Peripheral blood signature of vasodilator-responsive pulmonary arterial hypertension
- PMID: 25361553
- PMCID: PMC4308423
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.114.013317
Peripheral blood signature of vasodilator-responsive pulmonary arterial hypertension
Abstract
Background: Heterogeneity in response to treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a major challenge to improving outcome in this disease. Although vasodilator-responsive PAH (VR-PAH) accounts for a minority of cases, VR-PAH has a pronounced response to calcium channel blockers and better survival than vasodilator-nonresponsive PAH (VN-PAH). We hypothesized that VR-PAH has a different molecular cause from VN-PAH that can be detected in the peripheral blood.
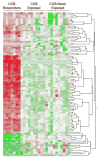
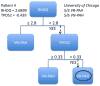
Methods and results: Microarrays of cultured lymphocytes from VR-PAH and VN-PAH patients followed at Vanderbilt University were performed with quantitative polymerase chain reaction performed on peripheral blood for the 25 most different genes. We developed a decision tree to identify VR-PAH patients on the basis of the results with validation in a second VR-PAH cohort from the University of Chicago. We found broad differences in gene expression patterns on microarray analysis including cell-cell adhesion factors and cytoskeletal and rho-GTPase genes. Thirteen of 25 genes tested in whole blood were significantly different: EPDR1, DSG2, SCD5, P2RY5, MGAT5, RHOQ, UCHL1, ZNF652, RALGPS2, TPD52, MKNL1, RAPGEF2, and PIAS1. Seven decision trees were built with the use of expression levels of 2 genes as the primary genes: DSG2, a desmosomal cadherin involved in Wnt/β-catenin signaling, and RHOQ, which encodes a cytoskeletal protein involved in insulin-mediated signaling. These trees correctly identified 5 of 5 VR-PAH patients in the validation cohort.
Conclusions: VR-PAH and VN-PAH can be differentiated with the use of RNA expression patterns in peripheral blood. These differences may reflect different molecular causes of the 2 PAH phenotypes. This biomarker methodology may identify PAH patients who have a favorable treatment response.
Keywords: biomarkers; pulmonary hypertension; treatment.
© 2014 American Heart Association, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Humbert M, Sitbon O, Chaouat A, Bertocchi M, Habib G, Gressin V, Yaici A, Weitzenblum E, Cordier JF, Chabot F, Dromer C, Pison C, Reynaud-Gaubert M, Haloun A, Laurent M, Hachulla E, Simonneau G. Pulmonary arterial hypertension in France: results from a national registry. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2006;173:1023–30. - PubMed
-
- Benza RL, Miller DP, Gomberg-Maitland M, Frantz RP, Foreman AJ, Coffey CS, Frost A, Barst RJ, Badesch DB, Elliott CG, Liou TG, McGoon MD. Predicting survival in pulmonary arterial hypertension: insights from the Registry to Evaluate Early and Long-Term Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Disease Management (REVEAL) Circulation. 2010;122:164–72. - PubMed
-
- Sitbon O, Humbert M, Jais X, Ioos V, Hamid AM, Provencher S, Garcia G, Parent F, Herve P, Simonneau G. Long-term response to calcium channel blockers in idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. Circulation. 2005;111:3105–11. - PubMed
-
- McLaughlin VV, Archer SL, Badesch DB, Barst RJ, Farber HW, Lindner JR, Mathier MA, McGoon MD, Park MH, Rosenson RS, Rubin LJ, Tapson VF, Varga J. ACCF/AHA 2009 expert consensus document on pulmonary hypertension a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation Task Force on Expert Consensus Documents and the American Heart Association developed in collaboration with the American College of Chest Physicians; American Thoracic Society, Inc.; and the Pulmonary Hypertension Association. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;53:1573–619. - PubMed
-
- Rich S, Brundage BH. High-dose calcium channel-blocking therapy for primary pulmonary hypertension: evidence for long-term reduction in pulmonary arterial pressure and regression of right ventricular hypertrophy. Circulation. 1987;76:135–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

