Depletion of the central metabolite NAD leads to oncosis-mediated cell death
- PMID: 25355314
- PMCID: PMC4271207
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.580159
Depletion of the central metabolite NAD leads to oncosis-mediated cell death
Abstract
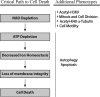
Depletion of the central metabolite NAD in cells results in broad metabolic defects leading to cell death and is a proposed novel therapeutic strategy in oncology. There is, however, a limited understanding of the underlying mechanisms that connect disruption of this central metabolite with cell death. Here we utilize GNE-617, a small molecule inhibitor of NAMPT, a rate-limiting enzyme required for NAD generation, to probe the pathways leading to cell death following NAD depletion. In all cell lines examined, NAD was rapidly depleted (average t½ of 8.1 h) following NAMPT inhibition. Concurrent with NAD depletion, there was a decrease in both cell proliferation and motility, which we attribute to reduced activity of NAD-dependent deacetylases because cells fail to deacetylate α-tubulin-K40 and histone H3-K9. Following depletion of NAD by >95%, cells lose the ability to regenerate ATP. Cell lines with a slower rate of ATP depletion (average t½ of 45 h) activate caspase-3 and show evidence of apoptosis and autophagy, whereas cell lines with rapid depletion ATP (average t½ of 32 h) do not activate caspase-3 or show signs of apoptosis or autophagy. However, the predominant form of cell death in all lines is oncosis, which is driven by the loss of plasma membrane homeostasis once ATP levels are depleted by >20-fold. Thus, our work illustrates the sequence of events that occurs in cells following depletion of a key metabolite and reveals that cell death caused by a loss of NAD is primarily driven by the inability of cells to regenerate ATP.
Keywords: ATP; Apoptosis; Cell Death; Cell Metabolism; GNE-617; NAMPT; Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD); Oncosis.
© 2014 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures






References
-
- Bogan K. L., Brenner C. (2008) Nicotinic acid nicotinamide and nicotinamide riboside: a molecular evaluation of NAD+ precursor vitamins in human nutrition. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 28, 115–130 - PubMed
-
- Hasmann M., Schemainda I. (2003) FK866, a highly specific noncompetitive inhibitor of nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase, represents a novel mechanism for induction of tumor cell apoptosis. Cancer Res. 63, 7436–7442 - PubMed
-
- Olesen U. H., Christensen M. K., Björkling F., Jäättelä M., Jensen P. B., Sehested M., Nielsen S. J. (2008) Anticancer agent CHS-828 inhibits cellular synthesis of NAD. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 367, 799–804 - PubMed
-
- Watson M., Roulston A., Bélec L., Billot X., Marcellus R., Bédard D., Bernier C., Branchaud S., Chan H., Dairi K., Gilbert K., Goulet D., Gratton M. O., Isakau H., Jang A., Khadir A., Koch E., Lavoie M., Lawless M., Nguyen M., Paquette D., Turcotte E., Berger A., Mitchell M., Shore G. C., Beauparlant P. (2009) The small molecule GMX1778 is a potent inhibitor of NAD+ biosynthesis: strategy for enhanced therapy in nicotinic acid phosphoribosyltransferase 1-deficient tumors. Mol. Cell. Biol. 29, 5872–5888 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Xiao Y., Elkins K., Durieux J. K., Lee L., Oeh J., Yang L. X., Liang X., DelNagro C., Tremayne J., Kwong M., Liederer B. M., Jackson P. K., Belmont L. D., Sampath D., O'Brien T. (2013) Dependence of tumor cell lines and patient derived tumors on the NAD salvage pathway renders them sensitive to NAMPT inhibition with GNE-618. Neoplasia 15, 1151–1160 - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

