P2Y6 receptor potentiates pro-inflammatory responses in macrophages and exhibits differential roles in atherosclerotic lesion development
- PMID: 25360548
- PMCID: PMC4216081
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0111385
P2Y6 receptor potentiates pro-inflammatory responses in macrophages and exhibits differential roles in atherosclerotic lesion development
Abstract
Background: P2Y(6), a purinergic receptor for UDP, is enriched in atherosclerotic lesions and is implicated in pro-inflammatory responses of key vascular cell types and macrophages. Evidence for its involvement in atherogenesis, however, has been lacking. Here we use cell-based studies and three murine models of atherogenesis to evaluate the impact of P2Y(6) deficiency on atherosclerosis.
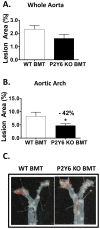
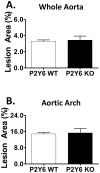
Methodology/principal findings: Cell-based studies in 1321N1 astrocytoma cells, which lack functional P2Y(6) receptors, showed that exogenous expression of P2Y(6) induces a robust, receptor- and agonist-dependent secretion of inflammatory mediators IL-8, IL-6, MCP-1 and GRO1. P2Y(6)-mediated inflammatory responses were also observed, albeit to a lesser extent, in macrophages endogenously expressing P2Y(6) and in acute peritonitis models of inflammation. To evaluate the role of P2Y(6) in atherosclerotic lesion development, we used P2Y(6)-deficient mice in three mouse models of atherosclerosis. A 43% reduction in aortic arch plaque was observed in high fat-fed LDLR knockout mice lacking P2Y(6) receptors in bone marrow-derived cells. In contrast, no effect on lesion development was observed in fat-fed whole body P2Y(6)xLDLR double knockout mice. Interestingly, in a model of enhanced vascular inflammation using angiotensin II, P2Y(6) deficiency enhanced formation of aneurysms and exhibited a trend towards increased atherosclerosis in the aorta of LDLR knockout mice.
Conclusions: P2Y(6) receptor augments pro-inflammatory responses in macrophages and exhibits a pro-atherogenic role in hematopoietic cells. However, the overall impact of whole body P2Y(6) deficiency on atherosclerosis appears to be modest and could reflect additional roles of P2Y(6) in vascular disease pathophysiologies, such as aneurysm formation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
P2Y6 deficiency limits vascular inflammation and atherosclerosis in mice.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014 Oct;34(10):2237-45. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.114.303585. Epub 2014 Aug 7. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014. PMID: 25104800
-
Reduced atherosclerotic lesions in P2Y1/apolipoprotein E double-knockout mice: the contribution of non-hematopoietic-derived P2Y1 receptors.Circulation. 2008 Aug 12;118(7):754-63. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.788927. Epub 2008 Jul 28. Circulation. 2008. PMID: 18663083
-
P2Y receptors and atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice.Br J Pharmacol. 2010 Jan 1;159(2):326-36. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00497.x. Epub 2009 Dec 24. Br J Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20050854 Free PMC article.
-
P2Y6 receptor: A promising therapeutic target for atherosclerosis.Eur J Pharmacol. 2025 Jul 5;998:177513. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2025.177513. Epub 2025 Mar 15. Eur J Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40097133 Review.
-
Primate models in women's health: inflammation and atherogenesis in female cynomolgus macaques (Macaca fascicularis).Am J Primatol. 2009 Sep;71(9):766-75. doi: 10.1002/ajp.20722. Am J Primatol. 2009. PMID: 19530126 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Microglia P2Y6 receptor is related to Parkinson's disease through neuroinflammatory process.J Neuroinflammation. 2017 Feb 20;14(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s12974-017-0795-8. J Neuroinflammation. 2017. PMID: 28219441 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-activity relationships of pyrimidine nucleotides containing a 5'-α,β-methylene diphosphonate at the P2Y6 receptor.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2021 Aug 1;45:128137. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2021.128137. Epub 2021 May 26. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2021. PMID: 34048882 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping the Binding Sites of UDP and Prostaglandin E2 Glyceryl Ester in the Nucleotide Receptor P2Y6.ChemMedChem. 2022 Apr 5;17(7):e202100683. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.202100683. Epub 2022 Jan 28. ChemMedChem. 2022. PMID: 35034430 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of a Selective P2Y6 Receptor Antagonist, MRS2578, on the Formation of Angiotensin II-Induced Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Apr 16;2020:1983940. doi: 10.1155/2020/1983940. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32382533 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory role of CD39 and CD73 in tumor immunity.Future Oncol. 2024;20(19):1367-1380. doi: 10.2217/fon-2023-0871. Epub 2024 Apr 23. Future Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38652041 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rubartelli A, Lotze MT (2007) Inside, outside, upside down: damage-associated molecular-pattern molecules (DAMPs) and redox. Trends Immunol 28: 429–436. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

