Melatonin augments apoptotic adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell treatment against sepsis-induced acute lung injury
- PMID: 25360211
- PMCID: PMC4212921
Melatonin augments apoptotic adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell treatment against sepsis-induced acute lung injury
Abstract
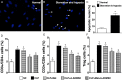
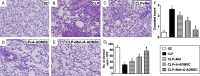
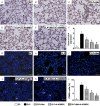
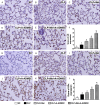
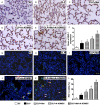
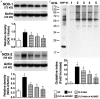
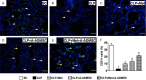
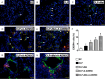
This study investigated whether combining melatonin and apoptotic adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (A-ADMSC) was superior to ADMSC alone in ameliorating sepsis-induced acute lung injury. Adult male Sprague-Dawley rats (n=50) were randomized equally into five groups: sham controls (SC), sepsis induced by cecal-ligation and puncture (CLP), CLP-melatonin, CLP-A-ADMSC, and CLP-melatonin-A-ADMSC. Circulating interleukin (IL)-6 at 6, 18, and 72 hrs, were highest in CLP and lowest in SC groups, higher in CLP-melatonin than CLP-A-ADMSC and CLP-melatonin-A-ADMSC groups, higher in CLP-A-ADMSC than CLP-melatonin-A-ADMSC groups (all p<0.001). Immune reactivity (indicated by circulating cytotoxic-, and regulatory-T cells) and WBC count at 72 h exhibited the same pattern as that of circulating IL-6 (all p<0.001). Changes in histological scoring of lung parenchyma and the number of CD68+ and CD14+ cells showed a similar pattern compared to that of IL-6 level in all groups (all p<0.001). Changes in protein expressions of inflammatory (oxidative stress, RANTES, TNF-α, NF-κB, MMP-9, MIP-1, IL-1β), apoptotic (cleaved caspase 3 and PARP, mitochondrial Bax), fibrotic (Smad3, TGF-β) markers and those of reactive-oxygen-species (NOX-1, NOX-2) displayed an identical pattern compared to that of circulating IL-6 in all groups (all p<0.001). Anti-oxidative capacities (GR+, GPx+, HO-1, NQO-1+) and angiogenesis marker (CXCR4+ cells) were lowest in SC group but highest in CLP-melatonin-A-ADMSC group, lower in CLP than CLP-melatonin and CLP-A-ADMSC groups, and lower in CLP-melatonin than CLP-A-ADMSC groups (all p<0.001). In conclusion, combined melatonin and A-ADMSC were superior to A-ADMSC alone in protecting the lung from sepsis-induced injury.
Keywords: Sepsis-induced organ injury; adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells; and melatonin; inflammation; oxidative stress; reactive oxygen species.
Figures



References
-
- Cronshaw HL, Daniels R, Bleetman A, Joynes E, Sheils M. Impact of the Surviving Sepsis Campaign on the recognition and management of severe sepsis in the emergency department: are we failing? Emerg Med J. 2011;28:670–675. - PubMed
-
- Dellinger RP, Levy MM, Carlet JM, Bion J, Parker MM, Jaeschke R, Reinhart K, Angus DC, Brun-Buisson C, Beale R, Calandra T, Dhainaut JF, Gerlach H, Harvey M, Marini JJ, Marshall J, Ranieri M, Ramsay G, Sevransky J, Thompson BT, Townsend S, Vender JS, Zimmerman JL, Vincent JL International Surviving Sepsis Campaign Guidelines Committee; American Association of Critical-Care Nurses; American College of Chest Physicians; American College of Emergency Physicians; Canadian Critical Care Society; European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases; European Society of Intensive Care Medicine; European Respiratory Society; International Sepsis Forum; Japanese Association for Acute Medicine; Japanese Society of Intensive Care Medicine; Society of Critical Care Medicine; Society of Hospital Medicine; Surgical Infection Society; World Federation of Societies of Intensive and Critical Care Medicine. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: international guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock: 2008. Crit Care Med. 2008;36:296–327. - PubMed
-
- Tipler PS, Pamplin J, Mysliwiec V, Anderson D, Mount CA. Use of a protocolized approach to the management of sepsis can improve time to first dose of antibiotics. J Crit Care. 2013;28:148–151. - PubMed
-
- Angus DC, Linde-Zwirble WT, Lidicker J, Clermont G, Carcillo J, Pinsky MR. Epidemiology of severe sepsis in the United States: analysis of incidence, outcome, and associated costs of care. Crit Care Med. 2001;29:1303–1310. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
