Diagnostic yield of transbronchial cryobiopsy in non-neoplastic lung disease: a retrospective case series
- PMID: 25366106
- PMCID: PMC4223742
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2466-14-171
Diagnostic yield of transbronchial cryobiopsy in non-neoplastic lung disease: a retrospective case series
Abstract
Background: Due to the small amount of alveolar tissue in transbronchial biopsy (TBB) by forceps, the diagnosis of diffuse, parenchymal lung diseases (DPLD) is inherently problematic, with an overall low yield. The use of cryotechnique in bronchoscopy, including TBB by cryoprobe, has revealed new opportunities in the endoscopical diagnosis of malignant and non-malignant lung diseases.
Methods: To evaluate TBB by cryotechnique for non-neoplastic lung diseases, we analyzed 52 patients (mean age 63 ± 13 years) with unclear DPLD. These individuals underwent bronchoscopy with TBB by cryoprobe. Thereafter histopathological results were compared with the clinically evaluated diagnosis.
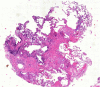
Results: No major complications were seen. Mean specimen diameter in the histological biopsies was 6.9 ± 4.4 mm (Range 2 - 22 mm). A correlation between clinical and histopathological diagnoses was found in 79% of cases (41/52). In the case of UIP (usual interstitial pneumonia) pattern, the concordance was 10/15 (66%).
Conclusion: Based on these results TBB by cryotechnique would appear to be a safe and useful method that reveals new perspectives for the endoscopical diagnosis of DPLD.
Figures

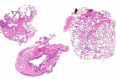

References
-
- Katzenstein AL. Katzenstein and Askin’s Surgical Pathology of Non-Neoplastic Lung Disease. 4. Philadelphia, USA: Saunders Company; 2006.
Pre-publication history
-
- The pre-publication history for this paper can be accessed here:http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2466/14/171/prepub
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

