Developmental guidance of the retroflex tract at its bending point involves Robo1-Slit2-mediated floor plate repulsion
- PMID: 25366972
- PMCID: PMC4485949
- DOI: 10.1007/s00429-014-0932-4
Developmental guidance of the retroflex tract at its bending point involves Robo1-Slit2-mediated floor plate repulsion
Abstract
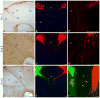
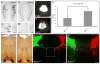
The retroflex tract contains medial habenula efferents that target the hindbrain interpeduncular complex and surrounding areas. This tract displays a singular course. Initially, habenular axons extend ventralwards in front of the pretectum until they reach the basal plate. Next, they avoid crossing the local floor plate, sharply changing course caudalwards (the retroflexion alluded by the tract name) and navigate strictly antero-posteriorly across basal pretectum, midbrain and isthmus. Once they reach rhombomere 1, the habenular axons criss-cross the floor plate several times within the interpeduncular nuclear complex as they innervate it. Here we described the timing and details of growth phenomena as these axons navigate to their target. The first dorsoventral course apparently obeys Ntn1 attraction. We checked the role of local floor plate signaling in the decision to avoid the thalamic floor plate and bend caudalwards. Analyzing the altered floor and basal plates of Gli2 knockout mice, we found a contralateral projection of most habenular axons, plus ulterior bizarre navigation rostralwards. This crossing phenotype was due to a reduced expression of Slit repulsive cues, suggesting involvement of the floor-derived Robo-Slit system in the normal guidance of this tract. Using Slit and Robo mutant mice, open neural tube and co-culture assays, we determined that Robo1-Slit2 interaction is specifically required for impeding that medial habenular axons cross the thalamic floor plate. This pathfinding mechanism is essential to establish the functionally important habenulo-interpeduncular connection.
Keywords: Axon guidance; Floor plate; Habenula; Retroflex tract; Robo-Slit.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures




References
-
- Andres KH, Düring von M, Veh RW. Subnuclear organization of the rat habenular complexes. J Comp Neurol. 1999;407:130–150. - PubMed
-
- Bagri A, Marín O, Plump AS, Mak J, Pleasure SJ, Rubenstein JLR, Tessier-Lavigne M. Slit proteins prevent midline crossing and determine the dorsoventral position of major axonal pathways in the mammalian forebrain. Neuron. 2002;33:233–248. - PubMed
-
- Brose K, Bland KS, Wang KH, Arnott D, Henzel W, Goodman CS, Tessier-Lavigne M, Kidd T. Slit proteins bind Robo receptors and have an evolutionarily conserved role in repulsive axon guidance. Cell. 1999;96:795–806. - PubMed
-
- Charron F, Stein E, Jeong J, McMahon AP, Tessier-Lavigne M. The morphogen sonic hedgehog is an axonal chemoattractant that collaborates with netrin-1 in midline axon guidance. Cell. 2003;113:11–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

