Systemic treatment in EGFR-ALK NSCLC patients: second line therapy and beyond
- PMID: 25364578
- PMCID: PMC4197428
- DOI: 10.7497/j.issn.2095-3941.2014.03.003
Systemic treatment in EGFR-ALK NSCLC patients: second line therapy and beyond
Abstract
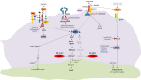
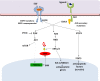
Lung cancer is the most frequently diagnosed cancer and a leading cause of cancer mortality worldwide, with adenocarcinoma being the most common histological subtype. Deeper understanding of the pathobiology of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) has led to the development of small molecules that target genetic mutations known to play critical roles in progression to metastatic disease and to influence response to targeted therapies. The principle goal of precision medicine is to define those patient populations most likely to respond to targeted therapies. However, the cancer genome landscape is composed of relatively few "mountains" [representing the most commonly mutated genes like KRAS, epidermal growth factor (EGFR), and anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)] and a vast number of "hills" (representing low frequency but potentially actionable mutations). Low-frequency lesions that affect a druggable gene product allow a relatively small population of cancer patients for targeted therapy to be selected.
Keywords: Lung cancer; TKI resistance; anaplastic lymphoma kinase fusions (ALK fusions); epidermal growth factor (EGFR); tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs).
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest are disclosed.
Figures
References
-
- Rosell R, Bivona TG, Karachaliou N. Genetics and biomarkers in personalisation of lung cancer treatment. Lancet 2013;382:720-731 - PubMed
-
- Rosell R, Carcereny E, Gervais R, Vergnenegre A, Massuti B, Felip E, et al. Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 2012;13:239-246 - PubMed
-
- Soda M, Choi YL, Enomoto M, Takada S, Yamashita Y, Ishikawa S, et al. Identification of the transforming EML4-ALK fusion gene in non-small-cell lung cancer. Nature 2007;448:561-566 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
