Hypoxic signaling during tissue repair and regenerative medicine
- PMID: 25365172
- PMCID: PMC4264139
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms151119791
Hypoxic signaling during tissue repair and regenerative medicine
Abstract
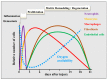
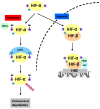
In patients with chronic wounds, autologous tissue repair is often not sufficient to heal the wound. These patients might benefit from regenerative medicine or the implantation of a tissue-engineered scaffold. Both wound healing and tissue engineering is dependent on the formation of a microvascular network. This process is highly regulated by hypoxia and the transcription factors hypoxia-inducible factors-1α (HIF-1α) and -2α (HIF-2α). Even though much is known about the function of HIF-1α in wound healing, knowledge about the function of HIF-2α in wound healing is lacking. This review focuses on the function of HIF-1α and HIF-2α in microvascular network formation, wound healing, and therapy strategies.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Increased activation of the hypoxia-inducible factor pathway in varicose veins.J Vasc Surg. 2012 May;55(5):1427-39. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2011.10.111. Epub 2012 Jan 24. J Vasc Surg. 2012. PMID: 22277691
-
Identification of HIF-2α-regulated genes that play a role in human microvascular endothelial sprouting during prolonged hypoxia in vitro.Angiogenesis. 2017 Feb;20(1):39-54. doi: 10.1007/s10456-016-9527-4. Epub 2016 Oct 3. Angiogenesis. 2017. PMID: 27699500 Free PMC article.
-
Lenticular cytoprotection. Part 1: the role of hypoxia inducible factors-1α and -2α and vascular endothelial growth factor in lens epithelial cell survival in hypoxia.Mol Vis. 2013;19:1-15. Epub 2013 Jan 2. Mol Vis. 2013. PMID: 23335846 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired Neovascularization in Aging.Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2020 Mar 1;9(3):111-126. doi: 10.1089/wound.2018.0912. Epub 2020 Jan 24. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2020. PMID: 31993253 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A narrative review of research progress on the relationship between hypoxia-inducible factor-2α and wound angiogenesis.Ann Palliat Med. 2021 Apr;10(4):4882-4888. doi: 10.21037/apm-21-450. Ann Palliat Med. 2021. PMID: 33966427 Review.
Cited by
-
N-Acetyl-L-Cysteine Reduces Fibrosis and Improves Muscle Function After Acute Compartment Syndrome Injury.Mil Med. 2020 Jan 7;185(Suppl 1):25-34. doi: 10.1093/milmed/usz232. Mil Med. 2020. PMID: 32074330 Free PMC article.
-
The diverse functions of DYRK2 in response to cellular stress.Histol Histopathol. 2024 Nov;39(11):1427-1434. doi: 10.14670/HH-18-744. Epub 2024 Apr 8. Histol Histopathol. 2024. PMID: 38656683 Review.
-
Potential of pomegranate fruit extract (Punica granatum Linn.) to increase vascular endothelial growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor expressions on the post-tooth extraction wound of Cavia cobaya.Vet World. 2017 Aug;10(8):999-1003. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2017.999-1003. Epub 2017 Aug 27. Vet World. 2017. PMID: 28919696 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the HIFs, buts and maybes of hypoxia signalling in disease: lessons from zebrafish models.Dis Model Mech. 2015 Nov;8(11):1349-60. doi: 10.1242/dmm.021865. Dis Model Mech. 2015. PMID: 26512123 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HIF-1-Independent Mechanisms Regulating Metabolic Adaptation in Hypoxic Cancer Cells.Cells. 2021 Sep 9;10(9):2371. doi: 10.3390/cells10092371. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34572020 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

