Activation of lymphoma-associated MyD88 mutations via allostery-induced TIR-domain oligomerization
- PMID: 25359991
- PMCID: PMC4282153
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2014-05-573188
Activation of lymphoma-associated MyD88 mutations via allostery-induced TIR-domain oligomerization
Abstract
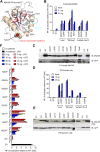
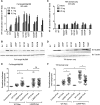
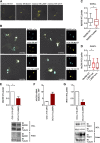
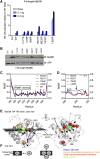
Myeloid differentiation 88 (MyD88) is the key signaling adapter of Toll-like and interleukin-1 receptors. Recurrent lymphoma-associated mutations, particularly Leu265Pro (L265P), within the MyD88 Toll/interleukin-1 receptor (TIR) domain sustain lymphoma cell survival due to constitutive nuclear factor κB signaling. We found that mutated TIR domains displayed an intrinsic propensity for augmented oligomerization and spontaneous formation of cytosolic Myddosome aggregates in lymphoma cell lines, mimicking the effect of dimerized TIR domains. Blocking of MyD88 oligomerization induced apoptosis. The L265P TIR domain can recruit the endogenous wild-type MyD88 for oligomer formation and hyperactivity. Molecular dynamics simulations and analysis of additional mutations suggest that constitutive activity is caused by allosteric oligomerization.
© 2014 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures
References
-
- Kawai T, Akira S. Toll-like receptors and their crosstalk with other innate receptors in infection and immunity. Immunity. 2011;34(5):637–650. - PubMed
-
- Yang G, Zhou Y, Liu X, et al. A mutation in MYD88 (L265P) supports the survival of lymphoplasmacytic cells by activation of Bruton tyrosine kinase in Waldenström macroglobulinemia. Blood. 2013;122(7):1222–1232. - PubMed
-
- Pettersen EF, Goddard TD, Huang CC, et al. UCSF Chimera—a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J Comput Chem. 2004;25(13):1605–1612. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

