Long-term outcomes in patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer after selective bladder-preserving combined-modality therapy: a pooled analysis of Radiation Therapy Oncology Group protocols 8802, 8903, 9506, 9706, 9906, and 0233
- PMID: 25366678
- PMCID: PMC4239302
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2014.57.5548
Long-term outcomes in patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer after selective bladder-preserving combined-modality therapy: a pooled analysis of Radiation Therapy Oncology Group protocols 8802, 8903, 9506, 9706, 9906, and 0233
Erratum in
-
Errata.J Clin Oncol. 2015 Mar 1;33(7):814. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2015.61.1491. J Clin Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25721580 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Purpose: Multiple prospective Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) protocols have evaluated bladder-preserving combined-modality therapy (CMT) for muscle-invasive bladder cancer (MIBC), reserving cystectomy for salvage treatment. We performed a pooled analysis of long-term outcomes in patients with MIBC enrolled across multiple studies.
Patients and methods: Four hundred sixty-eight patients with MIBC were enrolled onto six RTOG bladder-preservation studies, including five phase II studies (RTOG 8802, 9506, 9706, 9906, and 0233) and one phase III study (RTOG 8903). Overall survival (OS) was estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method, and disease-specific survival (DSS), muscle-invasive and non-muscle-invasive local failure (LF), and distant metastasis (DM) were estimated by the cumulative incidence method.
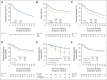
Results: The median age of patients was 66 years (range, 34 to 93 years), and clinical T stage was T2 in 61%, T3 in 35%, and T4a in 4% of patients. Complete response to CMT was documented in 69% of patients. With a median follow-up of 4.3 years among all patients and 7.8 years among survivors (n = 205), the 5- and 10-year OS rates were 57% and 36%, respectively, and the 5- and 10-year DSS rates were 71% and 65%, respectively. The 5- and 10-year estimates of muscle-invasive LF, non-muscle-invasive LF, and DM were 13% and 14%, 31% and 36%, and 31% and 35%, respectively.
Conclusion: This pooled analysis of multicenter, prospective RTOG bladder-preserving CMT protocols demonstrates long-term DSS comparable to modern immediate cystectomy studies, for patients with similarly staged MIBC. Given the low incidence of late recurrences with long-term follow-up, CMT can be considered as an alternative to radical cystectomy, especially in elderly patients not well suited for surgery.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00003930 NCT00055601.
© 2014 by American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest are found in the article online at
Figures

Comment in
-
Organ-sparing multimodality treatment for muscle-invasive bladder cancer: can we continue to ignore the evidence?J Clin Oncol. 2014 Dec 1;32(34):3787-8. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2014.58.5521. Epub 2014 Nov 3. J Clin Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25366679 No abstract available.
-
Re: Long-term outcomes in patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer after selective bladder-preserving combined-modality therapy: a pooled analysis of radiation therapy oncology group protocols 8802, 8903, 9506, 9706, 9906, and 0233.J Urol. 2015 Jun;193(6):1931-2. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2015.03.010. Epub 2015 Mar 13. J Urol. 2015. PMID: 25986789 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Re: Long-Term Outcomes in Patients with Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer After Selective Bladder-Preserving Combined-Modality Therapy: A Pooled Analysis of Radiation Therapy Oncology Group Protocols 8802, 8903, 9506, 9706, 9906, and 0233.Eur Urol. 2015 Jul;68(1):165-6. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2015.03.057. Eur Urol. 2015. PMID: 26088735 No abstract available.
-
Muskelinvasives Harnblasenkarzinom - Blasenerhaltende Therapie.Aktuelle Urol. 2015 Jul;46(4):271-2. doi: 10.1055/s-0035-1559850. Epub 2015 Jul 30. Aktuelle Urol. 2015. PMID: 26227116 German. No abstract available.
References
-
- Stein JP, Lieskovsky G, Cote R, et al. Radical cystectomy in the treatment of invasive bladder cancer: Long-term results in 1,054 patients. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19:666–675. - PubMed
-
- Dalbagni G, Genega E, Hashibe M, et al. Cystectomy for bladder cancer: A contemporary series. J Urol. 2001;165:1111–1116. - PubMed
-
- Zehnder P, Studer UE, Skinner EC, et al. Super extended versus extended pelvic lymph node dissection in patients undergoing radical cystectomy for bladder cancer: A comparative study. J Urol. 2011;186:1261–1268. - PubMed
-
- Madersbacher S, Hochreiter W, Burkhard F, et al. Radical cystectomy for bladder cancer today: A homogeneous series without neoadjuvant therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:690–696. - PubMed
-
- Hautmann RE, Gschwend JE, de Petriconi RC, et al. Cystectomy for transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder: Results of a surgery only series in the neobladder era. J Urol. 2006;176:486–492. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

