A MATLAB tool for pathway enrichment using a topology-based pathway regulation score
- PMID: 25367050
- PMCID: PMC4255424
- DOI: 10.1186/s12859-014-0358-2
A MATLAB tool for pathway enrichment using a topology-based pathway regulation score
Abstract
Background: Handling the vast amount of gene expression data generated by genome-wide transcriptional profiling techniques is a challenging task, demanding an informed combination of pre-processing, filtering and analysis methods if meaningful biological conclusions are to be drawn. For example, a range of traditional statistical and computational pathway analysis approaches have been used to identify over-represented processes in microarray data derived from various disease states. However, most of these approaches tend not to exploit the full spectrum of gene expression data, or the various relationships and dependencies. Previously, we described a pathway enrichment analysis tool created in MATLAB that yields a Pathway Regulation Score (PRS) by considering signalling pathway topology, and the overrepresentation and magnitude of differentially-expressed genes (J Comput Biol 19:563-573, 2012). Herein, we extended this approach to include metabolic pathways, and described the use of a graphical user interface (GUI).
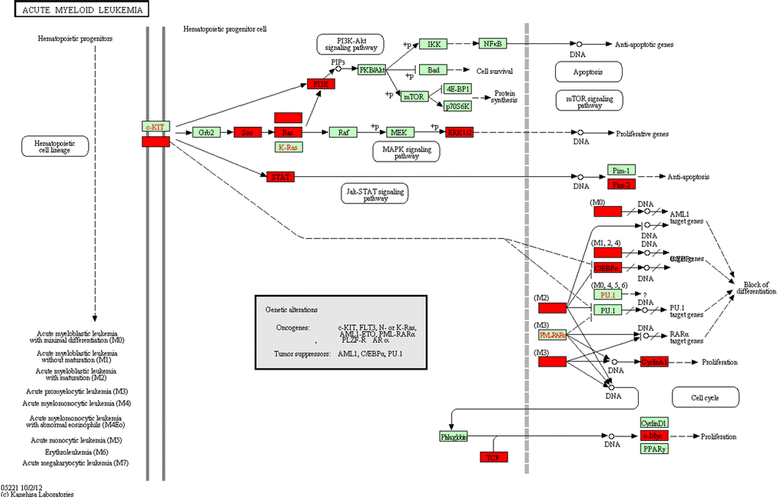
Results: Using input from a variety of microarray platforms and species, users are able to calculate PRS scores, along with a corresponding z-score for comparison. Further pathway significance assessment may be performed to increase confidence in the pathways obtained, and users can view Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway diagrams marked-up to highlight impacted genes.
Conclusions: The PRS tool provides a filter in the isolation of biologically-relevant insights from complex transcriptomic data.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A topology-based score for pathway enrichment.J Comput Biol. 2012 May;19(5):563-73. doi: 10.1089/cmb.2011.0182. Epub 2012 Apr 2. J Comput Biol. 2012. PMID: 22468678
-
MADNet: microarray database network web server.Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Jul 1;36(Web Server issue):W332-5. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn289. Epub 2008 May 14. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008. PMID: 18480121 Free PMC article.
-
GeneMesh: a web-based microarray analysis tool for relating differentially expressed genes to MeSH terms.BMC Bioinformatics. 2010 Apr 1;11:166. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-166. BMC Bioinformatics. 2010. PMID: 20359363 Free PMC article.
-
Co-expression analysis of metabolic pathways in plants.Methods Mol Biol. 2009;553:247-64. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60327-563-7_12. Methods Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19588109 Review.
-
Bioinformatics analysis of microarray data.Methods Mol Biol. 2009;573:259-84. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60761-247-6_15. Methods Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19763933 Review.
Cited by
-
Pathway-Informed Classification System (PICS) for Cancer Analysis Using Gene Expression Data.Cancer Inform. 2016 Jul 27;15:151-61. doi: 10.4137/CIN.S40088. eCollection 2016. Cancer Inform. 2016. PMID: 27486299 Free PMC article.
-
ToPASeq: an R package for topology-based pathway analysis of microarray and RNA-Seq data.BMC Bioinformatics. 2015 Oct 29;16:350. doi: 10.1186/s12859-015-0763-1. BMC Bioinformatics. 2015. PMID: 26514335 Free PMC article.
-
Kinetic changes of intestinal microbiota in the course of intestinal sensitization.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 6;7(49):81197-81207. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12797. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27783988 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zeeberg BR, Feng W, Wang G, Wang MD, Fojo AT, Sunshine M, Narasimhan S, Kane DW, Reinhold WC, Lababidi S, Bussey KJ, Riss J, Barrett JC, Weinstein JN. GoMiner: a resource for biological interpretation of genomic and proteomic data. Genome Biol. 2003;4(4):R28. doi: 10.1186/gb-2003-4-4-r28. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

