Aortic dissection during antiangiogenic therapy with sunitinib. A case report
- PMID: 25351639
- PMCID: PMC10876365
- DOI: 10.1590/1516-3180.2013.7380002
Aortic dissection during antiangiogenic therapy with sunitinib. A case report
Abstract
Context: Sunitinib is an antiangiogenic drug that has been approved for treating metastatic renal cancer. Its action as a tyrosine kinase inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptors (VEGFRs) and other angiogenesis receptors may lead to adverse effects such as hypertension and heart failure. However, reports in the literature on an association between sunitinib therapy and acute aortic dissection are rare.
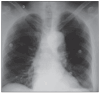
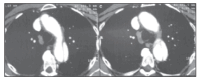
Case report: We report the case of a 68-year-old man with metastatic renal carcinoma who developed acute aortic dissection during sunitinib therapy. He had no history of hypertension or any other risk factor for aortic dissection. After aortic dissection had been diagnosed, sunitinib was withdrawn and an aortic endoprosthesis was placed. Afterwards, the patient was treated clinically with antihypertensive drugs and new therapy for renal cancer consisting of temsirolimus, an inhibitor of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway.
Conclusion: Hypertension is a common event when antiangiogenic drugs are used in oncology. However, knowledge of other severe cardiovascular events that may occur in these patients, such as acute aortic dissection, is important. Adequate control over arterial pressure and frequent monitoring of patients during the first days of antiangiogenic therapy is essential for early diagnosis of possible adverse events.
CONTEXTO:: Sunitinibe é uma droga antiangiogênica aprovada para tratamento de câncer renal metastático. Sua ação como inibidor de tirosina quinase de receptores de fatores de crescimento do endotélio vascular (VEGFR) e de outros receptores de angiogênese pode levar a eventos adversos como hipertensão e insuficiência cardíaca. No entanto, é escassa na literatura a associação da terapia com sunitinibe e dissecção aguda de aorta.
RELATO DE CASO:: Relatamos o caso de um paciente do sexo masculino de 68 anos com câncer renal metastático que desenvolveu dissecção aguda de aorta durante tratamento com sunitinibe. O paciente não tinha histórico prévio de hipertensão nem outro fator de risco para dissecção de aorta. Após diagnóstico da dissecção de aorta, a droga foi suspensa e o paciente foi submetido à colocação de endoprótese na aorta, evoluindo posteriormente com controle clínico da pressão arterial e nova terapia para câncer renal com tensirolimo, um inibidor da via proteína alvo da rapamicina em mamíferos (mTOR).
CONCLUSÕES:: A hipertensão é um evento comum com uso de drogas antiangiogênicas na oncologia. No entanto, é importante o conhecimento de outros eventos cardiovasculares graves, como dissecção aguda de aorta, que podem ocorrer nesses pacientes. Controle adequado da pressão arterial e monitorização frequente dos pacientes nos primeiros dias de terapia antiangiogênica são essenciais para diagnóstico precoce de possíveis eventos graves.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Acute aortic dissection in a patient receiving multiple tyrosine kinase inhibitors for 5 years.Aktuelle Urol. 2014 Mar;45(2):132-4. doi: 10.1055/s-0033-1363274. Epub 2014 Apr 3. Aktuelle Urol. 2014. PMID: 24700069
-
Aortic dissection in a patient treated by sunitinib for metastatic renal cell carcinoma.Ann Oncol. 2010 Jan;21(1):186-7. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdp480. Epub 2009 Oct 29. Ann Oncol. 2010. PMID: 19875754 No abstract available.
-
Hypertension as a biomarker of efficacy in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with sunitinib.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2011 May 4;103(9):763-73. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djr128. Epub 2011 Apr 28. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2011. PMID: 21527770 Free PMC article.
-
Response to sorafenib after sunitinib-induced acute heart failure in a patient with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: case report and review of the literature.Pharmacotherapy. 2009 Apr;29(4):473-8. doi: 10.1592/phco.29.4.473. Pharmacotherapy. 2009. PMID: 19323623 Review.
-
Sunitinib, hypertension, and heart failure: a model for kinase inhibitor-mediated cardiotoxicity.Curr Hypertens Rep. 2011 Dec;13(6):430-5. doi: 10.1007/s11906-011-0229-4. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2011. PMID: 21931979 Review.
Cited by
-
Potential synergistic effects of lenvatinib and aspirin in aortic dissection: a case report and literature review.Front Oncol. 2025 Apr 22;15:1520770. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1520770. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40330834 Free PMC article.
-
Aortic dissection in a patient treated with anlotinib for metastatic lung squamous cell carcinoma.Thorac Cancer. 2020 Feb;11(2):461-464. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13288. Epub 2019 Dec 31. Thorac Cancer. 2020. PMID: 31891239 Free PMC article.
-
Secukinumab and Black Garlic Downregulate OPG/RANK/RANKL Axis and Devitalize Myocardial Interstitial Fibrosis Induced by Sunitinib in Experimental Rats.Life (Basel). 2023 Jan 22;13(2):308. doi: 10.3390/life13020308. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36836664 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor tyrosine kinase inhibitor targeted therapy: a potential cause of an acute aortic dissection lesser known to the emergency physician.BMJ Case Rep. 2021 Oct 27;14(10):e245653. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2021-245653. BMJ Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 34706918 Free PMC article.
-
Aneurysm and Artery Dissection Following the Use of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Inhibitor: A Real-World Analysis Using a Spontaneous Reporting System.J Am Heart Assoc. 2021 Dec 7;10(23):e020844. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.121.020844. Epub 2021 Nov 30. J Am Heart Assoc. 2021. PMID: 34845918 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Tomczak P, et al. Sunitinib versus interferon alpha in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2007;356(2):115–124. - PubMed
-
- Bragalone DL. Bragalone DL. Drug information handbook for oncology. Hudson: Lexi-Comp; 2011. Sunitinib; pp. 1168–1174.
-
- Golledge J, Eagle KA. Acute aortic dissection. Lancet. 2008;372(9632):55–66. - PubMed
-
- Edeline J, Laguerre B, Rolland Y, Patard JJ. Aortic dissection in a patient treated by sunitinib for metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Ann Oncol. 2010;21(1):186–187. - PubMed
-
- Kirchner H, Strumberg D, Bahl A, Overkamp F. Patient-based strategy for systemic treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2010;10(4):585–596. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous