Physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling and simulation in pediatric drug development
- PMID: 25353188
- PMCID: PMC4260000
- DOI: 10.1038/psp.2014.45
Physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling and simulation in pediatric drug development
Abstract
Increased regulatory demands for pediatric drug development research have fostered interest in the use of modeling and simulation among industry and academia. Physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling offers a unique modality to incorporate multiple levels of information to estimate age-specific pharmacokinetics. This tutorial will serve to provide the reader with a basic understanding of the procedural steps to developing a pediatric PBPK model and facilitate a discussion of the advantages and limitations of this modeling technique.
Figures

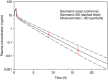
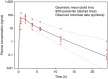
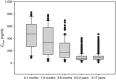
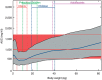
References
-
- Edginton A.N., Theil F.P., Schmitt W., Willmann S. Whole body physiologically-based pharmacokinetic models: their use in clinical drug development. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2008;4:1143–1152. - PubMed
-
- Zhao P., et al. Applications of physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling and simulation during regulatory review. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011;89:259–267. - PubMed
-
- Huang S.M., Abernethy D.R., Wang Y., Zhao P., Zineh I. The utility of modeling and simulation in drug development and regulatory review. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013;102:2912–2923. - PubMed
-
- Poulin P., et al. PHRMA CPCDC initiative on predictive models of human pharmacokinetics, part 5: prediction of plasma concentration-time profiles in human by using the physiologically-based pharmacokinetic modeling approach J. Pharm. Scie-pub ahead of print 3 May 2011. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

