Treatment for epilepsy in pregnancy: neurodevelopmental outcomes in the child
- PMID: 25354543
- PMCID: PMC7390020
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD010236.pub2
Treatment for epilepsy in pregnancy: neurodevelopmental outcomes in the child
Abstract
Background: Accumulating evidence suggests an association between prenatal exposure to antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) and increased risk of both physical anomalies and neurodevelopmental impairment. Neurodevelopmental impairment is characterised by either a specific deficit or a constellation of deficits across cognitive, motor and social skills and can be transient or continuous into adulthood. It is of paramount importance that these potential risks are identified, minimised and communicated clearly to women with epilepsy.
Objectives: To assess the effects of prenatal exposure to commonly prescribed AEDs on neurodevelopmental outcomes in the child and to assess the methodological quality of the evidence.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Epilepsy Group Specialized Register (May 2014), Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) in The Cochrane Library (2014, Issue 4), MEDLINE (via Ovid) (1946 to May 2014), EMBASE (May 2014), Pharmline (May 2014) and Reprotox (May 2014). No language restrictions were imposed. Conference abstracts from the last five years were reviewed along with reference lists from the included studies.
Selection criteria: Prospective cohort controlled studies, cohort studies set within pregnancy registers and randomised controlled trials were selected for inclusion. Participants were women with epilepsy taking AED treatment; the two control groups were women without epilepsy and women with epilepsy who were not taking AEDs during pregnancy.
Data collection and analysis: Three authors (RB, JW and JG) independently selected studies for inclusion. Data extraction and risk of bias assessments were completed by five authors (RB, JW, AS, NA, AJM). The primary outcome was global cognitive functioning. Secondary outcomes included deficits in specific cognitive domains or prevalence of neurodevelopmental disorders. Due to substantial variation in study design and outcome reporting only limited data synthesis was possible.
Main results: Twenty-two prospective cohort studies were included and six registry based studies. Study quality varied. More recent studies tended to be larger and to report individual AED outcomes from blinded assessments, which indicate improved methodological quality.The developmental quotient (DQ) was lower in children exposed to carbamazepine (CBZ) (n = 50) than in children born to women without epilepsy (n = 79); mean difference (MD) of -5.58 (95% confidence interval (CI) -10.83 to -0.34, P = 0.04). The DQ of children exposed to CBZ (n = 163) was also lower compared to children of women with untreated epilepsy (n = 58) (MD -7.22, 95% CI -12.76 to - 1.67, P = 0.01). Further analysis using a random-effects model indicated that these results were due to variability within the studies and that there was no significant association with CBZ. The intelligence quotient (IQ) of older children exposed to CBZ (n = 150) was not lower than that of children born to women without epilepsy (n = 552) (MD -0.03, 95% CI -3.08 to 3.01, P = 0.98). Similarly, children exposed to CBZ (n = 163) were not poorer in terms of IQ in comparison to the children of women with untreated epilepsy (n = 87) (MD 1.84, 95% CI -2.13 to 5.80, P = 0.36). The DQ in children exposed to sodium valproate (VPA) (n = 123) was lower than the DQ in children of women with untreated epilepsy (n = 58) (MD -8.72, 95% -14.31 to -3.14, P = 0.002). The IQ of children exposed to VPA (n = 76) was lower than for children born to women without epilepsy (n = 552) (MD -8.94, 95% CI -11.96 to -5.92, P < 0.00001). Children exposed to VPA (n = 89) also had lower IQ than children born to women with untreated epilepsy (n = 87) (MD -8.17, 95% CI -12.80 to -3.55, P = 0.0005).In terms of drug comparisons, in younger children there was no significant difference in the DQ of children exposed to CBZ (n = 210) versus VPA (n=160) (MD 4.16, 95% CI -0.21 to 8.54, P = 0.06). However, the IQ of children exposed to VPA (n = 112) was significantly lower than for those exposed to CBZ (n = 191) (MD 8.69, 95% CI 5.51 to 11.87, P < 0.00001). The IQ of children exposed to CBZ (n = 78) versus lamotrigine (LTG) (n = 84) was not significantly different (MD -1.62, 95% CI -5.44 to 2.21, P = 0.41). There was no significant difference in the DQ of children exposed to CBZ (n = 172) versus phenytoin (PHT) (n = 87) (MD 3.02, 95% CI -2.41 to 8.46, P = 0.28). The IQ abilities of children exposed to CBZ (n = 75) were not different from the abilities of children exposed to PHT (n = 45) (MD -3.30, 95% CI -7.91 to 1.30, P = 0.16). IQ was significantly lower for children exposed to VPA (n = 74) versus LTG (n = 84) (MD -10.80, 95% CI -14.42 to -7.17, P < 0.00001). DQ was higher in children exposed to PHT (n = 80) versus VPA (n = 108) (MD 7.04, 95% CI 0.44 to 13.65, P = 0.04). Similarly IQ was higher in children exposed to PHT (n = 45) versus VPA (n = 61) (MD 9.25, 95% CI 4.78 to 13.72, P < 0.0001). A dose effect for VPA was reported in six studies, with higher doses (800 to 1000 mg daily or above) associated with a poorer cognitive outcome in the child. We identified no convincing evidence of a dose effect for CBZ, PHT or LTG. Studies not included in the meta-analysis were reported narratively, the majority of which supported the findings of the meta-analyses.
Authors' conclusions: The most important finding is the reduction in IQ in the VPA exposed group, which are sufficient to affect education and occupational outcomes in later life. However, for some women VPA is the most effective drug at controlling seizures. Informed treatment decisions require detailed counselling about these risks at treatment initiation and at pre-conceptual counselling. We have insufficient data about newer AEDs, some of which are commonly prescribed, and further research is required. Most women with epilepsy should continue their medication during pregnancy as uncontrolled seizures also carries a maternal risk.
Conflict of interest statement
RB has provided expert opinion regarding child outcomes following prenatal exposure to AEDs and has contributed to studies funded by Sanofi Aventis and UCB Pharma. NA has been sponsored to attend educational meetings and conferences in epilepsy over the last five years by UCB Pharma, GSK and Boehringer Ingelheim, and has participated in regional advisory Board meetings for Eisai on their products eslicarbazepine and zonisamide. AM has been sponsored to attend a conference and has had research funding from Pfizer Ltd. Also a consortium of pharmaceutical companies (GSK, EISAI, UCB Pharma) funded the National Audit of Seizure Management in Hospitals (NASH) through grants paid to University of Liverpool. No further conflicts of interests declared.
Clarification statement added from the Co‐ordinating Editor on 8 June 2020: This review was found by the Cochrane Funding Arbiters, post‐publication, to be noncompliant with the
Figures
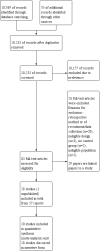
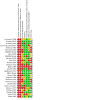


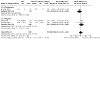





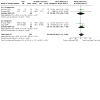



































































Comment in
-
Antiepileptic drug use during pregnancy: sodium valproate is associated with lower offspring IQ.Evid Based Nurs. 2015 Oct;18(4):109. doi: 10.1136/eb-2014-102045. Epub 2015 Mar 3. Evid Based Nurs. 2015. PMID: 25736074 No abstract available.
References
References to studies included in this review
Arulmozhi 2006 {published data only}
-
- Arulmozhi T, Dhanaraj M, Rangaraj R, Vengatesan A. Physical growth and psychomotor development of infants exposed to antiepileptic drugs in utero. Neurology India 2006;54(1):42-6. - PubMed
Bromley 2010 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Bromley R, Mawer G, Love J, Kelly J, Purdy L, McEwan L et al. Early cognitive development in children born to women with epilepsy: a prospective report. Epilepsia 2010;51(10):2058-65. - PubMed
-
- Bromley R. Personal communication with R. Bromley. 2013.
Bromley 2013 {published data only}
-
- Bromley R. Autism spectrum disorders following in utero exposure to antiepileptic drugs. Neurology 2008;71:1923-5. - PubMed
Cummings 2011/2013 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Cummings C, Stewart M, Stevenson M, Morrow M, Nelson J. Neurodevelopment of children exposed in utero to lamotrigine, sodium valproate and carbamazepine. Archives of Disease in Childhood 2011;96:643-7. - PubMed
-
- Cummings C. Personal communication with C Cummings. 2013.
D'Souza 1991 {published data only}
Eriksson 2005 {published data only}
-
- Eriksson K, Viinikainen K, Monkkonen A, Aikia M, Nieminen P, Heinonen et al. Children exposed to valproate in utero-population based evaluation of risks and confounding factors for long-term neurocognitive development. Epilepsy Research 2005;65:189-200. - PubMed
-
- Viinikainen K. The effects of valproate exposure in utero on behavior and the need for educational support in school-aged children. Epilepsy and Behavior 2006;9:636-40. - PubMed
FINNISH Study {published data only}
-
- Gaily E, Kantola-Sorsa E, Granstrom M. Intelligence of children of epileptic mothers. The Journal of Pediatrics 1988;113(4):677-84. - PubMed
-
- Gaily E, Kantola-Sorsa E, Granstrom M. Specific cognitive dysfunction in children with epileptic mothers. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology 1990;32:403-14. - PubMed
-
- Granstrom M. In: Development of the children of epileptic mothers: Preliminary results from the prospective Helskiinki Study. Epilepsy, Pregnancy, and the Child. 1982 edition. New York: Raven Press.
Gaily 2004 {published data only}
-
- Gaily E, Kantola-Sorsa E, Hiilesmaa V et al. Normal intelligence in children with prenatal exposure to carbamazepine. Neurology 2004;62:28-32. - PubMed
-
- Kantola-Sorsa E, Gaily E, Isoaho M, Korkman M. Neuropsychological outcomes in children of mothers with epilepsy. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society 2007;13:642-52. - PubMed
GERMAN Study {published data only}
-
- Hattig H, Helge H, Steinhausen HC. Infants of epileptic mothers: Developmental scores at 18 months. Advances in Epileptology. Vol. 16. New York: Raven Press, 1987.
-
- Hattig H, Steinhausen HC. Psychobiology and Early Development. North Holland: Elsevier Science Publishers, 1987.
-
- Jager Roman S, Fating D, Koch et al. Somatic parameters, diseases and psychomotor development in the offspring of epileptic parents. In: Pregnancy, Epilepsy, and the Child. New York: Raven Press, 1982:425-32.
-
- Koch S, Jager-Roman E, Losche G, Nau H, Rating D, Helge H. Antiepileptic drug treatment in pregnancy: drug side effects in the neonate and neurological outcome. Acta Paediatrica 1996;84:739-46. - PubMed
-
- Koch S, Titze K, Zimmerman R, Schroder M, Lehmkuhl U, Rauh H. Long-term neuropsychological consequences of maternal epilepsy and anticonvulsant treatment during pregnancy for school-age children and adolescents. Epilepsia 1999;40(9):1237-43. - PubMed
Hanson 1976 {published data only}
-
- Hanson J, Myrianthopoulos N, Harvey M, Smith D. Risks to offspring of women treated with hydantoin anticonvulsants, with emphasis on the fetal hydantoin syndrome. Journal of Pediatrics 1976;89(4):662-8. - PubMed
Hill 1974 {published data only}
-
- Hill R, Verniaud W, Horning M, McCulley L, Morgan N. Infants exposed in utero to antiepileptic drugs: A prospective study. American Journal of Diseases in Childhood 1974;127:645-53. - PubMed
-
- Hill R, Verniaud W, Rettig G, Tennyson L, Craig J. Relationship between antiepileptic drug exposure of the infant and developmental potential. In: Janz et al, editors(s). Epilepsy, Pregnancy, and the Child. New York: Raven Press, 1982:409-17.
Hirano 2004 {published data only}
-
- Fujioka K, Kaneko S, Hirano T et al. A study of the psychomotor development of the offspring of epileptic mothers. 1984.
-
- Hirano T, Fujioka K, Okada M, Iwasa H, Kaneko S. Physical and psychomotor development in the offspring born to mothers with epilepsy. Epilepsia 2004;45 Suppl 8:53-7. - PubMed
-
- Nomura Y, Takebe Y, Nomura Y, Shinagawa S, Kaneko S, Sato T. The physical and mental development of infants born to mothers treated with antiepileptic drugs. 1984.
Jackson 2013 {unpublished data only}
-
- James F, Walshaw D, Kelly T, Lynch S, Jackson M. Neurodevelopmental outcome of infants born to mothers taking antiepileptic drugs in pregnancy: Results of a prospective population based study in the North of England.
Jones 1989 {published data only}
-
- Jones K, Lacro R, Johnson K, Adams J. Patern of malformations in the children of women treated with carbamazepine during pregnancy. The New England Journal of Medicine 1989;320(25):1661-6. - PubMed
Leavitt 1992 {published data only}
-
- Leavitt A, Yerby M, Robinson N, Sells C, Erickson D. Epilepsy in pregnancy: developmental outcome of offspring at 12 months. Neurology 1992;42(5):141-3. - PubMed
Nadebaum 2011 {published data only}
-
- Nadebaum C, Anderson V, Vajda F, Reutens D, Barton S, Wood A. Language skills of school-aged children prenatally exposed to antiepileptic drugs. Neurology 2011;76:719-26. - PubMed
-
- Nadebaum C, Anderson V, Vajda F, Reutens D, Barton S, Wood A. The Australian brain and cognition and antiepileptic drugs study: IQ in school-aged children exposed to sodium valproate and polytherapy. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society 2011;17:133-42. - PubMed
NEAD Study {published and unpublished data}
Ornoy 1996 {published data only}
Regesta 1996 {published data only}
-
- Regesta T. The risk of malformations and developmental disturbances in children exposed to antiepileptic drugs: a prospective controlled study. Bollettino Lega Italiana Epilessia 1996;95(96):351-4.
-
- Tanganelli P, Regesta G. Epilepsy, pregnancy, and major birth anomalies: An Itialian prospective controlled study. Neurology 1992;42 Suppl 5:89-93. - PubMed
Rihtman 2012 {published data only}
-
- Rihtman T, Parush S, Ornoy A. Preliminary findings of the developmental effects of in utero exposure to topiramate. Reproductive Toxicology 2012;34(3):308-11. - PubMed
Rihtman 2013 {published data only}
-
- Rihtman T, Parush S, Ornoy A. Developmental outcomes at preschool age after fetal exposure to valproic acid and lamotrigine: Cognitive, motor, sensory and behavioral function. Reproductive Toxicology 2013;41:115-25. - PubMed
Rovet 1995 {published data only}
-
- Gladstone D, Bologa M, Maguire C, Pastuszak A, Koren G. Course of pregnancy and fetal outcome following maternal exposure to carbamazepine and phenytoin; a prospective study. Reproductive Toxicology 1992;6:257-61. - PubMed
-
- Rovet J, Cole S, Nulman I, Scolnik D, Altmann D, Koren G. Effects of maternal epilepsy on children's neurodevelopment. Child Neuropsychology 1995;1(2):150-7.
-
- Scolnik D, Nulman I, Rovet J, Gladstone D, Czuchta D et al. Neurodevelopment of children exposed in utero to phenytoin and carbamazepine monotherapy. JAMA 1994;271(10):767-70. - PubMed
Shallcross 2011 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Shallcross R, Bromley RL, Cheyne CP et al. In utero exposure to levetiracetam vs valproate: Development and language at 3 years of age. Neurology 2014;82:213-21. - PubMed
-
- Shallcross R. Child development following In utero exposure: A comparison of novel and established antiepileptic drug treatment. Thesis: University of Liverpool 2011.
Sobczyz 1977 {published data only}
-
- Sobczyk W, Dowzenko A, Krasicka J. Investigation of children of mothers treated in pregnancy with anticonvulsants. Neurologia i Neurochirurgia Polska 1977;11(1):59-63. - PubMed
Thomas 2007 {published data only}
-
- Thomas S, Sukumaran S, Lukose N, George A, Sarma P. Intellectual and language functions in children of mothers with epilepsy. Epilepsia 2007;48(12):2234-40. - PubMed
Thomas 2008 {published data only}
-
- Thomas S, Ajaykumar B, Singhu K, Nair M, George B, Sarma P. Motor and mental development of infants exposed to antiepileptic drugs in utero. Epilepsy and Behavior 2008;13:229-36. - PubMed
Veiby 2013 {published data only}
Wide 2002 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Wide K, Henning E, Eomson T, Winbladh B. Psychomotor development in preschool children exposed to antiepileptic drugs in utero. Acta Paediatrica 2002;91:409-14. - PubMed
-
- Wide K, Winbladh B, Tomson T, Sars-Zimmer K, Berggren E. Psychomotor development and minor anomalies in children exposed to antiepileptic drugs in utero: a prospective population-based study. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology 2000;42:87-92. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Annegers 1974 {published data only}
-
- Annegers J, Elveback L, Hauser A, Kurland L. Do anticonvulsants have a teratogenic effect? Archives of Neurology 1974;31:364-73. - PubMed
Antiga 2010 {published data only}
-
- Antiga E, Monetti V, Fallica E et al. Cognitive development in children born to mothers with epilepsy [Epilessia e gravidanza: valutazione dello sviluppo cognitivo nei bambini nati da donne con epilessia]. Bollettino Lega Italiana Epilessia 2010;140:154-5.
Dean 2002 {published data only}
Dessens 2000 {published data only}
-
- Dessens A, Cohen-Kettenis P, Mellenbergh G, Koppe J, de Poll N, Boer K. Association of prenatal phenobarbital and phenytoin exposure with small head size at birth with learning problems. Acta Paediatrica 2000;89:533-41. - PubMed
Forsberg 2011 {published data only}
-
- Forsberg L, Wide K, Kallen B. School performance at age 16 in children exposed to antiepileptic drugs in utero - A population-based study. Epilepsia 2011;52(2):364-9. - PubMed
Holmes 2000 {published data only}
-
- Holmes L, Rosenberger P, Harvey E, Khoshbin S, Ryan L. Intelligence and physical features of children of women with epilepsy. Teratology 2000;61:196-202. - PubMed
Holmes 2005 {published data only}
-
- Holmes L, Coull B, Dorfman J, Rosenberger P. The correlation of deficits in IQ with midface and digit hypoplasia in children exposed in utero to anticonvulsant drugs. Journal of Pediatrics 2005;146:118-22. - PubMed
Jakubowska 1981 {published data only}
-
- Jakubowska T, Koziak M, Lipczynska-Lojkowska W, Niedzielska K, Witkowska-Olearska K, Zielinski J. Health status of children born to mothers with epilepsy [Ocena stanu zdrowia dzieci matek chorych na padaczke]. Neurologia i Neurochirurgia Polska 1981;15(3):303-8. - PubMed
Kelly 1984 {published data only}
-
- Kelly T, Edwards P, Rein M, Miller J, Dreifuss F. Teratogenicity of anticonvulsant drugs 2: a prospective study. American Journal of Medical Genetics 1984;19:435-43. - PubMed
Kozhokaru 2010 {published data only}
-
- Kozhokaru A, Karlov V, Zhydkova I, Serkina A. Intellectual, psychomotor and speech development of children born to mothers with epilepsy. Zhurnal Nevropatologii i Psikhiatrii Imeni 2010;110(2):25-30. - PubMed
Latis 1982 {published data only}
-
- Latis G, Battino D, Boldi B et al. Preliminary data of a neuropediatric follow-up of infants born to epileptic mothers. In: Janz et al, editors(s). Epilepsy, Pregnancy and the Child. New York: Raven Press, 1982:419-23.
Lekwuwa 1995 {published data only}
-
- Lekwuwa G, Adewole I, Thompson M. Antiepileptic drugs and teratogenicity in Nigerians. Transanction of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1995;89:227. - PubMed
Majewski 1981 {published data only}
-
- Majewski F, Steger M, Richter B, Gill J, Rabe F. The teratogenicity of hydantoins and barbiturates in humans, with considerations on the etiology of malformations and cerebral disturbances in the children of epileptic parents. Biological Research in Pregnancy 1981;2(1):94-102. - PubMed
Meador 2010 {published data only}
Moore 2000 {published data only}
Mortensen 1996 {published data only}
-
- Mortensen E, Reinisch J, Sanders S, Rubin D. Intelligensdefekter som senfølge af praenatal eksposition for phenobarbital fenemal. [Delayed effects of prenatal exposure to phenobarbital on intelligence Phenemal]. Ugeskrift for Laeger 1996;158(46):6589-94. - PubMed
-
- Reinisch J, Sanders S, Mortensen E, Rubin D. In utero exposure to phenobarbital and intelligence deficits in adult men. JAMA 1995;274(19):1518-25. - PubMed
Mortensen 2003 {published data only}
-
- Mortensen J, Olsen J, Larsen H, Bendsen, Obel C, Sorensen H. Psychomotor development in children exposed in utero to benzodiazepines, antidepressants, neuroleptics, and anti-epileptics. European Journal of Epidemiology 2003;18:769-71. - PubMed
Oyen 2007 {published data only}
-
- Oyen N, Vollset S, Eide M, Bjerkedal T, Skjaerven R. Maternal epilepsy and offsprings' adult intelligence: A population-based study from Norway. Epilepsia 2007;48(9):1731-8. - PubMed
Parisi 2003 {published data only}
-
- Parisi P, Francia A, Vanacore N, Fiore S, Gillonardo A, Manfredi M. Psychomotor development and general movements in offspring of women with epilepsy and anticonvulsant therapy. Early Human Development 2003;74:97-108. - PubMed
Perinola 1992 {published data only}
-
- Perinola T, Buttiglione M, Margari L. Antiepileptic drugs in pregnancy: late effects on the children's cognitive abilities. Acta Neurologia 1992;14(4-6):543-6. - PubMed
Rasalam 2005 {published data only}
-
- Rasalam A, Hailey H, Williams J et al. Characteristics of fetal anticonvulsant syndrome associated autistic disorder. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology 2005;47:551-5. - PubMed
Sereno‐Colo 1984 {published data only}
-
- Sereno-Colo J, Dominguez F, Gutierrez J. Tratamiento de la gestante epileptica con carbamacepina. Ginecologia y Obstetricia de Mexico 1984;52(329):231-5. - PubMed
Steinhausen 1982 {published data only}
-
- Steinhausen HC, Nestler V, Huth H. Psychopathology and mental functions in the offspring of alcoholic and epileptic mothers. Journal of the American Academy of Child Psychiatry 1982;21(3):268-73. - PubMed
Vanoverloop 1992 {published data only}
-
- Vanoverloop D, Schnell R, Harvey E, Holmes L. The effects of prenatal exposure to phenytoin and other anticonvulsants on intellectual function at 4 to 8 years of age. Neurotoxicology and Teratology 1992;14:329-35. - PubMed
Vert 1982 {published data only}
-
- Deblay M, Vert P, Andre M. Children of epileptic mothers [L'enfant de mere epileptique]. La Nouvelle Presse Mediciale 1982;11(3):173-6. - PubMed
-
- Vert P, Deblay M, Andre M. Follow-up study on growth and neurologic development of children born to epileptic mothers. In: Janz et al, editors(s). Epilepsy, Pregnancy, and the Child. New York: Raven Press, 1982:433-6.
Yamatogi 1993 {published data only}
-
- Yamatogi Y, Oka E, Satoh M, Kobayashi K, Yoshinaga H, Ohtahara S. A prospective follow-up of the offspring of epileptic patients. The Japanese Journal of Psychiatry and Neurology 1993;47(2):309-11. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Adams 2000 Abstract {unpublished data only}
-
- Adams JHE, Holmes LB. Cognitive deficits following gestational monotherapy with phenobarbital and carbamazepine. Neurotoxicology and Teratology 2000;22:466.
Jovic 2011 Abstract {unpublished data only}
-
- Jovic N, Knezevic-Pogancev M, Ignjatovic MP. Cognitive functions at 6 years of age after fetal exposure to antiepileptic drugs used in mothers with juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. European Neuropsychopharmacology 2011;21(2):169.
Nadebaum 2011 Abstract {unpublished data only}
-
- Nadebaum C, Anderson V, Vajda F, Wood A. Academic achievement of Australian children prenatally exposed to antiepileptic drugs. International Epilepsy Congress. 2011. - PubMed
Wood 2011 Abstract {unpublished data only}
-
- Wood AG, Nadebaum C, Anderson VA, Reutens D, Barton S, O'Brien T, Vajda FV. Valproate dose is an independent risk factor for autism spectrum disorder: Evidence from prospective assessments in the Australian brain, cognition and antiepileptic drugs study. 29th International Epilepsy Congress .
Additional references
Ackers 2009
-
- Ackers R, Besag FM, Wade A, Murray ML, Wong IC. Changing trends in antiepileptic drug prescribing in girls of child-bearing potential. Archive of Disease in Childhood 2009;94(6):443-7. - PubMed
Adab 2001
Adab 2004
Adab 2004b
Ardinger 1988
-
- Ardinger H, Atkin J, Blackston R, Elsas L, Clarren S, Livingstone S et al. Verification of the fetal valproate syndrome phenotype. American Journal of Medical Genetics 1988;29(1):171-85. - PubMed
Ardnt 2005
-
- Arndt TL, Stodgell CJ, Rodier PM. The teratology of autism. International Journal of Developmental Neuroscience 2005;23(2-3):189-99. - PubMed
Banach 2010
-
- Banach R, Boskovic R, Einarson T, Koren G. Long-term developmental outcome of children of women with epilepsy, unexposed or exposed prenatally to antiepileptic drugs. A meta-analysis of cohort studies. Drug Safety 2010;33(1):73-9. - PubMed
Baron 2004
-
- Baron I. Neuropsychological Evaluation of the Child. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2004.
Bittigau 2003
-
- Bittigau P, Sifringer M, Ikonomidou C. Antiepileptic drugs and apoptosis in the developing brain. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 2003;993:103-14. - PubMed
Bossi 1982
-
- Bossi L. Neonatal period including drug disposition in new borns: Review of the literature. In: Janz D, Dam M, Richens A, Bossi L, Helge H, Schmidt D, editors(s). Epilepsy, Pregnancy and the Child. New York: Ravens press, 1982:327-42.
Brent 2004
-
- Brent R. Environmental causes of human congenital malformations: the pediatrician's role in dealing with these complex clinical problems caused by a multiplicity of environmental and genetic factors. Pediatrics 2004;13(4):957-68. - PubMed
Bromley 2009
Bromley 2010
-
- Bromley RL, Mawer G, Love J, Kelly J, Purdy L, McEwan L et al. Early cognitive development in children born to women with epilepsy: A prospective report. Epilepsia 2010;51(10):2058-65. - PubMed
Charlton 2011
-
- Charlton RA, Weil JG, Cunnington MC, Ray S, Vries CS. Comparing the General Practice Research Database and the UK Epilepsy and Pregnancy Register as tools for postmarketing teratogen surveillance: anticonvulsants and the risk of major congenital malformations. Drug Safety 34;2:157-71. - PubMed
Chevallier 1989
-
- Chevallier B, Negre V, Bidat E, Lagardere B. Fetal valproate syndrome and somatic and psychomotor development. Archives Francaises Pediatrie 1989;46:627-30. - PubMed
Christensen 2013
Christianson 1994
-
- Christianson A, Chesler N, Kromberg J. Fetal valproate syndrome: Clinical and neurodevelopmental features in two sibling pairs. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology 1994;36:357-69. - PubMed
Clayton‐Smith 1995
Cummings 2011
-
- Cummings C, Stewart M, Stevenson M, Morrow J, Nelson J. Neurodevelopment of children exposed in utero to lamotrigine, sodium valproate and carbamazepine. Archives of Disease in Childhood 2011;96:943-7. - PubMed
Dean 2002
Deary 2007
-
- Deary IJ, Stran S, Smith P, Fernandes C. Intelligence and educational achievement. Intelligence 2007;35:13-21.
Friedman 2012
-
- Friedman JM. ABCDXXX: The obscenity of postmarketing surveillance for teratogenic effects. Birth Defects Research A. Clinical and Molecular Teratology 2012;94(8):670-6. - PubMed
Gaily 2004
-
- Gaily E, Kantola-Sorsa E, Hiilesmaa V, Isoaho M, Matila R, Kotila M. Normal intelligence in children with prenatal exposure to carbamazepine. Neurology 2004;62:28-32. - PubMed
Guyatt 2008
Hanson 1976
-
- Hanson JW, Myrianthopoulos NC, Sedgwick-Harvey MA, Smith DW. Risks to the offspring of women treated with hydantoin anticonvulsants, with emphasis on the fetal hydantoin syndrome. The Journal of Pediatrics 1976;89:662-8. - PubMed
Hauser 1990
-
- Hauser W, Hesdorffer D. Epilepsy: Frequency, causes and consequences. New York: Demos Publications, 1990.
Hernandez‐Diaz 2012
-
- Hernandez-Diaz S, Smith CR, Shen A, Mittendorf R, Hauser WA, Yerby M. Comparative safety of antiepileptic drugs during pregnancy. Neurology 2012;78(21):1692-9. - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane-handbook.org.
Hill 1982
-
- Hill RM, Verniaud WM, Rettig GM, Tennyson LM, Craig JP. Relationship between antiepileptic drug exposure of the infant and developmental potential. In: Janz D, Dam M, Richens A, Bossi L, Helge H, Schmidt D, editors(s). Epilepsy, Pregnancy and the Child. New York: Ravens Press, 1982:409-17.
Huth 1982
-
- Huth H, Steinhausen HC, Helge H. Mental development in children of epileptic parents. In: Janz D, Dam M, Richens A, Bossi L, Helge H, Schmidt D, editors(s). Epilepsy, Pregnancy and the Child. New York: Ravens Press, 1982:437-41.
Kantola‐Sorsa 2007
-
- Kantola-Sorsa E, Gaily E, Isoaho M, Korkman M. Neuropsychological outcomes in children of mothers with epilepsy. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society 2007;13(4):642-52. - PubMed
Kirkham 2010
-
- Kirkham J, Dwan K, Altman D et al. The impact of outcome reporting bias in randomised controlled trials on a cohort of systematic reviews. BMJ 2010;340:c365. - PubMed
Lindhout 1992
-
- Lindhout D, Meinardi H, Meijer J, Nau H. Antiepileptic drugs and teratogenesis in two consecutive cohorts: Changes in prescription policy paralleled by changes in pattern of malformations. Neurology 1992;42:94-110. - PubMed
Mawhinney 2013
-
- Mawhinney E, Craig J, Morrow J, Russell A, Smithson WH, Parsons L et al. Levetiracetam in pregnancy: results from the UK and Ireland epilepsy and pregnancy registers. Neurology 2013;80(4):400-5. - PubMed
Meador 2008
Meador 2009
Meador 2009b
Meador 2011
Metcalfe 2012
-
- Metcalfe A, Roberts JI, Abdulla F, Wiebe S, Hanson A, Federico P, Jette N. Patient knowledge about issues related to pregnancy in epilepsy: a cross-sectional study. Epilepsy and Behavior 2012;24(1):65-69. - PubMed
Miyazaki 2005
-
- Miyazaki K, Narita N, Narita M. Maternal administration of thalidomide or valproic acid causes abnormal serotonergic neurons in the offspring: Implications for pathogenesis of autism. International Journal of Developmental Neuroscience 2005;23:287-97. - PubMed
Moore 2000
Nadebaum 2011
-
- Nadebaum C, Anderson V, Vajda F, Reutens D, Barton S, Wood A. The Australian brain and cognition and antiepileptic drugs study: IQ in school-aged children exposed to sodium valproate and polytherapy. Journal of International Neuropsychological Society 2011;17:1-10. - PubMed
Nicolai 2008
-
- Nicolai J, Vles JSH, Aldenkamp AP. Neurodevelopmental delay in children exposed to antiepileptic drugs in utero: A critical review directed at structural study-bias. Journal of the Neurological Sciences 2008;271(1-2):1-14. - PubMed
Rasalam 2005
-
- Rasalam AD, Hailey H, Williams JH, Moore SJ, Turnpenny PD, Lloyd DJ et al. Charateristics of fetal anticonvulsant syndrome associated autistic disorder. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology 2005;47(8):551-5. - PubMed
Roberts 2011
-
- Roberts JI, Metcalfe A, Abdulla F, Wiebe S, Hanson A, Federico P, Jette N. Neurologists' and neurology residents' knowledge of issues related to pregnancy for women with epilepsy. Epilepsy and Behavior 2011;22(2):358-63. - PubMed
Steinhausen 1994
-
- Steinhausen HC, Losche G, Koch S, Helge H. The psychological development of children of epileptic parents. I. Study design and comparative findings. Acta Paediatrica 1994;83:955-60. - PubMed
Titze 2008
-
- Titze K, Koch S, Helge H, Lehmkuhl U, Rauh H, Steinhausen H-C. Prenatal and family risks of children born to mothers with epilepsy: effects on cognitive development. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology 2008;50(2):117-22. - PubMed
Tomson
-
- Tomson T, Battino D, Bonizzoni E, Craig J, Lindhout D, Sabers A et al. Dose-dependent risk of malformations with antiepileptic drugs: An analysis of data from the EURAP epilepsy and pregnancy registry. Lancet Neurology 2011;10(7):609-17. - PubMed
Tomson 2011
-
- Tomson T, Battino D, Bonizzoni E, Craig J, Lindhout D, Sabers A et al. Dose-dependent risk of malformation with antiepileptic drugs: An analysis of data from the EURAP epilepsy and pregnancy registry. Lancet Neurology 2011;10(7):609-17. - PubMed
Veiby 2013
-
- Veiby G, Engelsen BA, Gilhus NE. Early child development and exposure to antiepileptic drugs prenatally and through breastfeeding: a prospective cohort study on children of women with epilepsy. JAMA Neurology 2013;70(11):1367-74. - PubMed
Williams 1997
-
- Williams P, Hersh J. A male with fetal valproate syndrome and autism. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology 1997;39:632-4. - PubMed
Winter 1987
Yerby 1994
-
- Yerby MS. Pregnancy, teratogenesis and epilepsy. Neurological Clinics 1994;12:749-71. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

