Alternative approaches to Hsp90 modulation for the treatment of cancer
- PMID: 25367392
- PMCID: PMC4406230
- DOI: 10.4155/fmc.14.89
Alternative approaches to Hsp90 modulation for the treatment of cancer
Abstract
Hsp90 is responsible for the conformational maturation of newly synthesized polypeptides (client proteins) and the re-maturation of denatured proteins via the Hsp90 chaperone cycle. Inhibition of the Hsp90 N-terminus has emerged as a clinically relevant strategy for anticancer chemotherapeutics due to the involvement of clients in a variety of oncogenic pathways. Several immunophilins, co-chaperones and partner proteins are also necessary for Hsp90 chaperoning activity. Alternative strategies to inhibit Hsp90 function include disruption of the C-terminal dimerization domain and the Hsp90 heteroprotein complex. C-terminal inhibitors and Hsp90 co-chaperone disruptors prevent cancer cell proliferation similar to N-terminal inhibitors and destabilize client proteins without induction of heat shock proteins. Herein, current Hsp90 inhibitors, the chaperone cycle, and regulation of this cycle will be discussed.
Figures


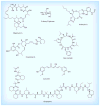

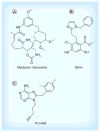

References
-
- Pratt WB. The role of heat shock proteins in regulating the function, folding, and trafficking of the glucocorticoid receptor. J Biol Chem. 1993;268(29):21455–21458. - PubMed
-
- Csermely P, Schnaider T, SoTi C, Prohászka Z, Nardai G. The 90-kDa molecular chaperone family: structure, function, and clinical applications. A comprehensive review. Pharmacol Ther. 1998;79(2):129–168. - PubMed
-
- Taipale M, Jarosz DF, Lindquist S. HSP90 at the hub of protein homeostasis: emerging mechanistic insights. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010;11(7):515–528. - PubMed
-
- Li J, Soroka J, Buchner J. The Hsp90 chaperone machinery: conformational dynamics and regulation by co-chaperones. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1823(3):624–635. - PubMed
-
- Li J, Buchner J. Structure, function and regulation of the Hsp90 machinery. Biomed J. 2013;36(3):106–117. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
