Down-regulating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator-1 beta alleviates the proinflammatory effect of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes through inhibiting extracellular signal-regulated kinase, p38 and nuclear factor-kappaB activation
- PMID: 25367151
- PMCID: PMC4237730
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-014-0472-6
Down-regulating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator-1 beta alleviates the proinflammatory effect of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes through inhibiting extracellular signal-regulated kinase, p38 and nuclear factor-kappaB activation
Abstract
Introduction: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory disease leading to joint destruction and disability. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator-1 beta (PGC-1β) is a transcriptional coactivator that plays important roles in regulating multiple aspects of energy metabolism and cytokine signaling pathways. PGC-1β overexpression leads to the attenuation of macrophage-mediated inflammation. In this study, we aimed to determine the expression of PGC-1β in RA synovium and fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS), and explore the mechanisms of PGC-1β on both the proinflammatory effects and apoptosis in RA-FLS.
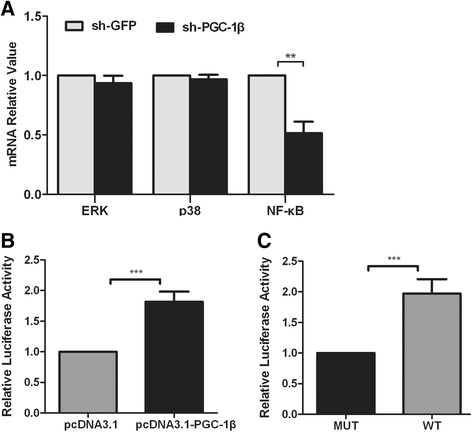
Methods: Synovium was obtained from 31 patients with active RA, as well as 13 osteoarthritis (OA) and 10 orthopedic arthropathies (Orth.A) as "less inflamed" disease controls. FLS were then isolated and cultured. Synovial PGC-1β expression was determined by immunohistochemistry staining, while FLS PGC-1β expression was detected by immunofluorescence staining, quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) assay and western blot. PGC-1β was depleted by lentivirus sh-RNA, and up-regulated by pcDNA3.1- PGC-1β. The expression of proinflammatory cytokines, matrix metalloproteinases and receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB ligand was analyzed by qPCR, cytometric bead array and western blot. The expression of mitogen-activated protein kinases and nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-κB) was determined by qPCR and western blot. Besides, cell apoptosis was examined using flow cytometry. The interaction between PGC-1β and NF-κB was performed by dual-luciferase reporter gene assays.
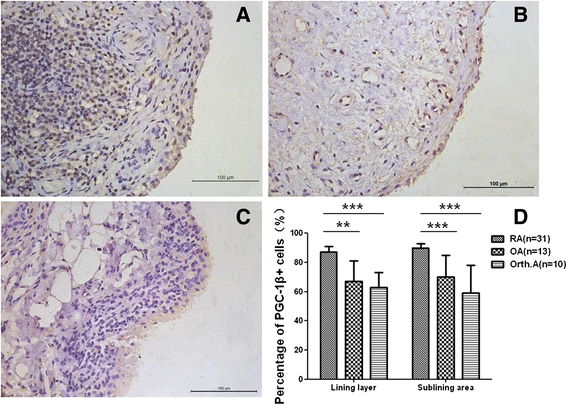
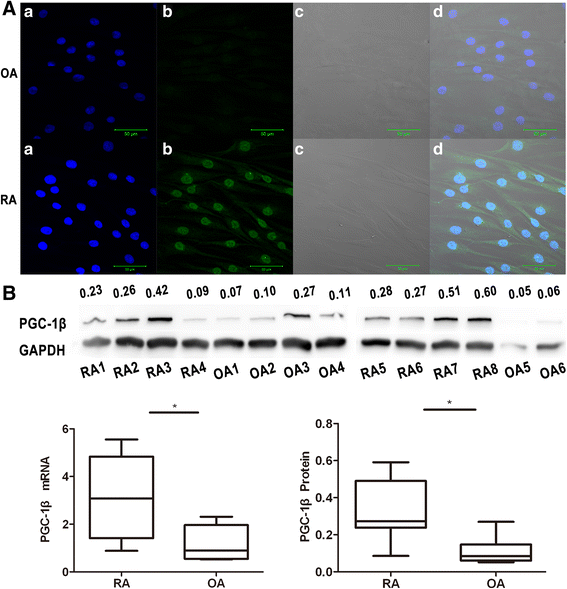
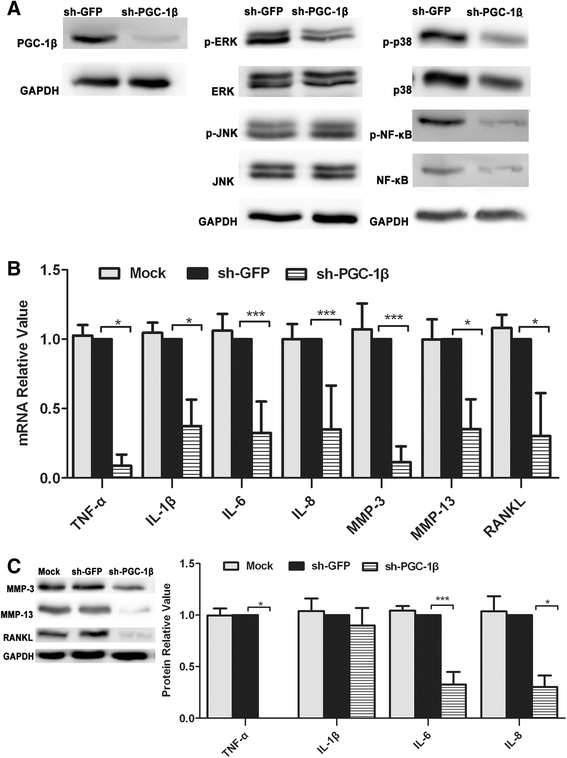
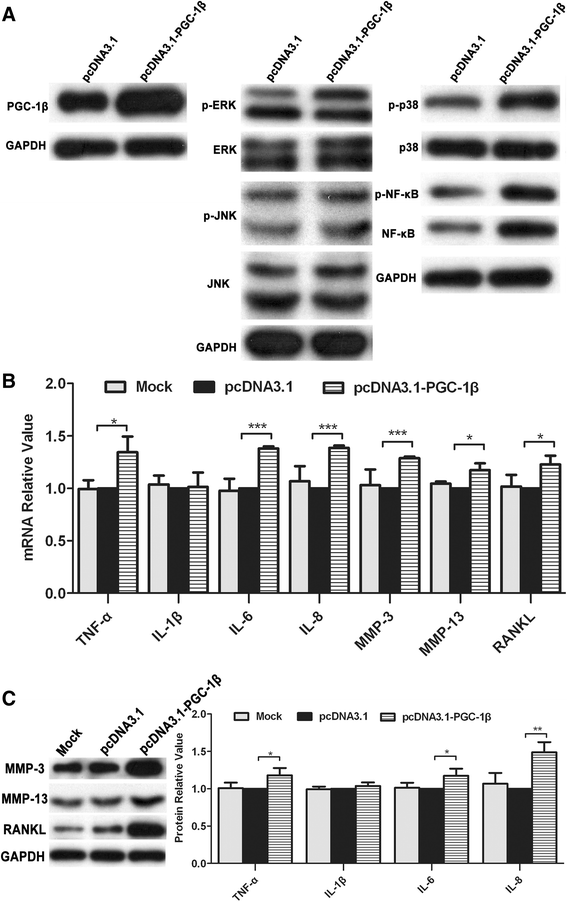
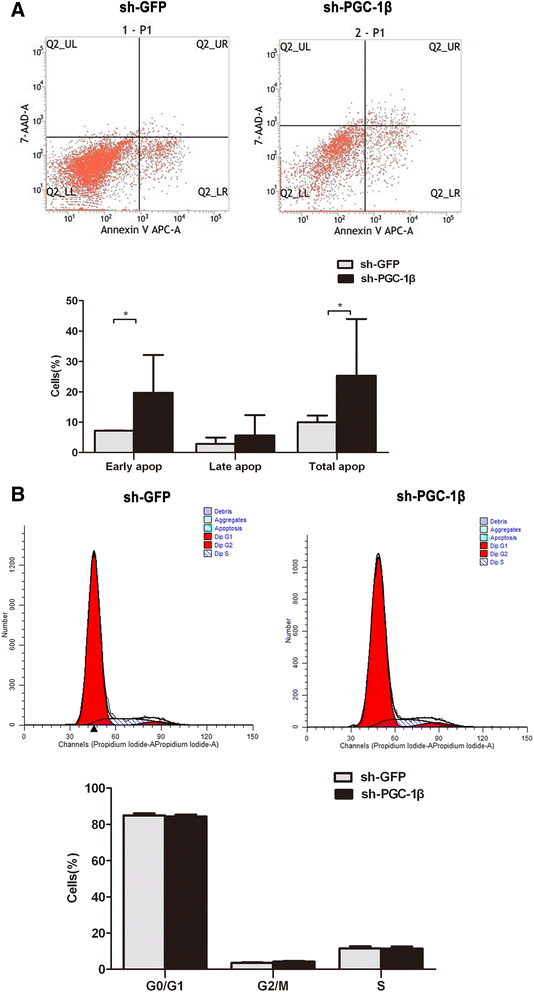
Results: (A) Synovial PGC-1β was over-expressed in RA patients compared with OA or Orth.A patients. (B) PGC-1β expression significantly increased in RA-FLS compared with OA-FLS. (C) PGC-1β mediated the expression of proinflammatory cytokines and apoptosis through extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), p38 and NF-κB in RA-FLS. (D) PGC-1β mediated NF-κB transcription in RA-FLS, but did not affect ERK and p38.
Conclusion: The results indicate that PGC-1β may play important roles in the proinflammatory effects and apoptosis of RA-FLS.
Figures
References
-
- Jackson JR, Minton JA, Ho ML, Wei N, Winkler JD. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in synovial fibroblasts is induced by hypoxia and interleukin 1beta. J Rheumatol. 1997;24:1253–1259. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

