Phosphotyrosine profiling identifies ephrin receptor A2 as a potential therapeutic target in esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma
- PMID: 25366905
- PMCID: PMC4309511
- DOI: 10.1002/pmic.201400379
Phosphotyrosine profiling identifies ephrin receptor A2 as a potential therapeutic target in esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma
Abstract
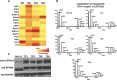
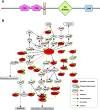
Esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma (ESCC) is one of the most common malignancies in Asia. Currently, surgical resection of early-stage tumor is the best available treatment. However, most patients present late when surgery is not an option. Data suggest that chemotherapy regimens are inadequate for clinical management of advanced cancer. Targeted therapy has emerged as one of the most promising approaches to treat several malignancies. A prerequisite for developing targeted therapy is prior knowledge of proteins and pathways that drive proliferation in malignancies. We carried out phosphotyrosine profiling across four different ESCC cell lines and compared it to non-neoplastic Het-1A cell line to identify activated tyrosine kinase signaling pathways in ESCC. A total of 278 unique phosphopeptides were identified across these cell lines. This included several tyrosine kinases and their substrates that were hyperphosphorylated in ESCC. Ephrin receptor A2 (EPHA2), a receptor tyrosine kinase, was hyperphosphorylated in all the ESCC cell lines used in the study. EPHA2 is reported to be oncogenic in several cancers and is also known to promote metastasis. Immunohistochemistry-based studies have revealed EPHA2 is overexpressed in nearly 50% of ESCC. We demonstrated EPHA2 as a potential therapeutic target in ESCC by carrying out siRNA-based knockdown studies. Knockdown of EPHA2 in ESCC cell line TE8 resulted in significant decrease in cell proliferation and invasion, suggesting it is a promising therapeutic target in ESCC that warrants further evaluation.
Keywords: Biomedicine; In vivo labeling; Mass spectrometry; Post-translational modifications.
© 2014 The Authors. PROTEOMICS published by Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures


Similar articles
-
EphA2 overexpression correlates with poor prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Int J Cancer. 2003 Feb 20;103(5):657-63. doi: 10.1002/ijc.10860. Int J Cancer. 2003. PMID: 12494475
-
Epigenetic silencing of HIC1 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and drives progression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Oncotarget. 2015 Nov 10;6(35):38151-65. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5832. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26510908 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of MiR-31 stimulates expression of LATS2 via the hippo pathway and promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017 Nov 16;36(1):161. doi: 10.1186/s13046-017-0622-1. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 29145896 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted therapy of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: the NRF2 signaling pathway as target.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2018 Dec;1434(1):164-172. doi: 10.1111/nyas.13681. Epub 2018 May 11. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2018. PMID: 29752726 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Chromosomal and genomic aberrations in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma].Yi Chuan. 2012 May;34(5):519-25. doi: 10.3724/sp.j.1005.2012.00519. Yi Chuan. 2012. PMID: 22659423 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Exosome-mediated miR-25/miR-203 as a potential biomarker for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: improving early diagnosis and revealing malignancy.Transl Cancer Res. 2021 Dec;10(12):5174-5182. doi: 10.21037/tcr-21-1123. Transl Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 35116367 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions between EGFR and EphA2 promote tumorigenesis through the action of Ephexin1.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Jun 6;13(6):528. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-04984-6. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 35668076 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphotyrosine profiling of human cerebrospinal fluid.Clin Proteomics. 2018 Sep 12;15:29. doi: 10.1186/s12014-018-9205-1. eCollection 2018. Clin Proteomics. 2018. PMID: 30220890 Free PMC article.
-
Tyrosine Phosphoproteomics of Patient-Derived Xenografts Reveals Ephrin Type-B Receptor 4 Tyrosine Kinase as a Therapeutic Target in Pancreatic Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jul 7;13(14):3404. doi: 10.3390/cancers13143404. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34298619 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-Omics Analysis to Characterize Cigarette Smoke Induced Molecular Alterations in Esophageal Cells.Front Oncol. 2020 Nov 5;10:1666. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01666. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33251127 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pennathur, A. , Gibson, M. K. , Jobe, B. A. , Luketich, J. D. , Oesophageal carcinoma. Lancet 2013, 381, 400–412. - PubMed
-
- Jemal, A. , Bray, F. , Center, M. M. , Ferlay, J. et al., Global cancer statistics.CA Cancer J. Clin. 2011, 61, 69–90. - PubMed
-
- Kashyap, M. K. , Marimuthu, A. , Kishore, C. J. , Peri, S. et al., Genomewide mRNA profiling of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma for identification of cancer biomarkers. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2009, 8, 36–46. - PubMed
-
- Kashyap, M. K. , Pawar, H. A. , Keerthikumar, S. , Sharma, J. et al., Evaluation of protein expression pattern of stanniocalcin 2, insulin‐like growth factor‐binding protein 7, inhibin beta A and four and a half LIM domains 1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Biomark. 2012, 12, 1–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

