Retinal thickness measurement obtained with spectral domain optical coherence tomography assisted optical biopsy accurately correlates with ex vivo histology
- PMID: 25360629
- PMCID: PMC4216007
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0111203
Retinal thickness measurement obtained with spectral domain optical coherence tomography assisted optical biopsy accurately correlates with ex vivo histology
Abstract
Background: This study determines 'correlation constants' between the gold standard histological measurement of retinal thickness and the newer spectral-domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT) technology in adult C57BL/6 mice.
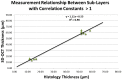
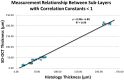
Methods: Forty-eight eyes from adult mice underwent SD-OCT imaging and then were histologically prepared for frozen sectioning with H&E staining. Retinal thickness was measured via 10x light microscopy. SD-OCT images and histological sections were standardized to three anatomical sites relative to the optic nerve head (ONH) location. The ratios between SD-OCT to histological thickness for total retinal thickness (TRT) and six sublayers were defined as 'correlation constants'.
Results: Mean (± SE) TRT for SD-OCT and histological sections was 210.95 µm (± 1.09) and 219.58 µm (± 2.67), respectively. The mean 'correlation constant' for TRT between the SD-OCT and histological sections was 0.96. The retinal thickness for all sublayers measured by SD-OCT vs. histology were also similar, the 'correlation constant' values ranged from 0.70 to 1.17. All SD-OCT and histological measurements demonstrated highly significant (p<0.01) strong positive correlations.
Conclusion: This study establishes conversion factors for the translation of ex vivo data into in vivo information; thus enhancing the applicability of SD-OCT in translational research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Reproducibility of spectral-domain optical coherence tomography total retinal thickness measurements in mice.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010 Dec;51(12):6519-23. doi: 10.1167/iovs.10-5662. Epub 2010 Jun 23. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010. PMID: 20574022 Free PMC article.
-
Dose-dependent retinal changes following sodium iodate administration: application of spectral-domain optical coherence tomography for monitoring of retinal injury and endogenous regeneration.Curr Eye Res. 2014 Oct;39(10):1033-41. doi: 10.3109/02713683.2014.892996. Epub 2014 Mar 24. Curr Eye Res. 2014. PMID: 24661221
-
Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography in Awake Rabbits Allows Identification of the Visual Streak, a Comparison with Histology.Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2020 Apr 23;9(5):13. doi: 10.1167/tvst.9.5.13. eCollection 2020 Apr. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2020. PMID: 32821485 Free PMC article.
-
[Optical coherence tomography--high-resolution tissue imaging, but not histology!].Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 2014 Jul;231(7):709-17. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1368451. Epub 2014 Jul 3. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 2014. PMID: 24992238 Review. German.
-
Clinical applications of spectral domain optical coherence tomography in retinal diseases.Biomed J. 2016 Apr;39(2):107-20. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2016.04.003. Epub 2016 Jun 20. Biomed J. 2016. PMID: 27372166 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Morphometric and Microstructural Changes During Murine Retinal Development Characterized Using In Vivo Optical Coherence Tomography.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021 Oct 4;62(13):20. doi: 10.1167/iovs.62.13.20. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021. PMID: 34698774 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrahigh Resolution Mouse Optical Coherence Tomography to Aid Intraocular Injection in Retinal Gene Therapy Research.J Vis Exp. 2018 Nov 2;(141):10.3791/55894. doi: 10.3791/55894. J Vis Exp. 2018. PMID: 30451216 Free PMC article.
-
Scale Adjustments to Facilitate Two-Dimensional Measurements in OCT Images.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 25;10(6):e0131154. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0131154. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26110792 Free PMC article.
-
Intravitreal injection of adenosine A2A receptor antagonist reduces neuroinflammation, vascular leakage and cell death in the retina of diabetic mice.Sci Rep. 2019 Nov 20;9(1):17207. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-53627-y. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31748653 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Global and Local Alterations in Retinal Layer Thickness in Ins2 (Akita) Diabetic Mice by Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography.J Ophthalmol. 2018 Feb 20;2018:7253498. doi: 10.1155/2018/7253498. eCollection 2018. J Ophthalmol. 2018. PMID: 29675273 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yehoshua Z, Rosenfeld PJ (2012) Strategies for following dry age-related macular degeneration. Ophthalmic Res 48 Suppl 16–10. - PubMed
-
- Gloesmann M, Hermann B, Schubert C, Sattmann H, Ahnelt PK, et al. (2003) Histologic correlation of pig retina radial stratification with ultrahigh-resolution optical coherence tomography. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 44(4): 1696–1703. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

