Ephrin type‑A receptor 2 regulates sensitivity to paclitaxel in nasopharyngeal carcinoma via the phosphoinositide 3‑kinase/Akt signalling pathway
- PMID: 25351620
- PMCID: PMC4262504
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2014.2799
Ephrin type‑A receptor 2 regulates sensitivity to paclitaxel in nasopharyngeal carcinoma via the phosphoinositide 3‑kinase/Akt signalling pathway
Abstract
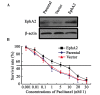
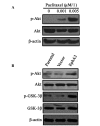
Ephrin type‑A receptor 2 (EphA2) is a receptor tyrosine kinase that is associated with cancer cell metastasis. There has been little investigation into its impact on the regulation of sensitivity to paclitaxel in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). In the present study, upregulation of EphA2 expression enhanced the survival of NPC 5‑8F cells, compared with control cells exposed to the same concentrations of paclitaxel. Flow cytometry and western blot analysis demonstrated that over‑expression of EphA2 decreased NPC cancer cell sensitivity to paclitaxel by regulating paclitaxel‑mediated cell cycle progression but not apoptosis in vitro. This was accompanied by alterations in the expression of cyclin‑dependent kinase inhibitors, p21 and p27, and of inactive phosphorylated‑retinoblastoma protein. Furthermore, paclitaxel stimulation and EphA2 over‑expression resulted in activation of the phosphoinositide 3‑kinase (PI3K)/Akt signalling pathway in NPC cells. Inhibition of the PI3K/Akt signalling pathway restored sensitivity to paclitaxel in 5‑8F cells over‑expressing EphA2, which indicated that the PI3K/Akt pathway is involved in EphA2‑mediated paclitaxel sensitivity. The current study demonstrated that EphA2 mediates sensitivity to paclitaxel via the regulation of the PI3K/Akt signalling pathway in NPC.
Figures



References
-
- Huober J, Fasching PA, Hanusch C, Rezai M, Eidtmann H, et al. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy with paclitaxel and everolimus in breast cancer patients with non-responsive tumours to epirubicin/cyclophosphamide (EC) ± bevacizumab - results of the randomised GeparQuinto study (GBG 44) Eur J Cancer. 2013;49:2284–2293. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2013.02.027. - DOI - PubMed
-
- van der Burg ME, Vergote I, Onstenk W, Boere IA, Leunen K, et al. Long-term results of weekly paclitaxel carboplatin induction therapy: an effective and well-tolerated treatment in patients with platinum-resistant ovarian cancer. Eur J Cancer. 2013;49:1254–1263. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2012.11.027. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

