The L7Ae protein binds to two kink-turns in the Pyrococcus furiosus RNase P RNA
- PMID: 25361963
- PMCID: PMC4245976
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gku994
The L7Ae protein binds to two kink-turns in the Pyrococcus furiosus RNase P RNA
Abstract
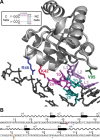
The RNA-binding protein L7Ae, known for its role in translation (as part of ribosomes) and RNA modification (as part of sn/oRNPs), has also been identified as a subunit of archaeal RNase P, a ribonucleoprotein complex that employs an RNA catalyst for the Mg(2+)-dependent 5' maturation of tRNAs. To better understand the assembly and catalysis of archaeal RNase P, we used a site-specific hydroxyl radical-mediated footprinting strategy to pinpoint the binding sites of Pyrococcus furiosus (Pfu) L7Ae on its cognate RNase P RNA (RPR). L7Ae derivatives with single-Cys substitutions at residues in the predicted RNA-binding interface (K42C/C71V, R46C/C71V, V95C/C71V) were modified with an iron complex of EDTA-2-aminoethyl 2-pyridyl disulfide. Upon addition of hydrogen peroxide and ascorbate, these L7Ae-tethered nucleases were expected to cleave the RPR at nucleotides proximal to the EDTA-Fe-modified residues. Indeed, footprinting experiments with an enzyme assembled with the Pfu RPR and five protein cofactors (POP5, RPP21, RPP29, RPP30 and L7Ae-EDTA-Fe) revealed specific RNA cleavages, localizing the binding sites of L7Ae to the RPR's catalytic and specificity domains. These results support the presence of two kink-turns, the structural motifs recognized by L7Ae, in distinct functional domains of the RPR and suggest testable mechanisms by which L7Ae contributes to RNase P catalysis.
© The Author(s) 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A novel double kink-turn module in euryarchaeal RNase P RNAs.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Jul 7;45(12):7432-7440. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx388. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 28525600 Free PMC article.
-
Solution structure of an archaeal RNase P binary protein complex: formation of the 30-kDa complex between Pyrococcus furiosus RPP21 and RPP29 is accompanied by coupled protein folding and highlights critical features for protein-protein and protein-RNA interactions.J Mol Biol. 2009 Nov 13;393(5):1043-55. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2009.08.068. Epub 2009 Sep 3. J Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19733182 Free PMC article.
-
Cooperative RNP assembly: complementary rescue of structural defects by protein and RNA subunits of archaeal RNase P.J Mol Biol. 2011 Aug 12;411(2):368-83. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2011.05.012. Epub 2011 Jun 12. J Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21683084 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for activation of an archaeal ribonuclease P RNA by protein cofactors.Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2017 Sep;81(9):1670-1680. doi: 10.1080/09168451.2017.1353404. Epub 2017 Jul 17. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28715256 Review.
-
RNase P: interface of the RNA and protein worlds.Trends Biochem Sci. 2006 Jun;31(6):333-41. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2006.04.007. Epub 2006 May 6. Trends Biochem Sci. 2006. PMID: 16679018 Review.
Cited by
-
Protein cofactors and substrate influence Mg2+-dependent structural changes in the catalytic RNA of archaeal RNase P.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Sep 20;49(16):9444-9458. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab655. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 34387688 Free PMC article.
-
Elucidation of structure-function relationships in Methanocaldococcus jannaschii RNase P, a multi-subunit catalytic ribonucleoprotein.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Aug 12;50(14):8154-8167. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac595. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 35848927 Free PMC article.
-
A novel double kink-turn module in euryarchaeal RNase P RNAs.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Jul 7;45(12):7432-7440. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx388. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 28525600 Free PMC article.
-
The many faces of RNA-based RNase P, an RNA-world relic.Trends Biochem Sci. 2021 Dec;46(12):976-991. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2021.07.005. Epub 2021 Sep 9. Trends Biochem Sci. 2021. PMID: 34511335 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sequence Analysis and Comparative Study of the Protein Subunits of Archaeal RNase P.Biomolecules. 2016 Apr 20;6(2):22. doi: 10.3390/biom6020022. Biomolecules. 2016. PMID: 27104580 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Liu F., Altman S, editors. Ribonuclease P. New York, NY: Springer; 2010.
-
- Holzmann J., Frank P., Löffler E., Bennett K.L., Gerner C., Rossmanith W. RNase P without RNA: identification and functional reconstitution of the human mitochondrial tRNA processing enzyme. Cell. 2008;135:462–474. - PubMed
-
- Gobert A., Gutmann B., Taschner A., Gößringer M., Holzmann J., Hartmann R.K., Rossmanith W., Giegé P. A single Arabidopsis organellar protein has RNase P activity. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2010;17:740–744. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

