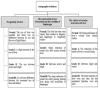
Data from a randomized and controlled trial of LCarnitine prescription for the treatment for Non- Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
- PMID: 25352725
- PMCID: PMC4209366
- DOI: 10.6026/97320630010575
Data from a randomized and controlled trial of LCarnitine prescription for the treatment for Non- Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Abstract
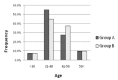
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) consists of a range of complication. The disease describes clinical , para clinical and pathological conditions from simple steatosis in non-alcoholic steato hepatitis (NASH) to fibrosis, cirrhosis and hepato cellular carcinoma. Therefore, it is of interest to evaluate the grade of fatty liver and Liver Function Test in NAFLD patients. We collected samples and data from 80 patients referred to gastrointestinal clinic of Emam Reza hospital with sonography diagnosed NAFLD and were evaluated in two groups in a randomized clinical trial. The effects of L-Carnitine (500 mg) prescription twice a day on liver enzymes and echogenicity changes in case group was documented and compared with the control group. The mean age of the patients was 40.7±8 in the age range of 25 to 62 years old with 66 (82.5%) male and 14 (17.5%) female patients. Data show that fatty liver changes were not significantly different in the two groups (P=0.23). It is observed that the ALT was the only enzyme with significant changes (P=0.01) after a 24-week interval. It is also noted that the difference in fatty liver sonographic grading was also significant in the two groups (P=0.0001). Thus, proper therapeutic protocols can be adopted beside diet and weight loss to control the disease trend in consideration to the significant changes observed both in enzymatic levels and sonographic grading between the two groups of patients with NAFLD.
Keywords: L-carnitine; Liver Function; NAFLD.
Figures
References
-
- Byrne CD, et al. Clin Sci. 2009;116:539. - PubMed
-
- Bahrololumi SS, et al. Razi Journal of Medical Sciences. 2014;20:66.
-
- Neuschwander‐Tetri BA, et al. Hepatology. 2003;37:1202. - PubMed
-
- Harrison SA, Di Bisceglic AM. Drugs. 2003;63:2379. - PubMed
-
- Day CP, James OF. Gastroenterology. 1998;114:842. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources