Cationic lipid-mediated delivery of proteins enables efficient protein-based genome editing in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 25357182
- PMCID: PMC4289409
- DOI: 10.1038/nbt.3081
Cationic lipid-mediated delivery of proteins enables efficient protein-based genome editing in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
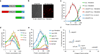
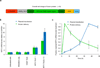
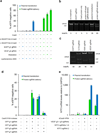
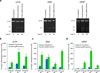
Efficient intracellular delivery of proteins is needed to fully realize the potential of protein therapeutics. Current methods of protein delivery commonly suffer from low tolerance for serum, poor endosomal escape and limited in vivo efficacy. Here we report that common cationic lipid nucleic acid transfection reagents can potently deliver proteins that are fused to negatively supercharged proteins, that contain natural anionic domains or that natively bind to anionic nucleic acids. This approach mediates the potent delivery of nM concentrations of Cre recombinase, TALE- and Cas9-based transcription activators, and Cas9:sgRNA nuclease complexes into cultured human cells in media containing 10% serum. Delivery of unmodified Cas9:sgRNA complexes resulted in up to 80% genome modification with substantially higher specificity compared to DNA transfection. This approach also mediated efficient delivery of Cre recombinase and Cas9:sgRNA complexes into the mouse inner ear in vivo, achieving 90% Cre-mediated recombination and 20% Cas9-mediated genome modification in hair cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare competing financial interests: the co-authors have filed a provisional patent application related to this work. J.K.J. and D.R.L. are consultants for Editas Medicine, a company that applies genome-editing technologies. J.K.J. is a consultant for Horizon Discovery. JKJ has financial interests in Editas Medicine and Transposagen Biopharmaceuticals. JKJ’s interests were reviewed and are managed by Massachusetts General Hospital and Partners HealthCare in accordance with their conflict of interest policies. M.L.M. is currently an employee of Editas Medicine.
Figures

References
-
- Putney SD, Burke PA. Improving protein therapeutics with sustained-release formulations. Nat. Biotechnol. 1998;16:153–157. - PubMed
-
- Mullen L, et al. Latent cytokines for targeted therapy of inflammatory disorders. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2014;11:101–110. - PubMed
-
- Song E, et al. Antibody mediated in vivo delivery of small interfering RNAs via cell-surface receptors. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005;23:709–717. - PubMed
-
- Leader B, Baca QJ, Golan DE. Protein therapeutics: a summary and pharmacological classification. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008;7:21–39. - PubMed
-
- Hartung SD, et al. Correction of Metabolic, Craniofacial, and Neurologic Abnormalities in MPS I Mice Treated at Birth with Adeno-associated Virus Vector Transducing the Human α-L-Iduronidase Gene. Mol. Ther. 2004;9:866–875. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

