DBC1 is a suppressor of B cell activation by negatively regulating alternative NF-κB transcriptional activity
- PMID: 25362179
- PMCID: PMC4259264
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1401798
DBC1 is a suppressor of B cell activation by negatively regulating alternative NF-κB transcriptional activity
Abstract
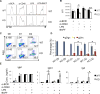
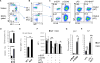
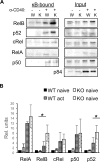
CD40 and BAFFR signaling play important roles in B cell proliferation and Ig production. In this study, we found that B cells from mice with deletion of Dbc1 gene (Dbc1(-/-)) show elevated proliferation, and IgG1 and IgA production upon in vitro CD40 and BAFF, but not BCR and LPS stimulation, indicating that DBC1 inhibits CD40/BAFF-mediated B cell activation in a cell-intrinsic manner. Microarray analysis and chromatin immunoprecipitation experiments reveal that DBC1 inhibits B cell function by selectively suppressing the transcriptional activity of alternative NF-κB members RelB and p52 upon CD40 stimulation. As a result, when immunized with nitrophenylated-keyhole limpet hemocyanin, Dbc1(-/-) mice produce significantly increased levels of germinal center B cells, plasma cells, and Ag-specific Ig. Finally, loss of DBC1 in mice leads to higher susceptibility to experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis. Our study identifies DBC1 as a novel regulator of B cell activation by suppressing the alternative NF-κB pathway.
Copyright © 2014 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure of Conflicts of Interest. The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

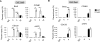

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

