Neurologic complications in infective endocarditis: identification, management, and impact on cardiac surgery
- PMID: 25360207
- PMCID: PMC4212418
- DOI: 10.1177/1941874414537077
Neurologic complications in infective endocarditis: identification, management, and impact on cardiac surgery
Abstract
Neurologic complications of infective endocarditis (IE) are common and frequently life threatening. Neurologic events are not always obvious. The prediction and management of neurologic complications of IE are not easily approached algorithmically, and the impact they have on timing and ability to surgically repair or replace the affected valve often requires a painstaking evaluation and joint effort across multiple medical disciplines in order to achieve the best possible outcome. Although specific recommendations are always tailored to the individual patient, there are some guiding principles that can be used to help direct the decision-making process. Herein, we review the pathophysiology, epidemiology, manifestations, and diagnosis of neurological complications of IE and further consider the impact they have on clinical decision making.
Keywords: bacterial endocarditis; brain abscess; infectious disease; intracerebral hemorrhage; meningitis; mycotic aneurysm; stroke.
Conflict of interest statement
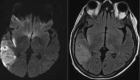
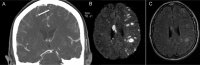
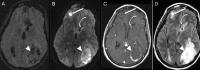
Figures
References
-
- Hoen B, Duval X. Infective endocarditis. N Engl J Med. 2013;369 (8):785. - PubMed
-
- Hoen B, Duval X. Clinical practice. Infective endocarditis. N Engl J Med. 2013;368 (15):1425–1433 - PubMed
-
- Sy RW, Kritharides L. Health care exposure and age in infective endocarditis: results of a contemporary population-based profile of 1536 patients in Australia. Eur Heart J. 2010;31 (15):1890–1897 - PubMed
-
- Keynan Y, Rubinstein E. Pathophysiology of infective endocarditis. Curr Infect Dis Rep. 2013;15 (4):342–346 - PubMed
-
- Chan KL, Dumesnil JG, Cujec B, et al. A randomized trial of aspirin on the risk of embolic events in patients with infective endocarditis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003;42 (5):775–780 - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
