Purinergic signalling and immune cells
- PMID: 25352330
- PMCID: PMC4272370
- DOI: 10.1007/s11302-014-9427-2
Purinergic signalling and immune cells
Abstract
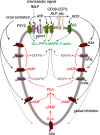
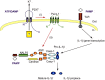
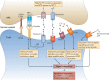
This review article provides a historical perspective on the role of purinergic signalling in the regulation of various subsets of immune cells from early discoveries to current understanding. It is now recognised that adenosine 5'-triphosphate (ATP) and other nucleotides are released from cells following stress or injury. They can act on virtually all subsets of immune cells through a spectrum of P2X ligand-gated ion channels and G protein-coupled P2Y receptors. Furthermore, ATP is rapidly degraded into adenosine by ectonucleotidases such as CD39 and CD73, and adenosine exerts additional regulatory effects through its own receptors. The resulting effect ranges from stimulation to tolerance depending on the amount and time courses of nucleotides released, and the balance between ATP and adenosine. This review identifies the various receptors involved in the different subsets of immune cells and their effects on the function of these cells.
Figures


References
-
- Idzko M, Hammad H, van Nimwegen M, Kool M, Willart MA, Muskens F, Hoogsteden HC, Luttmann W, Ferrari D, Di Virgilio F, Virchow JC, Jr, Lambrecht BN. Extracellular ATP triggers and maintains asthmatic airway inflammation by activating dendritic cells. Nat Med. 2007;13:913–919. - PubMed
-
- Elliott MR, Chekeni FB, Trampont PC, Lazarowski ER, Kadl A, Walk SF, Park D, Woodson RI, Ostankovich M, Sharma P, Lysiak JJ, Harden TK, Leitinger N, Ravichandran KS. Nucleotides released by apoptotic cells act as a find-me signal to promote phagocytic clearance. Nature. 2009;461:282–286. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

