ERK and β-arrestin interaction: a converging point of signaling pathways for multiple types of cell surface receptors
- PMID: 25361946
- PMCID: PMC4975872
- DOI: 10.1177/1087057114557233
ERK and β-arrestin interaction: a converging point of signaling pathways for multiple types of cell surface receptors
Abstract
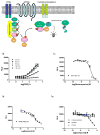
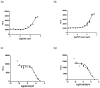
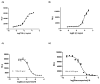
β-Arrestin, a signal adaptor protein, mediates intracellular signal transductions through protein-protein interactions by bringing two or more proteins in proximity. Extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), a protein kinase in the family of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), is involved in various receptor signal pathways. Interaction of ERK with β-arrestin or formation of ERK/β-arrestin signal complex occurs in response to activation of a variety of cell surface receptors. The ERK/β-arrestin signal complex may be a common transducer to converge a variety of extracellular stimuli to similar downstream intracellular signaling pathways. By using a cell-based protein-protein interaction LinkLight assay technology, we demonstrate a direct interaction between ERK and β-arrestin in response to extracellular stimuli, which can be sensitively and quantitatively monitored. Activations of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs), and cytokine receptors promote formation of the ERK/β-arrestin signal complex. Our data indicate that the ERK/β-arrestin signal complex is a common transducer that participates in a variety of receptor signaling pathways. Furthermore, we demonstrate that receptor antagonists or kinase inhibitors can block the agonist-induced ERK and β-arrestin interaction. Thus, the ERK/β-arrestin interaction assay is useful for screening of new receptor modulators.
Keywords: ERK; extracellular signal-regulated kinases; protein-protein interactions; β-arrestin.
© 2014 Society for Laboratory Automation and Screening.
Conflict of interest statement
H.E. has the commercial interests of the patented LinkLight technology. The other authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
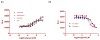
References
-
- Lefkowitz RJ, Whalen EJ. beta-arrestins: traffic cops of cell signaling. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2004;16:162–8. - PubMed
-
- Hupfeld CJ, Olefsky JM. Regulation of receptor tyrosine kinase signaling by GRKs and beta-arrestins. Annu Rev Physiol. 2007;69:561–77. - PubMed
-
- Lanner F, Rossant J. The role of FGF/Erk signaling in pluripotent cells. Development. 2010;137:3351–60. - PubMed
-
- Hwang YS, Jeong M, Park JS, et al. Interleukin-1 beta stimulates IL-8 expression through MAP kinase and ROS signaling in human gastric carcinoma cells. Oncogene. 2004;23:6603–6611. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

