The clinical and biological significance of STAT1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 25355139
- PMCID: PMC4233059
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-791
The clinical and biological significance of STAT1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Loss of STAT1 (Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription-1) has been implicated in the pathobiology of a number of cancer types. Nonetheless, the biological and clinical significance of STAT1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinomas (ESCC) has not been comprehensively studied.
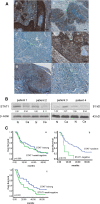
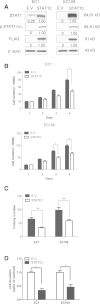
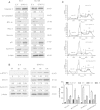
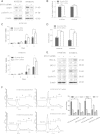
Methods: Using immunohistochemistry, we detected the STAT1 expression in a cohort of ESCC patients; In-vitro experiments, we used enforced gene transfection of STAT1C into two STAT1- weak/negative ESCC cell lines and siRNA knockdown of STAT1 in two STAT1-strong ESCC cell lines to detect STAT1 function in ESCC.
Results: We found that the expression of STAT1 was heterogeneous in ESCC, with 64 (49.0%) strongly positive cases, 59 (45.0%) weakly positive cases and 8 (6.1%) negative cases. STAT1 expression inversely correlated with the depth of tumor invasion and tumor size (p=0.047 and p=0.029, respectively, Chi square). Furthermore, patients with STAT1-strong/weak tumors had a significantly longer survival compared to those with STAT1-negative tumors (33.6 months versus 13.1 months, p=0.019). In patients carrying tumors of aggressive cytology (n=50), those with STAT1-strong tumors survived significantly longer than those with STAT1-weak/negative tumors (34.6 months versus 20.5 months, p=0.011). Our in-vitro experiments revealed that STAT1 is proapoptotic and inhibitory to cell-cycle progression and colony formation. Lastly, we found evidence that STAT1 signaling in ESCC cells down-regulated the expression and/or activity of NF-κB and STAT3, both of which are known to have oncogenic potential.
Conclusion: To conclude, our findings suggest that STAT1 is a tumor suppressor in ESCC. Loss of STAT1, which is frequent in ESCC, contributes to the pathogenesis of these tumors.
Figures



Similar articles
-
ERK expression and its correlation with STAT1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Oncotarget. 2017 Jul 11;8(28):45249-45258. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16902. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28431406 Free PMC article.
-
STAT3 expression, activity and functional consequences of STAT3 inhibition in esophageal squamous cell carcinomas and Barrett's adenocarcinomas.Oncogene. 2014 Jun 19;33(25):3256-66. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.298. Epub 2013 Aug 5. Oncogene. 2014. PMID: 23912451
-
Correlation of STAT1 with apoptosis and cell-cycle markers in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 1;9(12):e113928. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113928. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25438156 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular interplay of pro-inflammatory transcription factors and non-coding RNAs in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Tumour Biol. 2017 Jun;39(6):1010428317705760. doi: 10.1177/1010428317705760. Tumour Biol. 2017. PMID: 28618941 Review.
-
Steering of carcinoma progression by the YIN/YANG interaction of STAT1/STAT3.Biosci Trends. 2017 Mar 22;11(1):1-8. doi: 10.5582/bst.2016.01250. Epub 2017 Feb 2. Biosci Trends. 2017. PMID: 28154246 Review.
Cited by
-
STAT1 inhibits T-cell exhaustion and myeloid derived suppressor cell accumulation to promote antitumor immune responses in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Int J Cancer. 2020 Mar 15;146(6):1717-1729. doi: 10.1002/ijc.32781. Epub 2019 Nov 29. Int J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 31709529 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of LRP/LR with siRNA inhibits several cancer hallmarks in lung cancer cells.FEBS Open Bio. 2023 Feb;13(2):323-340. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.13544. Epub 2023 Jan 13. FEBS Open Bio. 2023. PMID: 36579897 Free PMC article.
-
SP140 inhibits STAT1 signaling, induces IFN-γ in tumor-associated macrophages, and is a predictive biomarker of immunotherapy response.J Immunother Cancer. 2022 Dec;10(12):e005088. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2022-005088. J Immunother Cancer. 2022. PMID: 36600652 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Potential Biomarkers Using Integrative Approach: A Case Study of ESCC.SN Comput Sci. 2023;4(2):114. doi: 10.1007/s42979-022-01492-4. Epub 2022 Dec 21. SN Comput Sci. 2023. PMID: 36573207 Free PMC article.
-
Dichotomal functions of phosphorylated and unphosphorylated STAT1 in hepatocellular carcinoma.J Mol Med (Berl). 2019 Jan;97(1):77-88. doi: 10.1007/s00109-018-1717-7. Epub 2018 Nov 19. J Mol Med (Berl). 2019. PMID: 30456450 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adámková L, Soucková K, Kovarík J. Transcription protein STAT1: biology and relation to cancer. Folia Biol (Praha) 2007;53(1):1–6. - PubMed
-
- Max Parkin D, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002 CA cancer. J Clin. 2002;2005(55):74–108. - PubMed
Pre-publication history
-
- The pre-publication history for this paper can be accessed here:http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2407/14/791/prepub
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

