Biobehavioral mechanisms of topiramate's effects on alcohol use: an investigation pairing laboratory and ecological momentary assessments
- PMID: 25353306
- PMCID: PMC4414660
- DOI: 10.1111/adb.12192
Biobehavioral mechanisms of topiramate's effects on alcohol use: an investigation pairing laboratory and ecological momentary assessments
Abstract
Topiramate reduces drinking, but little is known about the mechanisms that precipitate this effect. This double-blind randomized placebo-controlled study assessed the putative mechanisms by which topiramate reduces alcohol use among 96 adult non-treatment-seeking heavy drinkers in a laboratory-based alcohol cue reactivity assessment and in the natural environment using ecological momentary assessment methods. Topiramate reduced the quantity of alcohol heavy drinkers consumed on drinking days and reduced craving while participants were drinking but did not affect craving outside of drinking episodes in either the laboratory or in the natural environment. Topiramate did not alter the stimulant or sedative effects of alcohol ingestion during the ascending limb of the blood alcohol curve. A direct test of putative mechanisms of action using multilevel structural equation mediation models showed that topiramate reduced drinking indirectly by blunting alcohol-induced craving. These findings provide the first real-time prospective evidence that topiramate reduces drinking by reducing alcohol's priming effects on craving and highlight the importance of craving as an important treatment target of pharmacotherapy for alcoholism.
Keywords: Craving; medication action; topiramate.
© 2014 Society for the Study of Addiction.
Conflict of interest statement
RS is a consultant for D&A Pharma, CT San Remo and Transcept Pharmaceuticals. Otherwise, the authors have no conflicts to disclose.
Figures
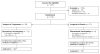
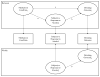

Similar articles
-
Effects of topiramate on urge to drink and the subjective effects of alcohol: a preliminary laboratory study.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2008 Mar;32(3):489-97. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2007.00592.x. Epub 2008 Jan 22. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2008. PMID: 18215213 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of topiramate on neural responses to alcohol cues in treatment-seeking individuals with alcohol use disorder: preliminary findings from a randomized, placebo-controlled trial.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2021 Jul;46(8):1414-1420. doi: 10.1038/s41386-021-00968-w. Epub 2021 Feb 8. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2021. PMID: 33558678 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Oral topiramate reduces the consequences of drinking and improves the quality of life of alcohol-dependent individuals: a randomized controlled trial.Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2004 Sep;61(9):905-12. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.61.9.905. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2004. PMID: 15351769 Clinical Trial.
-
Topiramate in the new generation of drugs: efficacy in the treatment of alcoholic patients.Curr Pharm Des. 2010;16(19):2103-12. doi: 10.2174/138161210791516404. Curr Pharm Des. 2010. PMID: 20482511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Topiramate in Alcohol Use Disorders: Review and Update.CNS Drugs. 2015 May;29(5):383-95. doi: 10.1007/s40263-015-0244-0. CNS Drugs. 2015. PMID: 25899459 Review.
Cited by
-
Rate of alcohol consumption in the daily life of adolescents and emerging adults.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019 Nov;236(11):3111-3124. doi: 10.1007/s00213-019-05262-8. Epub 2019 May 19. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019. PMID: 31104151 Free PMC article.
-
Active Ingredients of Treatment and Client Mechanisms of Change in Behavioral Treatments for Alcohol Use Disorders: Progress 10 Years Later.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2015 Oct;39(10):1852-62. doi: 10.1111/acer.12848. Epub 2015 Sep 7. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2015. PMID: 26344200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mobile alcohol biosensors and pharmacotherapy development research.Alcohol. 2019 Dec;81:149-160. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2018.07.012. Epub 2018 Aug 3. Alcohol. 2019. PMID: 31679765 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Topiramate decreases the salience of motivationally relevant visual cues among smokers with alcohol use disorder.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2022 Mar;46(3):384-395. doi: 10.1111/acer.14771. Epub 2022 Jan 31. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2022. PMID: 35037278 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Real-time assessment of alcohol craving and naltrexone treatment responsiveness in a randomized clinical trial.Addict Behav. 2018 Aug;83:72-78. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2018.01.009. Epub 2018 Jan 10. Addict Behav. 2018. PMID: 29395188 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Baltieri DA, Daró FR, Ribeiro PL, de Andrade AG. Comparing topiramate with naltrexone in the treatment of alcohol dependence. Addiction. 2008;103:2035–2044. - PubMed
-
- Carney MA, Tennen H, Affleck G, Del Boca FK, Kranzler HR. Levels and patterns of alcohol consumption using timeline follow-back, daily diaries and real-time “electronic interviews”. J Stud Alcohol. 1998;59:447–454. - PubMed
-
- Corrao G, Bagnardi V, Zambon A, La Vecchia C. A meta-analysis of alcohol consumption and the risk of 15 diseases. Prev Med. 2004;38:613–619. - PubMed
-
- Davidson D, Camara P, Swift R. Behavioral effects and pharmacokinetics of low dose intravenous alcohol in humans. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1997;21:1294–1299. - PubMed
-
- Del Boca FK, Kranzler HR, Brown J, Korner PF. Assessment of medication compliance in alcoholics through UV light detection of a riboflavin tracer. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1996;20:1412–1417. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

