSM 2009
-
- American College of Sports Medicine. Progression models in resistance training for healthy adults. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 2009;41(3):687‐708. - PubMed
ACSM 2009a
-
- American College of Sports Medicine. ACSM's Guidelines for Exercise Testing and Prescription. 8th Edition. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2009.
Adsuar 2012
-
- Adsuar JC, Pozo‐Cruz B, Parraca JA, Olivares PR, Gusi N. Whole body vibration improves the single‐leg stance static balance in women with fibromyalgia: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Sports Medicine & Physical Fitness 2012;52(1):85‐91. - PubMed
Alentorn‐Geli 2008
-
- Alentorn‐Geli E, Padilla J, Moras G, Lazaro Haro C, Fernandez‐Sola J. Six weeks of whole‐body vibration exercise improves pain and fatigue in women with fibromyalgia. Journal of Alternative & Complementary Medicine 2008;14(8):975‐81. - PubMed
Altan 2009
-
- Altan L, Korkmaz N, Bingol U, Gunay B. Effect of pilates training on people with fibromyalgia syndrome: a pilot study. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2009;90(12):1983‐8. - PubMed
Anderson 1995
-
- Anderson KO, Dowds BN, Pelletz RE, Edwards WT, Peeters Asdourian C. Development and initial validation of a scale to measure self‐efficacy beliefs in patients with chronic pain. Pain 1995;63(1):77‐84. - PubMed
Arnold 2008
Arnold 2013
Baptista 2012
-
- Baptista AS, Villela AL, Jones A, Natour J. Effectiveness of dance in patients with fibromyalgia: a randomized, single‐blind, controlled study. Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology 2012;30(6 Suppl 74):18‐23. - PubMed
Bartels 2007
Bartels 2009
-
- Bartels EM, Dreyer L, Jacobsen S, Jespersen A, Bliddal H, Danneskiold‐Samsoe B. Fibromyalgia, diagnosis and prevalence. Are gender differences explainable?. Ugeskrift for Laeger 2009;171(49):3588‐92. - PubMed
Bates 1996
-
- Bates A, Hanson N. Aquatic Exercise Therapy. Philadelphia: WB Saunders Co., 1996.
Bender 2005
-
- Bender T, Karagülle Z, Balint G, Gutenbrunner C, Balint PV, Sukenik S. Hydrotherapy, balneotherapy, and spa treatment in pain management. Rheumatology International 2005;25(3):220‐4. - PubMed
Bennett 1989
-
- Bennett RM, Clark SR, Goldberg L, Nelson D, Bonafede RP, Porter J, et al. Aerobic fitness in patients with fibrositis. A controlled study of respiratory gas exchange and 133xenon clearance from exercising muscle. Arthritis and Rheumatism 1989;32(4):454‐60. - PubMed
Bennett 1998
-
- Bennett RM, Clark SC, Walczyk J. A randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study of growth hormone in the treatment of fibromyalgia. American Journal of Medicine 1998;104(3):227‐31. - PubMed
Bergner 1981
-
- Bergner M, Bobbitt RA, Carter WB, Gilson BS. The Sickness Impact Profile: development and final revision of a health status measure. Medical Care 1981;19(8):787‐805. - PubMed
Bernardy 2013
Bircan 2008
-
- Bircan C, Karasel SA, Akgun B, El O, Alper S. Effects of muscle strengthening versus aerobic exercise program in fibromyalgia. Rheumatology International 2008;28(6):527‐32. - PubMed
Bojner 2006
-
- Bojner Horwitz E, Kowalski J, Theorell T, Anderberg UM. Dance/movement therapy in fibromyalgia patients: changes in self‐figure drawings and their relation to verbal self‐rating scales. Arts in Psychotherapy 2006;33(1):11‐25.
Bond 1995
-
- Bond AJ, Shine P, Bruce M. Validation of visual analogue scales in anxiety. International Journal of Methods in Psychiatric Research 1995;5(1):1‐9.
Boomershine 2012
Brachaniec 2009
Bressan 2008
-
- Bressan LR, Matsutani LA, Assumpcao A, Marques AP, Cabral CMN. Effects of muscle stretching and physical conditioning as physical therapy treatment for patients with fibromyalgia [Portuguese]. Revista Brasileira de Fisioterapia/Brazilian Journal of Physical Therapy 2008;12(2):88‐93.
Buchheld 2001
-
- Buchheld N, Grossman P, Walach H. Measuring mindfulness in insight meditation (Vipassana) and meditation‐based psychotherapy: the development of the Freiburg Mindfulness Inventory (FMI). Journal for Meditation and Meditation Research 2001;1(1):11‐34.
Buckelew 1998
-
- Buckelew SP, Conway R, Parker J, Deuser WE, Read J, Witty TE, et al. Biofeedback/relaxation training and exercise interventions for fibromyalgia: a prospective trial. Arthritis and Rheumatism 1998;11(3):196‐209. - PubMed
Burckhardt 1991
-
- Burckhardt CS, Clark SR, Bennett RM. The fibromyalgia impact questionnaire: development and validation. Journal of Rheumatology 1991;18(5):728‐33. - PubMed
Burckhardt 1994
-
- Burckhardt CS, Mannerkorpi K, Hedenberg L, Bjelle A. A randomized, controlled clinical trial of education and physical training for women with fibromyalgia. Journal of Rheumatology 1994;21(4):714‐20. - PubMed
Burckhardt 2003
Busija 2011
-
- Busija L, Pausenberger E, Haines TP, Haymes S, Buchbinder R, Osborne RH. Adult measures of general health and health‐related quality of life: Medical Outcomes Study Short Form 36‐Item (SF‐36) and Short Form 12‐Item (SF‐12) Health Surveys, Nottingham Health Profile (NHP), Sickness Impact Profile (SIP), Medical Outcomes Study Short Form 6D (SF‐6D), Health Utilities Index Mark 3 (HUI3), Quality of Well‐Being Scale (QWB), and Assessment of Quality of Life (AQoL). Arthritis Care and Research 2011;63 Suppl 11:S383‐412. - PubMed
Buysse 1989
-
- Buysse DJ, Reynolds CF III, Monk TH, Berman SR, Kupfer DJ. The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index: a new instrument for psychiatric practice and research. Psychiatry Research 1989;28(2):193‐213. - PubMed
Callahan 1988
-
- Callahan LF, Brooks RH, Pincus T. Further analysis of learned helplessness in rheumatoid arthritis using a "Rheumatology Attitudes Index". Journal of Rheumatology 1988;15(3):418‐26. - PubMed
Cardoso 2001
-
- Cardoso JR, Atallah ÁN, Cardoso AP, Carvalho SS, Garanhani MM, Lavado EL, et al. Aquatic therapy exercise for treating rheumatoid arthritis. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2001, Issue 4. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003684] - DOI
Carson 2010
Carson 2012
Carville 2008
-
- Carville SF, Choy EH. Systematic review of discriminating power of outcome measures used in clinical trials of fibromyalgia. Journal of Rheumatology 2008;35(11):2094‐105. - PubMed
Carville 2008a
-
- Carville SF, Arendt‐Nielsen S, Bliddal H, Blotman F, Branco JC, Buskila D, et al. EULAR evidence‐based recommendations for the management of FM syndrome. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2008;67(4):536‐41. - PubMed
Cates 2008 [Computer program]
-
- Cates C. Visual Rx, Version 3. Cates C, 2008.
Cedraschi 2004
Charter of Physiotherapists 2009
-
- Charter of Physiotherapists. The definition of aquatic physiotherapy. Aqualines: The Hydrotherapy Association of Chartered Physiotherapists 2009;21(2):6.
Choy 2009
-
- Choy EH, Mease PJ. Key symptom domains to be assessed in fibromyalgia (outcome measures in rheumatoid arthritis clinical trials). Rheumatic Diseases Clinics of North America 2009;35(2):329‐37. - PubMed
Choy 2009a
Cohen 1988
-
- Cohen J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences. 2. Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 1988.
Cole 2004
-
- Cole AJ, Becker BE. Comprehensive Aquatic Therapy. 2nd Edition. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Inc., 2004.
Crofford 1998
-
- Crofford LJ. The hypothalamic‐pituitary‐adrenal stress axis in fibromyalgia and chronic fatigue syndrome. Zeitschrift für Rheumatologie 1998;57 Suppl 2:67‐71. - PubMed
Cuatrecasas 2007
Da Costa 2005
-
- Costa D, Abrahamowicz M, Lowensteyn I, Bernatsky S, Dritsa M, Fitzcharles MA, et al. A randomized clinical trial of an individualized home‐based exercise programme for women with fibromyalgia. Rheumatology 2005;44(11):1422‐7. - PubMed
Dadabhoy 2008
Dagfinrud 2008
de Boer 2004
-
- Boer AG, Lanschot JJ, Stalmeier PF, Sandick JW, Hulscher JB, Haes JC, et al. Is a single‐item visual analogue scale as valid, reliable and responsive as multi‐item scales in measuring quality of life?. Quality of Life Research 2004;13(2):311‐20. - PubMed
Deare 2013
Deeks 2011
-
- Deeks JJ, Higgins JPT, Altman DG. Chapter 9: Analysing data and undertaking meta‐analyses. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Demir‐Gocmen 2013
-
- Demir‐Gocmen D, Altan L, Korkmaz N, Arabaci R. Effect of supervised exercise program including balance exercises on the balance status and clinical signs in patients with fibromyalgia. Rheumatology International 2013;33(3):743‐50. - PubMed
Derogatis 2010
-
- Derogatis LR, Unger R. Symptom checklist‐90‐revised. In: Weiner IB, Craighead WE editor(s). Corsini Encyclopedia of Psychology. Vol. 1‐2, John Wiley & Sons, Inc, 2010. [Online ISBN: 9780470479216]
Derry 2012
Devins 2001
-
- Devins GM, Dion R, Pelletier LG, Shapiro CM, Abbey S, Raiz LR, et al. Structure of lifestyle disruptions in chronic disease: a confirmatory factor analysis of the Illness Intrusiveness Ratings Scale. Medical Care 2001;39(10):1097‐104. - PubMed
Diener 1985
-
- Diener E, Emmons RA, Larsen RJ, Griffin S. The Satisfaction With Life Scale. Journal of Personality Assessment 1985;49(1):71‐5. - PubMed
Dixon 1981
Dupuy 1984
-
- Dupuy HJ. The psychological general well‐being (PGWB) index. In: Wenger N editor(s). Assessment of Quality of Life in Clinical Trials of Cardiovascular Therapies. New York: Le Jacq, 1984:170‐83.
Durstine 2013
-
- Durstine JL, Gordon B, Wang Z, Luo X. Chronic disease and the link to physical activity. Journal of Sport and Health Science 2013;2(1):3‐11.
Field 2003
-
- Field T, Delage J, Hernandez Reif M. Movement and massage therapy reduce fibromyalgia pain. Journal of Bodywork and Movement Therapies 2003;7(1):49‐52.
Fontaine 2007
-
- Fontaine KR, Haas S. Effects of lifestyle physical activity on health status, pain, and function in adults with fibromyalgia syndrome. Journal of Musculoskeletal Pain 2007;15(1):3‐9.
Fontaine 2010
Fontaine 2011
Garber 2011
-
- Garber CE, Blissmer B, Deschenes MR, Franklin BA, Lamonte MJ, Lee IM, et al. American College of Sports Medicine position stand. Quantity and quality of exercise for developing and maintaining cardiorespiratory, musculoskeletal, and neuromotor fitness in apparently healthy adults: guidance for prescribing exercise. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 2011;43(7):1334‐59. - PubMed
Garcia‐Martinez 2011
-
- Garcia‐Martinez AM, Paz JA, Marquez S. Effects of an exercise programme on self‐esteem, self‐concept and quality of life in women with fibromyalgia: a randomized controlled trial. Rheumatology International 2011;32(7):1869‐76. - PubMed
Genc 2002
-
- Genc A, Sagiroglu E. Comparison of two different exercise programs in fibromyalgia treatment [Turkish]. Fizyoterapi Rehabilitasyon 2002;13(2):90‐5.
Geytenbeek 2002
-
- Geytenbeek J. Evidence for effective hydrotherapy. Physiotherapy 2002;88(9):514‐29.
Glass 2008
-
- Glass JM. Fibromyalgia and cognition. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 2008;69 Suppl 2:20‐4. - PubMed
Glass 2011
Goldenberg 2004
-
- Goldenberg DL, Burckhardt C, Crofford L. Management of fibromyalgia syndrome. JAMA 2004;292(19):2388‐95. - PubMed
Gowans 1999
-
- Gowans SE, deHueck A, Voss S, Richardson M. A randomized, controlled trial of exercise and education for individuals with fibromyalgia. Arthritis Care and Research 1999;12(2):120‐8. - PubMed
Gowans 2007
-
- Gowans SE, deHueck A. Pool exercise for individuals with fibromyalgia. Current Opinion in Rheumatology 2007;19(2):168‐73. - PubMed
Gracely 2003
-
- Gracely RH, Grant MA, Giesecke T. Evoked pain measures in fibromyalgia. Best Practice & Research. Clinical Rheumatology 2003;17(4):593‐609. - PubMed
Griep 1993
-
- Griep EN, Boersma JW, de‐Kloet ER. Altered reactivity of the hypothalamic‐pituitary‐adrenal axis in the primary fibromyalgia syndrome [see comments]. Journal of Rheumatology 1993;20(3):469‐74. - PubMed
Gusi 2010
-
- Gusi N, Parraca JA, Olivares PR, Leal A, Adsuar JC. Tilt vibratory exercise and the dynamic balance in fibromyalgia: a randomized controlled trial. Arthritis Care and Research 2010;62(8):1072‐8. - PubMed
Hakkinen 2001
Hakkinen 2002
-
- Hakkinen K, Pakarinen A, Hannonen P, Hakkinen A, Airaksinen O, Valkeinen H, et al. Effects of strength training on muscle strength, cross‐sectional area, maximal electromyographic activity, and serum hormones in premenopausal women with fibromyalgia. Journal of Rheumatology 2002;29(6):1287‐95. - PubMed
Hamilton 1960
Hammond 2006
-
- Hammond A, Freeman K. Community patient education and exercise for people with fibromyalgia: a parallel group randomized controlled trial. Clinical Rehabilitation 2006;20(10):835‐46. - PubMed
Hauser 2010
Hauser 2010a
-
- Hauser W, Thieme K, Turk DC. Guidelines on the management of fibromyalgia syndrome ‐ a systematic review. European Journal of Pain 2010;14(1):5‐10. - PubMed
Hauser 2013
Heinrichs 1984
-
- Heinrichs DW, Hanlon TE, Carpenter WT Jr. The Quality of Life Scale: an instrument for rating the schizophrenic deficit syndrome. Schizophrenia Bulletin 1984;10(3):388‐98. - PubMed
Heyward 2010
-
- Heyward VH. Advanced Fitness Assessment and Exercise Prescription. 6. Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics, 2010.
Higgins 2011a
-
- Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Sterne JAC (editors). Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Higgins 2011b
-
- Higgins JPT, Deeks JJ, Altman DG (editors). Chapter 16: Special topics in statistics. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Hooten 2012
-
- Hooten WM, Qu W, Townsend CO, Judd JW. Effects of strength vs aerobic exercise on pain severity in adults with fibromyalgia: a randomized equivalence trial. Pain 2012;153(4):915‐23. - PubMed
Howley 2001
-
- Howley ET. Type of activity: resistance, aerobic and leisure versus occupational physical activity. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 2001;33(6 Suppl):S364‐9. - PubMed
Hunt 2000
-
- Hunt J, Bogg J. An evaluation of the impact of a fibromyalgia self‐management programme on patient morbidity and coping. Advances in Physiotherapy 2000;2(4):168‐75.
Huskisson 1976
-
- Huskisson EC, Jones J, Scott PJ. Application of visual‐analogue scales to the measurement of functional capacity. Rheumatology and Rehabilitation 1976;15(3):185‐7. - PubMed
Huskisson 1983
-
- Huskisson EC, Sturrock RD, Tugwell P. Measurement of patient outcome. British Journal of Rheumatology 1983;22:86‐9. - PubMed
Isomeri 1993
-
- Isomeri R, Mikkelsson M, Latikka P, Kammonen K. Effects of amitriptyline and cardiovascular fitness training on pain in patients with primary fibromyalgia. Journal of Musculoskeletal Pain 1993;1:253‐60.
Jones 2002
-
- Jones KD, Burckhardt CS, Clark SR, Bennett RM, Potempa KM. A randomized controlled trial of muscle strengthening versus flexibility training in fibromyalgia. Journal of Rheumatology 2002;29(5):1041‐8. - PubMed
Jones 2007
-
- Jones KD, Deodhar AA, Burckhardt CS, Perrin NA, Hanson GC, Bennett RM. A combination of 6 months of treatment with pyridostigmine and triweekly exercise fails to improve insulin‐like growth factor‐I levels in fibromyalgia, despite improvement in the acute growth hormone response to exercise. Journal of Rheumatology 2007;34(5):1103‐11. - PubMed
Jones 2007a
-
- Jones KD, Deodhar P, Lorentzen A, Bennett RM, Deodhar AA. Growth hormone perturbations in fibromyalgia: a review. Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism 2007;36(6):357‐79. - PubMed
Jones 2008
Jones 2009
-
- Jones KD, Liptan GL. Exercise interventions in fibromyalgia: clinical applications from the evidence. Rheumatic Diseases Clinics of North America 2009;35(2):373‐91. - PubMed
Jones 2012
Joshi 2009
-
- Joshi MN, Joshi R, Jain AP. Effect of amitriptyline vs. physiotherapy in management of fibromyalgia syndrome: what predicts a clinical benefit?. Journal of Postgraduate Medicine 2009;55(3):185‐9. - PubMed
Kayo 2011
-
- Kayo AH, Peccin MS, Sanches CM, Trevisani VF. Effectiveness of physical activity in reducing pain in patients with fibromyalgia: a blinded randomized clinical trial. Rheumatology International 2011;32(8):2285‐92. - PubMed
Keel 1998
-
- Keel PJ, Bodoky C, Gerhard U, Muller W. Comparison of integrated group therapy and group relaxation training for fibromyalgia. Clinical Journal of Pain 1998;14(3):232‐8. - PubMed
Kelley 2011
King 2002
-
- King SJ, Wessel J, Bhambhani Y, Sholter D, Maksymowych W. The effects of exercise and education, individually or combined, in women with fibromyalgia. Journal of Rheumatology 2002;29(12):2620‐7. - PubMed
Langhorst 2009
-
- Langhorst J, Musial F, Klose P, Hauser W. Efficacy of hydrotherapy in fibromyalgia syndrome‐‐a meta‐analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials. Rheumatology 2009;48(9):1155‐9. - PubMed
Lefebvre 2011
-
- Lefebvre C, Manheimer E, Glanville J. Chapter 6: Searching for studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Lemstra 2005
-
- Lemstra M, Olszynski WP. The effectiveness of multidisciplinary rehabilitation in the treatment of fibromyalgia: a randomized controlled trial. Clinical Journal of Pain 2005;21(2):166‐74. - PubMed
Lima 2013
-
- Lima TB, Dias JM, Mazuquin BF, Silva CT, Nogueira RM, Marques AP, et al. The effectiveness of aquatic physical therapy in the treatment of fibromyalgia: a systematic review with meta‐analysis. Clinical Rehabilitation 2013;27(10):892‐908. - PubMed
Liu 2012
-
- Liu W, Zahner L, Cornell M, Le T, Ratner J, Wang Y, et al. Benefit of Qigong exercise in patients with fibromyalgia: a pilot study. International Journal of Neuroscience 2012;122(11):657‐64. - PubMed
Lorig 1989
-
- Lorig K, Chastain RL, Ung E, Shoor S, Holman HR. Development and evaluation of a scale to measure perceived self‐efficacy in people with arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 1989;32(1):37‐44. - PubMed
Lue 1994
-
- Lue FA. Sleep and fibromyalgia. Journal of Musculoskeletal Pain 1994;2(3):89‐100.
Lynch 2012
Mannerkorpi 2010
Marcus 2011
-
- Marcus DA, Deodhar A. Introduction. Fibromyalgia. New York: Springer Science + Business Media, 2011:3‐7.
Marcus 2011a
-
- Marcus DA, Deodhar A. Non‐medication treatments. Fibromyalgia. New York, NY: Springer Science + Business Media, 2011:159‐74.
Martin 1996
-
- Martin L, Nutting A, MacIntosh BR, Edworthy SM, Butterwick D, Cook J. An exercise program in the treatment of fibromyalgia. Journal of Rheumatology 1996;23(6):1050‐3. - PubMed
Martin‐Nogueras 2012
-
- Martin‐Nogueras AM, Calvo‐Arenillas JI. Efficacy of physiotherapy treatment on pain and quality of life in patients with fibromyalgia [Spanish]. Rehabilitacion 2012;46(3):199‐206.
Matsutani 2007
-
- Matsutani LA, Marques AP, Ferreira EA, Assumpcao A, Lage LV, Casarotto RA, et al. Effectiveness of muscle stretching exercises with and without laser therapy at tender points for patients with fibromyalgia. Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology 2007;25(3):410‐5. - PubMed
Matsutani 2012
-
- Matsutani LA, Assumpcao A, Marques AP. Stretching and aerobic exercises in the treatment of fibromyalgia: pilot study [Portuguese]. Fisioterapia em Movimento 2012;25(2):411‐8.
McCain 1988
-
- McCain GA, Bell DA, Mai FM, Halliday PD. A controlled study of the effects of a supervised cardiovascular fitness training program on the manifestations of primary fibromyalgia. Arthritis and Rheumatism 1988;31(9):1135‐41. - PubMed
McLoughlin 2011
McNair 1981
-
- McNair PM, Lorr M, Droppleman LF. POMS Manual. San Diego, California: Educational and Industrial Testing Service, 1981.
McNalley 2006
-
- McNalley JD, Matheson DA, Bakowshy VS. The epidemiology of self‐reported fibromyalgia in Canada. Chronic Diseases in Canada 2006;27(1):9‐16. - PubMed
McVeigh 2008
-
- McVeigh JG, McGaughey H, Hall M, Kane P. The effectiveness of hydrotherapy in the management of fibromyalgia syndrome: a systematic review. Rheumatology International 2008;29(2):119‐30. - PubMed
Mease 2005
-
- Mease P. Fibromyalgia syndrome: review of clinical presentation, pathogenesis, outcome measures, and treatment. [erratum appears in J Rheumatol Suppl. 2005 Oct;32(10):2063]. Journal of Rheumatology. Supplement 2005;75:6‐21. - PubMed
Mease 2008
-
- Mease PJ, Arnold LM, Crofford LJ, Williams DA, Russell IJ, Humphrey L, et al. Identifying the clinical domains of fibromyalgia: contributions from clinician and patient Delphi exercises. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2008;59(7):952‐60. - PubMed
Mease 2009
Meenan 1992
-
- Meenan RF, Mason JH, Anderson JL, Guccione AA, Kazis LE. AIMS2: The content and properties of a revised and expanded Arthritis Impact Measurement Scales Health Status Questionnaire. Arthritis and Rheumatism 1992;1(1):1‐10. - PubMed
Mengshoel 1992
-
- Mengshoel AM, Komnaes HB, Forre O. The effects of 20 weeks of physical fitness training in female patients with fibromyalgia. Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology 1992;10(4):345‐9. - PubMed
Mengshoel 1993
-
- Mengshoel AM, Forre O. Physical fitness training in patients with fibromyalgia. Musculoskeletal pain 1993;1(4):267‐72.
Merskey 1994
-
- Merskey H, Bogduk N. Classifications of Chronic Pain: Descriptions and Definitions of Chronic Pain Syndromes and Definitions of Pain Terms. Seattle, WA: IASP, 1994.
Mitchell 2002 [Computer program]
-
- Mitchell M. Engauge Digitizer ‐ Digitizing Software. Version 4.1. Online, 2002. [digitizer.sourceforge.net]
Moore 2012
Moore 2014
Nichols 1994
-
- Nichols DS, Glenn TM. Effects of aerobic exercise on pain perception, affect, and level of disability in individuals with fibromyalgia. Physical Therapy 1994;74:327‐32. - PubMed
Noonan 2000
-
- Noonan V, Dean E. Submaximal exercise testing: clinical application and interpretation. Physical Therapy 2000;80(8):782‐807. - PubMed
Norregaard 1997
-
- Norregaard J, Lykkegaard JJ, Mehlsen J, Danneskiold Samsoe B. Exercise training in treatment of fibromyalgia. Journal of Musculoskeletal Pain 1997;5(1):71‐9.
O'Connor 2011
-
- O’Connor D, Green S, Higgins JPT (editors). Chapter 5: Defining the review question and developing criteria for including studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors), Cochrane Handbook of Systematic Reviews of Intervention. Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Olivares 2011
-
- Olivares PR, Gusi N, Parraca JA, Adsuar JC, Pozo‐Cruz B. Tilting whole body vibration improves quality of life in women with fibromyalgia: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine 2011;17(8):723‐8. - PubMed
Park 2000
-
- Park JH, Niermann KJ, Olsen N. Evidence for metabolic abnormalities in the muscles of patients with fibromyalgia. Current Rheumatology Reports 2000;2(2):131‐40. - PubMed
Park 2007
-
- Park J, Knudson S. Medically unexplained physical symptoms. Health Reports 2007;18(1):43‐7. - PubMed
Perraton 2009
Philadelphia Panel 2001
-
- Philadelphia Panel. Philadelphia Panel evidence‐based clinical practice guidelines on selected rehabilitation interventions for low back pain. Physical Therapy 2001;81(10):1641‐71. - PubMed
Pillemer 1997
-
- Pillemer SR, Bradley LA, Crofford LJ, Moldofsky H, Chrousos GP. The neuroscience and endocrinology of fibromyalgia. Arthritis and Rheumatism 1997;40(11):1928‐39. - PubMed
Ramsay 2000
-
- Ramsay C, Moreland J, Ho M, Joyce S, Walker S, Pullar T. An observer‐blinded comparison of supervised and unsupervised aerobic exercise regimens in fibromyalgia. Rheumatology 2000;39(5):501‐5. - PubMed
RevMan 2012 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.2. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2012.
Richards 2002
Rivera Redondo 2004
-
- Rivera Redondo J, Moratalla Justo C, Valdepenas Moraleda F, Garcia Velayos Y, Oses Puche JJ, Ruiz Zubero J, et al. Long‐term efficacy of therapy in patients with fibromyalgia: a physical exercise‐based program and a cognitive‐behavioral approach. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2004;51(2):184‐92. - PubMed
Rooks 2007
-
- Rooks DS, Gautam S, Romeling M, Cross ML, Stratigakis D, Evans B, et al. Group exercise, education, and combination self‐management in women with fibromyalgia: a randomized trial. Archives of Internal Medicine 2007;167(20):2192‐200. - PubMed
Rooks 2008
-
- Rooks DS. Talking to patients with fibromyalgia about physical activity and exercise. Current Opinion in Rheumatology 2008;20(2):208‐12. - PubMed
Sañudo 2010a
-
- Sanudo B, Hoyo M, Carrasco L, McVeigh JG, Corral J, Cabeza R, et al. The effect of 6‐week exercise programme and whole body vibration on strength and quality of life in women with fibromyalgia: a randomised study. Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology 2010;28(6 Suppl 63):S40‐5. - PubMed
Sañudo 2010b
-
- Sanudo B, Galiano D, Carrasco L, Blagojevic M, Hoyo M, Saxton J. Aerobic exercise versus combined exercise therapy in women with fibromyalgia syndrome: a randomized controlled trial. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2010;91(12):1838‐43. - PubMed
Sañudo 2010c
-
- Sanudo Corrales B, Galiano Orea D, Carrasco P ez L, Saxton J. Autonomous nervous system response and quality of life on women with fibromyalgia after a long‐term intervention with physical exercise [Spanish]. Rehabilitacion 2010;44(3):244‐9.
Sañudo 2011
-
- Sanudo B, Galiano D, Carrasco L, Hoyo M, McVeigh JG. Effects of a prolonged exercise program on key health outcomes in women with fibromyalgia: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine 2011;43(6):521‐6. - PubMed
Sañudo 2012
-
- Sañudo B, Hoyo M, Carrasco L, Rodriguez‐Blanco C, Oliva‐Pascual‐Vaca A, McVeigh JG. Effect of whole‐body vibration exercise on balance in women with fibromyalgia syndrome: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine 2012;18(2):158‐64. - PubMed
Schachter 2003
-
- Schachter CL, Busch AJ, Peloso P, Sheppard MS. The effects of short versus long bouts of aerobic exercise in sedentary women with fibromyalgia: a randomized controlled trial. Physical Therapy 2003;83(4):340‐58. - PubMed
Schmidt 2011
-
- Schmidt S, Grossman P, Schwarzer B, Jena S, Naumann J, Walach H. Treating fibromyalgia with mindfulness‐based stress reduction: results from a 3‐armed randomized controlled trial. Pain 2011;152(2):1838‐43. - PubMed
Schmidt‐Wilcke 2011
-
- Schmidt‐Wilcke T, Clauw DJ. Fibromyalgia: from pathophysiology to therapy. Nature Reviews. Rheumatology 2011;7(9):518‐27. - PubMed
Schünemann 2011
-
- Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Higgins JPT, Vist GE, Glasziou P, Guyatt GH. Chapter 11: Presenting results and 'Summary of findings' tables. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Sencan 2004
-
- Sencan S, Ak S, Karan A, Muslumanoglu L, Ozcan E, Berker E. A study to compare the therapeutic efficacy of aerobic exercise and paroxetine in fibromyalgia syndrome. Journal of Back & Musculoskeletal Rehabilitation 2004;17(2):57‐61.
Smith 2003
-
- Smith MT, Wegener ST. Measures of sleep: the Insomnia Severity Index, Medical Outcomes Study (MOS) Sleep Scale, Pittsburgh Sleep Diary (PSD), and Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI). Arthritis Care and Research 2003;49(S5):S184‐96.
Smythe 1981
-
- Smythe HA. Fibrositis and other diffuse musculoskeletal syndromes. In: Kelley WN, Harris ED Jr, Ruddy S, Sledge CB editor(s). Textbook of Rheumatology. 1st Edition. WB Saunders, 1981.
Sova 1992
-
- Sova R. Aquatics: the Complete Reference Guide for Aquatic Fitness Professionals. Boston: Jones and Bartlett, 1992.
Staud 2002
-
- Staud R. Evidence of involvement of central neural mechanisms in generating fibromyalgia pain. Current Rheumatology Reports 2002;4(4):299‐305. - PubMed
Sterne 2011
-
- Sterne JAC, Egger M, Moher D (editors). Chapter 10: Addressing reporting biases. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Tander 2008
-
- Tander B, Gunes S, Boke O, Alayli G, Kara N, Bagci H, et al. Polymorphisms of the serotonin‐2A receptor and catechol‐O‐methyltransferase genes: a study on fibromyalgia susceptibility. Rheumatology International 2008;28(7):685‐91. - PubMed
Tort 2012
Trew 2005
-
- Trew M, Everett T. Human Movement: An Introductory Text. 5th Edition. Edinburgh: Elsevier Churchill Livingstone, 2005.
Turk 2002
-
- Turk DC. Suffering and dysfunction in fibromyalgia syndrome. Journal of Musculoskeletal Pain 2002;10(1‐2):85‐96.
Uceyler 2013
Valencia 2009
-
- Valencia M, Alonso B, Alvarez MJ, Barrientos MJ, Ayan C, Sanchez VM. Effects of 2 physiotherapy programs on pain perception, muscular flexibility, and illness impact in women with fibromyalgia: a pilot study. Journal of Manipulative and Physiological Therapeutics 2009;32(1):84‐92. - PubMed
Valim 2003
-
- Valim V, Oliveira L, Suda A, Silva L, Assis M, Barros Neto T, et al. Aerobic fitness effects in fibromyalgia. Journal of Rheumatology 2003;30(5):1060‐9. - PubMed
Valkeinen 2004
-
- Valkeinen H, Alen M, Hannonen P, Hakkinen A, Airaksinen O, Hakkinen K. Changes in knee extension and flexion force, EMG and functional capacity during strength training in older females with fibromyalgia and healthy controls. Rheumatology 2004;43(2):225‐8. - PubMed
Valkeinen 2005
-
- Valkeinen H, Hakkinen K, Pakarinen A, Hannonen P, Hakkinen A, Airaksinen O, et al. Muscle hypertrophy, strength development, and serum hormones during strength training in elderly women with fibromyalgia. Scandinavian Journal of Rheumatology 2005;34(4):309‐14. - PubMed
Valkeinen 2008
-
- Valkeinen H, Alen M, Hakkinen A, Hannonen P, Kukkonen‐Harjula K, Hakkinen K. Effects of concurrent strength and endurance training on physical fitness and symptoms in postmenopausal women with fibromyalgia: a randomized controlled trial. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2008;89(9):1660‐6. - PubMed
van Koulil 2010
-
- Koulil S, Lankveld W, Kraaimaat FW, Helmond T, Vedder A, Hoorn H, et al. Tailored cognitive‐behavioral therapy and exercise training for high‐risk patients with fibromyalgia. Arthritis Care and Research 2010;62(10):1377‐85. - PubMed
van Santen 2002a
-
- Santen M, Bolwijn P, Verstappen F, Bakker C, Hidding A, Houben H, et al. A randomized clinical trial comparing fitness and biofeedback training versus basic treatment in patients with fibromyalgia. Journal of Rheumatology 2002;29(3):575‐81. - PubMed
van Santen 2002b
-
- Santen M, Bolwijn P, Landewe R, Verstappen F, Bakker C, Hidding A, et al. High or low intensity aerobic fitness training in fibromyalgia: does it matter?. Journal of Rheumatology 2002;29(3):582‐7. - PubMed
van Tulder 2003
-
- Tulder MW, Furlan A, Bombardier C, Bouter L. Updated method guidelines for systematic reviews in the Cochrane Collaboration Back Review Group. Spine 2003;28(12):1290‐9. - PubMed
Vargas 2004
-
- Vargas LG. Aquatic Therapy: Interventions and Applications. Idyll Arbor, 2004.
Verhagen 2004
Verhagen 2008
-
- Verhagen A, Bierma‐Zeinstra S, Lambeck J, Cardoso JR, Bie R, Boers M, et al. Balneotherapy for osteoarthritis. A Cochrane review. Journal of Rheumatology 2008;35(6):1118‐23. - PubMed
Verhagen 2012
-
- Verhagen AP, Cardoso JR, Bierma‐Zeinstra SM. Aquatic exercise & balneotherapy in musculoskeletal conditions. Best Practice & Research. Clinical Rheumatology 2012;26(3):335‐43. - PubMed
Verstappen 1997
-
- Verstappen FTJ, Santen‐Hoeuftt HMS, Bolwijn PH, Linden S, Kuipers H. Effects of a group activity program for fibromyalgia patients on physical fitness and well being. Journal of Musculoskeletal Pain 1997;5(4):17‐28.
Wang 2010
Ware 1993
-
- Ware JE, Snow KK, Kosinski M, Gandek B, New England Medical Center Hospital Health Institute. SF‐36 Health Survey: Manual and Interpretation Guide. The Health Institute, New England Medical Center, 1993.
WHO 2013
-
- World Health Organization. Health Topics ‐ Depression. http://www.who.int/topics/depression/en/ (accessed 18 August 2014).
Wiffen 2013
Wigers 1996
-
- Wigers SH, Stiles TC, Vogel PA. Effects of aerobic exercise versus stress management treatment in fibromyalgia. A 4.5 year prospective study. Scandinavian Journal of Rheumatology 1996;25(2):77‐86. - PubMed
Wolfe 1990
-
- Wolfe F, Smythe HA, Yunus MB, Bennett RM, Bombardier C, Goldenberg DL, et al. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of fibromyalgia. Report of the multicenter criteria committee. Arthritis and Rheumatism 1990;33(2):160‐72. - PubMed
Wolfe 1997a
-
- Wolfe F, Hawley DJ. Measurement of the quality of life in rheumatic disorders using the EuroQol. British Journal of Rheumatology 1997;36(7):786‐93. - PubMed
Wolfe 2004
-
- Wolfe F. Fatigue assessments in rheumatoid arthritis: comparative performance of visual analog scales and longer fatigue questionnaires in 7760 patients. Journal of Rheumatology 2004;31(10):1896‐902. - PubMed
Wolfe 2010
-
- Wolfe F, Clauw DJ, Fitzcharles MA, Goldenberg DL, Katz RS, Mease P, et al. The American College of Rheumatology preliminary diagnostic criteria for fibromyalgia and measurement of symptom severity. Arthritis Care and Research 2010;62(5):600‐10. - PubMed
Wolfe 2011
-
- Wolfe F, Clauw DJ, Fitzcharles MA, Goldenberg DL, Hauser W, Katz RS, et al. Fibromyalgia criteria and severity scales for clinical and epidemiological studies: a modification of the ACR preliminary diagnostic criteria for fibromyalgia. Journal of Rheumatology 2011;38(6):1113‐22. - PubMed
Yunus 1981
-
- Yunus M, Masi AT, Calabro JJ, Miller KA, Feigenbaum SL. Primary fibromyalgia (fibrositis): clinical study of 50 patients with matched normal controls. Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism 1981;11:151‐71. - PubMed
Yunus 1982
-
- Yunus M, Masi AT, Calabro JJ, Shah IK. Primary fibromyalgia. America Family Physician 1982;25(5):115‐21. - PubMed
Yunus 1984
-
- Yunus MB. Primary fibromyalgia syndrome: current concepts. Comprehensive Therapy 1984;10:21‐8. - PubMed
Yuruk 2008
-
- Yuruk OB, Gultekin Z. Comparison of two different exercise programs in women with fibromyalgia syndrome [Turkish]. Fizyoterapi Rehabilitasyon 2008;19(1):15‐23.
References to other published versions of this review
Busch 2001
-
- Busch AJ, Schachter CL, Peloso PM. Fibromyalgia and exercise training: a systematic review of randomized clinical trials. Physical Therapy Review 2001;6:287‐306.
Busch 2007
Busch 2008
-
- Busch AJ, Schachter CL, Overend TJ, Peloso PM, Barber KA. Exercise for fibromyalgia: a systematic review. Journal of Rheumatology 2008;35(6):1130‐44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

