A novel highly pathogenic H5N8 avian influenza virus isolated from a wild duck in China
- PMID: 25363159
- PMCID: PMC4262280
- DOI: 10.1111/irv.12289
A novel highly pathogenic H5N8 avian influenza virus isolated from a wild duck in China
Abstract
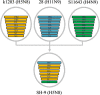
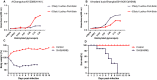
Migrating wild birds are considered natural reservoirs of influenza viruses and serve as a potential source of novel influenza strains in humans and livestock. During routine avian influenza surveillance conducted in eastern China, a novel H5N8 (SH-9) reassortant influenza virus was isolated from a mallard duck in China. blast analysis revealed that the HA, NA, PB1, PA, NP, and M segments of SH-9 were most closely related to the corresponding segments of A/duck/Jiangsu/k1203/2010 (H5N8). The SH-9 virus preferentially recognized avian-like influenza virus receptors and was highly pathogenic in mice. Our results suggest that wild birds could acquire the H5N8 virus from breeding ducks and spread the virus via migratory bird flyways.
Keywords: H5N8; highly pathogenic avian influenza virus; wild duck.
© 2014 The Authors. Influenza and Other Respiratory Viruses Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

