Differential inflammatory microRNA and cytokine expression in pulmonary sarcoidosis
- PMID: 25366387
- PMCID: PMC4359280
- DOI: 10.1007/s00005-014-0315-9
Differential inflammatory microRNA and cytokine expression in pulmonary sarcoidosis
Abstract
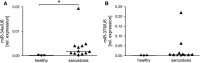
Sarcoidosis is a granulomatous disease of unknown etiology. The disease has an important inflammatory and immune component; however, its immunopathogenesis is not completely understood. Recently, the role of microRNAs (miRNAs), the small non-coding RNAs, has attracted attention as both being involved in pathogenesis and serving as disease markers. Accordingly, changes in the expression of some miRNAs have been also associated with different autoimmune pathologies. However, not much is known about the role of miRNAs in sarcoidosis. Therefore, the aim of this study was to compare the level of expression of selected miRNAs in healthy individuals and patients with sarcoidosis. We detected significantly increased level of miR-34a in peripheral blood mononuclear cells isolated from sarcoidosis patients. Moreover, significantly up-regulated levels of interferon (IFN)-γ, IFN-γ inducible protein (IP-10) and vascular endothelial growth factor were detected in sera of patients when compared to healthy subjects. Our results add to a known inflammatory component in sarcoidosis. Changes in the levels of miR-34a may suggest its involvement in the pathology of this disease.
Figures

References
-
- Bazan-Socha S, Zuk J, Plutecka H, et al. Collagen receptors alpha(1)beta(1) and alpha(2)beta(1) integrins are involved in transmigration of peripheral blood eosinophils, but not mononuclear cells through human microvascular endothelial cells monolayer. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2012;63:373–379. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

