Dendropanax morbifera Léveille extract facilitates cadmium excretion and prevents oxidative damage in the hippocampus by increasing antioxidant levels in cadmium-exposed rats
- PMID: 25362479
- PMCID: PMC4228155
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6882-14-428
Dendropanax morbifera Léveille extract facilitates cadmium excretion and prevents oxidative damage in the hippocampus by increasing antioxidant levels in cadmium-exposed rats
Abstract
Background: Dendropanax morbifera Léveille is used in herbal medicine as a cancer treatment. In this study, we investigated the effects of Dendropanax morbifera stem extract (DMS) on cadmium (Cd) excretion from the blood and kidney and brain tissues of rats exposed to cadmium, as well as the effects of DMS on oxidative stress and antioxidant levels in the hippocampus after Cd exposure.
Methods: Seven-week-old Sprague-Dawley rats were exposed to 2 mg/kg of cadmium by intragastric gavage and were orally administered 100 mg/kg of DMS for 4 weeks. Animals were sacrificed and Cd determination was performed using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. In addition, the effects of Cd and/or DMS on oxidative stress were assayed by measuring reactive oxygen species production, protein carbonyl modification, lipid peroxidation levels, and antioxidant levels in hippocampal homogenates.
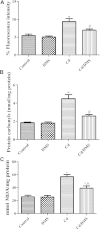
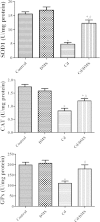
Results: Exposure to Cd significantly increased Cd content in the blood, kidneys, and hippocampi. DMS treatment significantly reduced Cd content in the blood and kidneys, but not in the hippocampi. Exposure to Cd significantly increased reactive oxygen species production, protein carbonyl modification, lipid peroxidation, total sulfhydryl content, reduced glutathione content, and glutathione reductase activity. In contrast, Cu, Zn-superoxide dismutase (SOD1), catalase (CAT), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), and glutathione-S-transferase (GST) activity in the hippocampus were significantly decreased after exposure to Cd, and administration of DMS significantly inhibited these Cd-induced changes.
Conclusion: These results indicate that DMS facilitates cadmium excretion from the kidneys, reduces cadmium-induced oxidative stress in the hippocampus, and modulates SOD1, CAT, GPx, and glutathione-S-transferase activities.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antioxidant effects of Dendropanax morbifera Léveille extract in the hippocampus of mercury-exposed rats.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015 Jul 23;15:247. doi: 10.1186/s12906-015-0786-1. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015. PMID: 26201852 Free PMC article.
-
Dendropanax morbifera Léveille extract ameliorates cadmium-induced impairment in memory and hippocampal neurogenesis in rats.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016 Nov 9;16(1):452. doi: 10.1186/s12906-016-1435-z. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016. PMID: 27829466 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Dendropanax morbifera Léveille extract on hypothyroidism-induced oxidative stress in the rat hippocampus.Food Sci Biotechnol. 2016 Dec 31;25(6):1761-1766. doi: 10.1007/s10068-016-0268-3. eCollection 2016. Food Sci Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 30263472 Free PMC article.
-
Plant Extracts and Isolated Compounds Reduce Parameters of Oxidative Stress Induced by Heavy Metals: An up-to-Date Review on Animal Studies.Curr Pharm Des. 2020;26(16):1799-1815. doi: 10.2174/1381612826666200407163408. Curr Pharm Des. 2020. PMID: 32264808 Review.
-
Insight into the oxidative stress induced by lead and/or cadmium in blood, liver and kidneys.Food Chem Toxicol. 2015 Apr;78:130-40. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2015.02.011. Epub 2015 Feb 11. Food Chem Toxicol. 2015. PMID: 25681546 Review.
Cited by
-
Antioxidant effects of Dendropanax morbifera Léveille extract in the hippocampus of mercury-exposed rats.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015 Jul 23;15:247. doi: 10.1186/s12906-015-0786-1. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015. PMID: 26201852 Free PMC article.
-
Leaf extracts from Dendropanax morbifera Léveille mitigate mercury-induced reduction of spatial memory, as well as cell proliferation, and neuroblast differentiation in rat dentate gyrus.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019 May 2;19(1):94. doi: 10.1186/s12906-019-2508-6. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019. PMID: 31046739 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Role of Quercetin in Cadmium-Induced Cholinergic Dysfunctions in Rat Brain by Modulating Mitochondrial Integrity and MAP Kinase Signaling.Mol Neurobiol. 2017 Aug;54(6):4560-4583. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-9950-y. Epub 2016 Jul 7. Mol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 27389774
-
Microwave-Assisted Dendropanax morbifera Extract for Cosmetic Applications.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 May 19;11(5):998. doi: 10.3390/antiox11050998. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35624862 Free PMC article.
-
Dendropanax morbifera Léveille extract ameliorates cadmium-induced impairment in memory and hippocampal neurogenesis in rats.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016 Nov 9;16(1):452. doi: 10.1186/s12906-016-1435-z. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016. PMID: 27829466 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kim SH, Hang YS, Han JG, Chung HG, Lee SW, Cho KJ. Genetic variation and population structure of Dendropanax morbifera Lév. (Araliaceae) in Korea. Silvae Genetica. 2006;55:7–13.
-
- Chung IM, Kim MY, Park WH, Moon HI. Antiatherogenic activity of Dendropanax morbifera essential oil in rats. Pharmazie. 2009;64:547–549. - PubMed
-
- Chung IM, Song HK, Kim SJ, Moon HI. Anticomplement activity of polyacetylenes from leaves of Dendropanax morbifera Léveille. Phytother Res. 2011;25:784–786. - PubMed
Pre-publication history
-
- The pre-publication history for this paper can be accessed here: http://www.biomedcentral.com/1472-6882/14/428/prepub
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

