Successful use of Alteplase during cardiopulmonary resuscitation following massive PE in a patient presenting with ischaemic stroke and haemorrhagic transformation
- PMID: 25362185
- PMCID: PMC4216893
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2013-200480
Successful use of Alteplase during cardiopulmonary resuscitation following massive PE in a patient presenting with ischaemic stroke and haemorrhagic transformation
Abstract
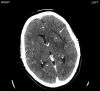
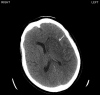
The management of patients with acute stroke regarding treatment of thromboembolism is supported by a limited evidence base. We present the case of a 55-year-old female patient who initially presented with an ischaemic cerebral infarct with haemorrhagic transformation. Her clinical recovery was complicated by cardiac arrest secondary to massive pulmonary embolism. This was successfully treated with cardiopulmonary resuscitation and thrombolysis using Alteplase, which led to a full recovery to the pre-arrest state with no evidence of haemorrhagic complication. The patient was successfully discharged to a specialist centre for on-going stroke rehabilitation with no additional neurological impact. Despite the limited evidence base we believe this case highlights that thrombolysis can be used in select patients with haemorrhagic transformation of stroke and serious thromboembolic complications to achieve a positive outcome.
2014 BMJ Publishing Group Ltd.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Successful thrombolytic therapy of post-operative massive pulmonary embolism after ultralong cardiopulmonary resuscitation: a case report and review of literature.Clin Respir J. 2017 May;11(3):383-390. doi: 10.1111/crj.12332. Epub 2015 Jul 24. Clin Respir J. 2017. PMID: 26083151 Review.
-
[Thrombolytic therapy during cardiopulmonary resuscitation for acute massive pulmonary embolism. A case report].Minerva Cardioangiol. 2001 Dec;49(6):433-6. Minerva Cardioangiol. 2001. PMID: 11733741 Italian.
-
Massive pulmonary embolism and cardiac arrest; thrombolytic therapy in a patient with recent intracranial surgery and glioblastoma multiforme.Am J Emerg Med. 2014 Nov;32(11):1441.e1-3. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2014.04.022. Epub 2014 May 20. Am J Emerg Med. 2014. PMID: 25009081
-
[Cardiac arrest caused by massive pulmonary embolism during treatment with tranexamic acid].Ugeskr Laeger. 2013 May 13;175(20):1426-7. Ugeskr Laeger. 2013. PMID: 23663400 Danish.
-
[Bolus injection of recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator during cardiopulmonary resuscitation in massive pulmonary embolism complicated with heart arrest. Report of 2 cases and review of the literature].Ital Heart J Suppl. 2003 May;4(5):420-3. Ital Heart J Suppl. 2003. PMID: 12848080 Review. Italian.
References
-
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Venous thromboembolism—reducing the risk: full guideline (CG92). London: NICE, 2010. http://guidance.nice.org.uk/CG92 (accessed 27 May 2013)
-
- Resuscitation Council (UK). Resuscitation Guidelines. Resuscitation Council (UK) 2010. http://www.resus.org.uk/pages/guide.htm (accessed 27 May 2013)
-
- McConnell MV, Solomon SD, Rayan ME. Regional right ventricular dysfunction detected by echocardiography in acute pulmonary embolism. Am J Cardiol 1996;78:469–73 - PubMed
-
- Handke M, Harloff A, Olschewski M, et al. . Patent foramen ovale and cryptogenic stroke in older patients. N Engl J Med 2007;357:2262. - PubMed
-
- Meissner I, Khandheria BK, Heit JA, et al. . Patent foramen ovale: innocent or guilty? Evidence from a prospective population-based study. J Am Coll Cardiol 2006;47:440. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
