Synthesis and surface functionalization of silica nanoparticles for nanomedicine
- PMID: 25364083
- PMCID: PMC4212223
- DOI: 10.1016/j.surfrep.2014.07.001
Synthesis and surface functionalization of silica nanoparticles for nanomedicine
Abstract
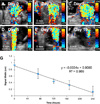
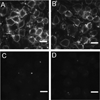
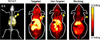
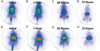
There are a wide variety of silica nanoformulations being investigated for biomedical applications. Silica nanoparticles can be produced using a wide variety of synthetic techniques with precise control over their physical and chemical characteristics. Inorganic nanoformulations are often criticized or neglected for their poor tolerance; however, extensive studies into silica nanoparticle biodistributions and toxicology have shown that silica nanoparticles may be well tolerated, and in some case are excreted or are biodegradable. Robust synthetic techniques have allowed silica nanoparticles to be developed for applications such as biomedical imaging contrast agents, ablative therapy sensitizers, and drug delivery vehicles. This review explores the synthetic techniques used to create and modify an assortment of silica nanoformulations, as well as several of the diagnostic and therapeutic applications.
Keywords: Ablative technology; Biodistribution; Biomedical imaging; Nanoparticles; Silica; Toxicology.
Figures


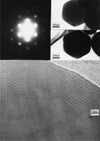
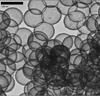

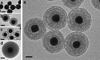

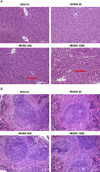






References
-
- Stöber W, Fink A, Bohn E. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1968;26:62–69.
-
- Choi H, Chen IW. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003;258:435–437. - PubMed
-
- Nozawa K, Gailhanou H, Raison L, Panizza P, Ushiki H, Sellier E, Delville JP, Delville MH. Langmuir. 2004;21:1516–1523. - PubMed
-
- Wang X-D, Shen Z-X, Sang T, Cheng X-B, Li M-F, Chen L-Y, Wang Z-S. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010;341:23–29. - PubMed
-
- van Blaaderen A, Vrij A. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1993;156:1–18.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
