PhTX-II a basic myotoxic phospholipase A₂ from Porthidium hyoprora snake venom, pharmacological characterization and amino acid sequence by mass spectrometry
- PMID: 25365526
- PMCID: PMC4247251
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins6113077
PhTX-II a basic myotoxic phospholipase A₂ from Porthidium hyoprora snake venom, pharmacological characterization and amino acid sequence by mass spectrometry
Abstract
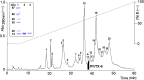
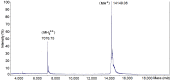
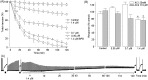
A monomeric basic PLA₂ (PhTX-II) of 14149.08 Da molecular weight was purified to homogeneity from Porthidium hyoprora venom. Amino acid sequence by in tandem mass spectrometry revealed that PhTX-II belongs to Asp49 PLA₂ enzyme class and displays conserved domains as the catalytic network, Ca²⁺-binding loop and the hydrophobic channel of access to the catalytic site, reflected in the high catalytic activity displayed by the enzyme. Moreover, PhTX-II PLA₂ showed an allosteric behavior and its enzymatic activity was dependent on Ca²⁺. Examination of PhTX-II PLA₂ by CD spectroscopy indicated a high content of alpha-helical structures, similar to the known structure of secreted phospholipase IIA group suggesting a similar folding. PhTX-II PLA₂ causes neuromuscular blockade in avian neuromuscular preparations with a significant direct action on skeletal muscle function, as well as, induced local edema and myotoxicity, in mice. The treatment of PhTX-II by BPB resulted in complete loss of their catalytic activity that was accompanied by loss of their edematogenic effect. On the other hand, enzymatic activity of PhTX-II contributes to this neuromuscular blockade and local myotoxicity is dependent not only on enzymatic activity. These results show that PhTX-II is a myotoxic Asp49 PLA₂ that contributes with toxic actions caused by P. hyoprora venom.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Biochemical and pharmacological characterization of PhTX-I a new myotoxic phospholipase A2 isolated from Porthidium hyoprora snake venom.Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2011 Aug;154(2):108-19. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpc.2011.03.013. Epub 2011 Apr 6. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21496495
-
Chemical modifications of PhTX-I myotoxin from Porthidium hyoprora snake venom: effects on structural, enzymatic, and pharmacological properties.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:103494. doi: 10.1155/2013/103494. Epub 2012 Dec 19. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 23484072 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of a phospholipase A2 from Bothrops asper venom: Insights into a new putative "myotoxic cluster".Biochimie. 2017 Feb;133:95-102. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2016.12.015. Epub 2016 Dec 27. Biochimie. 2017. PMID: 28034717
-
Snake venom Lys49 myotoxins: From phospholipases A(2) to non-enzymatic membrane disruptors.Toxicon. 2012 Sep 15;60(4):520-30. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2012.02.007. Epub 2012 Mar 3. Toxicon. 2012. PMID: 22781132 Review.
-
Cellular pathology induced by snake venom phospholipase A2 myotoxins and neurotoxins: common aspects of their mechanisms of action.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2008 Sep;65(18):2897-912. doi: 10.1007/s00018-008-8113-3. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2008. PMID: 18563294 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Isolation and Characterization of A2-EPTX-Nsm1a, a Secretory Phospholipase A2 from Malaysian Spitting Cobra (Naja sumatrana) Venom.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Dec 2;13(12):859. doi: 10.3390/toxins13120859. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34941697 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical characterization of Bothrops roedingeri Mertens, 1942 snake venom and its edematogenic, hemorrhagic, and myotoxic activities.Biomedica. 2020 Dec 2;40(4):682-692. doi: 10.7705/biomedica.5228. Biomedica. 2020. PMID: 33275347 Free PMC article. English, Spanish.
-
ACP-TX-I and ACP-TX-II, Two Novel Phospholipases A2 Isolated from Trans-Pecos Copperhead Agkistrodon contortrix pictigaster Venom: Biochemical and Functional Characterization.Toxins (Basel). 2019 Nov 14;11(11):661. doi: 10.3390/toxins11110661. Toxins (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31739403 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Campbell J.A., Lamar W.W. The Venomous Reptiles of the Western Hemisphere. Cornell University Press; Ithaca, NY, USA: 2004.
-
- Lomonte B., Rey-Suárez P., Tsai W.C., Angulo Y., Sasa M., Gutiérrez J.M., Calvete J.J. Snake venomics of the pit vipers Porthidium nasutum, Porthidium ophryomegas, and Cerrophidion godmani from Costa Rica: Toxicological and taxonomical insights. J. Proteomics. 2012;75:1675–1689. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2011.12.016. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Girón M.E., Estrella A., Sánchez E.E., Galán J., Tao W.A., Guerrero B., Salazar A.M., Rodríguez-Acosta A. Purification and characterization of a metalloproteinase, Porthidin-1, from the venom of Lansberg’s hog-nosed pit vipers (Porthidium lansbergii hutmanni) Toxicon. 2011;57:608–618. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2011.01.003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

