Programmed death ligand 1 expression and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in glioblastoma
- PMID: 25355681
- PMCID: PMC4490866
- DOI: 10.1093/neuonc/nou307
Programmed death ligand 1 expression and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in glioblastoma
Abstract
Background: Immune checkpoint inhibitors targeting programmed cell death 1 (PD1) or its ligand (PD-L1) showed activity in several cancer types.
Methods: We performed immunohistochemistry for CD3, CD8, CD20, HLA-DR, phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN), PD-1, and PD-L1 and pyrosequencing for assessment of the O6-methylguanine-methyltransferase (MGMT) promoter methylation status in 135 glioblastoma specimens (117 initial resection, 18 first local recurrence). PD-L1 gene expression was analyzed in 446 cases from The Cancer Genome Atlas.
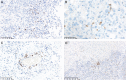
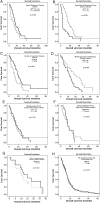
Results: Diffuse/fibrillary PD-L1 expression of variable extent, with or without interspersed epithelioid tumor cells with membranous PD-L1 expression, was observed in 103 of 117 (88.0%) newly diagnosed and 13 of 18 (72.2%) recurrent glioblastoma specimens. Sparse-to-moderate density of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) was found in 85 of 117 (72.6%) specimens (CD3+ 78/117, 66.7%; CD8+ 52/117, 44.4%; CD20+ 27/117, 23.1%; PD1+ 34/117, 29.1%). PD1+ TIL density correlated positively with CD3+ (P < .001), CD8+ (P < .001), CD20+ TIL density (P < .001), and PTEN expression (P = .035). Enrichment of specimens with low PD-L1 gene expression levels was observed in the proneural and G-CIMP glioblastoma subtypes and in specimens with high PD-L1 gene expression in the mesenchymal subtype (P = 5.966e-10). No significant differences in PD-L1 expression or TIL density between initial and recurrent glioblastoma specimens or correlation of PD-L1 expression or TIL density with patient age or outcome were evident.
Conclusion: TILs and PD-L1 expression are detectable in the majority of glioblastoma samples but are not related to outcome. Because the target is present, a clinical study with specific immune checkpoint inhibitors seems to be warranted in glioblastoma.
Keywords: glioblastoma; immune checkpoint; programmed death 1; programmed death ligand 1.
© The Author(s) 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Neuro-Oncology. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures


Comment in
-
Programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) as an immunotherapy target in patients with glioblastoma.Neuro Oncol. 2015 Aug;17(8):1043-5. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nov071. Epub 2015 May 10. Neuro Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25964311 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Preusser M, de Ribaupierre S, Wohrer A, et al. Current concepts and management of glioblastoma. Ann Neurol. 2011;70(1):9–21. - PubMed
-
- Chinot OL, Wick W, Mason W, et al. Bevacizumab plus radiotherapy-temozolomide for newly diagnosed glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(8):709–722. - PubMed
-
- Wen PY, Yung WK, Lamborn KR, et al. Phase I/II study of imatinib mesylate for recurrent malignant gliomas: North American Brain Tumor Consortium Study 99–08. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12(16):4899–4907. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

