Specific-detection of clinical samples, systematic functional investigations, and transcriptome analysis reveals that splice variant MUC4/Y contributes to the malignant progression of pancreatic cancer by triggering malignancy-related positive feedback loops signaling
- PMID: 25367394
- PMCID: PMC4236435
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-014-0309-8
Specific-detection of clinical samples, systematic functional investigations, and transcriptome analysis reveals that splice variant MUC4/Y contributes to the malignant progression of pancreatic cancer by triggering malignancy-related positive feedback loops signaling
Abstract
Background: MUC4 plays important roles in the malignant progression of human pancreatic cancer. But the huge length of MUC4 gene fragment restricts its functional and mechanism research. As one of its splice variants, MUC4/Y with coding sequence is most similar to that of the full-length MUC4 (FL-MUC4), together with alternative splicing of the MUC4 transcript has been observed in pancreatic carcinomas but not in normal pancreas. So we speculated that MUC4/Y might be involved in malignant progression similarly to FL-MUC4, and as a research model of MUC4 in pancreatic cancer. The conjecture was confirmed in the present study.
Methods: MUC4/Y expression was detected by real-time quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) using gene-specific probe in the clinic samples. The effects of MUC4/Y were observed by serial in vitro and in vivo experiments based on stable over-expressed cell model. The underlying mechanisms were investigated by sequence-based transcriptome analysis and verified by qRT-PCR, Western blot and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays.
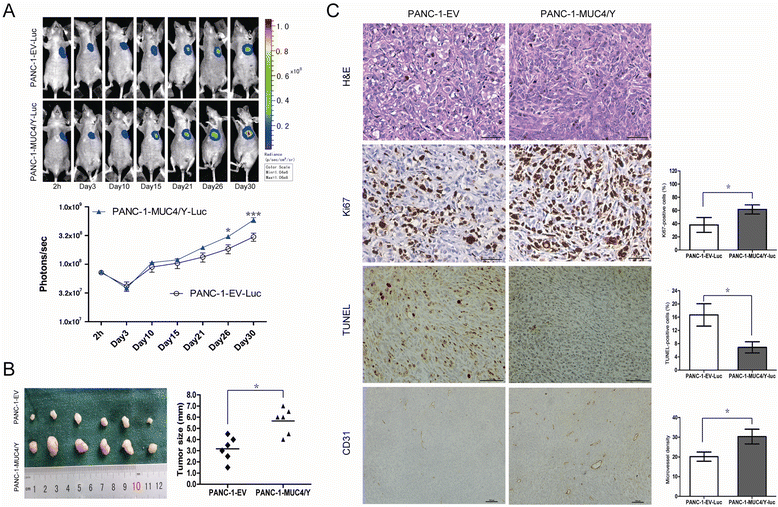
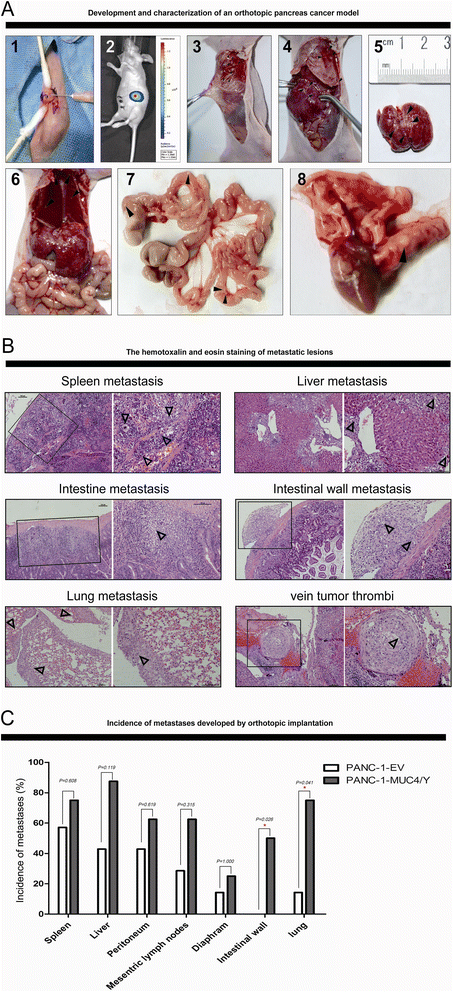
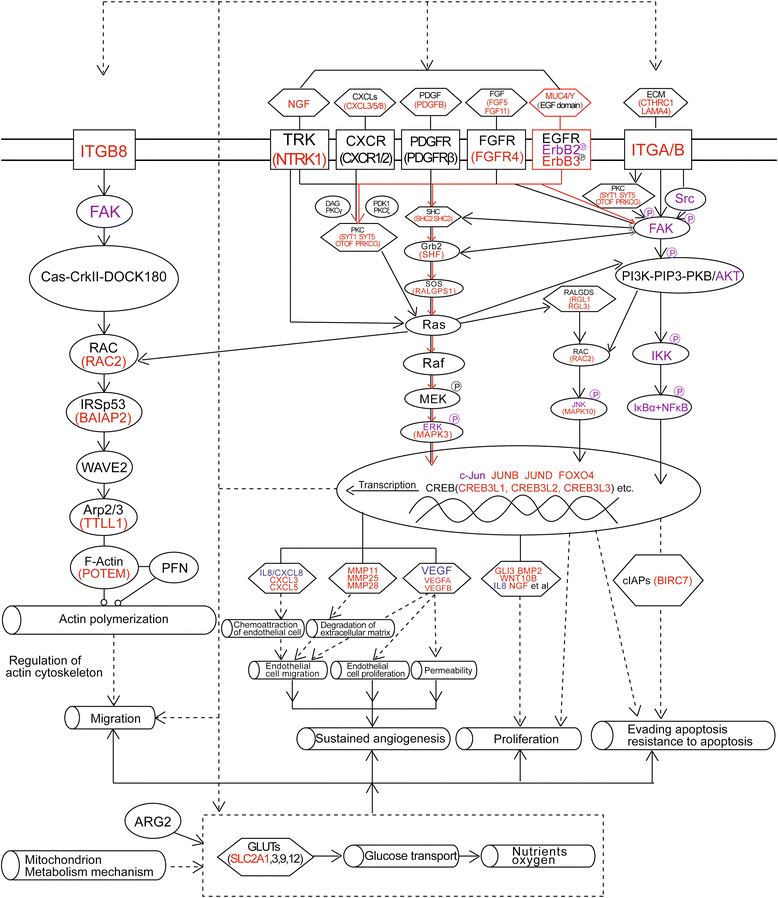
Results: The detection of clinical samples indicates that MUC4/Y is significantly positive-correlated with tumor invasion and distant metastases. Based on stable forced-expressed pancreatic cancer PANC-1 cell model, functional studies show that MUC4/Y enhances malignant activity in vitro and in vivo, including proliferation under low-nutritional-pressure, resistance to apoptosis, motility, invasiveness, angiogenesis, and distant metastasis. Mechanism studies indicate the novel finding that MUC4/Y triggers malignancy-related positive feedback loops for concomitantly up-regulating the expression of survival factors to resist adverse microenvironment and increasing the expression of an array of cytokines and adhesion molecules to affect the tumor milieu.
Conclusions: In light of the enormity of the potential regulatory circuitry in cancer afforded by MUC4 and/or MUC4/Y, repressing MUC4 transcription, inhibiting post-transcriptional regulation, including alternative splicing, or blocking various pathways simultaneously may be helpful for controlling malignant progression. MUC4/Y- expression model is proven to a valuable tool for the further dissection of MUC4-mediated functions and mechanisms.
Figures





References
-
- Porchet N, Nguyen VC, Dufosse J, Audie JP, Guyonnet-Duperat V, Gross MS, Denis C, Degand P, Bernheim A, Aubert JP. Molecular cloning and chromosomal localization of a novel human tracheo-bronchial mucin cDNA containing tandemly repeated sequences of 48 base pairs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991;175:414–422. doi: 10.1016/0006-291X(91)91580-6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gross MS, Guyonnet-Duperat V, Porchet N, Bernheim A, Aubert JP, Nguyen VC. Mucin 4 (MUC4) gene: regional assignment (3q29) and RFLP analysis. Ann Genet. 1992;35:21–26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

