Recombinant human leptin treatment in genetic lipodystrophic syndromes: the long-term Spanish experience
- PMID: 25367549
- PMCID: PMC4412649
- DOI: 10.1007/s12020-014-0450-4
Recombinant human leptin treatment in genetic lipodystrophic syndromes: the long-term Spanish experience
Abstract
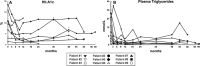
Lipodystrophies are a group of diseases mainly characterized by a loss of adipose tissue and frequently associated with insulin resistance, hypertriglyceridemia, and hepatic steatosis. In uncommon lipodystrophies, these complications frequently are difficult to control with conventional therapeutic approaches. This retrospective study addressed the effectiveness of recombinant methionyl leptin (metreleptin) for improving glucose metabolism, lipid profile, and hepatic steatosis in patients with genetic lipodystrophic syndromes. We studied nine patients (five females and four males) with genetic lipodystrophies [seven with Berardinelli-Seip syndrome, one with atypical progeroid syndrome, and one with type 2 familial partial lipodystrophy (FPLD)]. Six patients were children under age 9 years, and all patients had baseline triglycerides levels >2.26 mmol/L and hepatic steatosis; six had poorly controlled diabetes mellitus. Metreleptin was self-administered subcutaneously daily at a final dose that ranged between 0.05 and 0.24 mg/(kg day) [median: 0.08 mg/(kg day)] according to the body weight. The duration of treatment ranged from 9 months to 5 years, 9 months (median: 3 years). Plasma glucose, hemoglobin A1c (Hb A1c), lipid profile, plasma insulin and leptin, and hepatic enzymes were evaluated at baseline and at least every 6 months. Except for the patient with FPLD, metreleptin replacement significantly improved metabolic control (Hb A1c: from 10.4 to 7.1 %, p < 0.05). Plasma triglycerides were reduced 76 % on average, and hepatic enzymes decreased more than 65 %. This study extends knowledge about metreleptin replacement in genetic lipodystrophies, bearing out its effectiveness for long periods of time.
Figures

References
-
- Vantyghem MC, Balavoine AS, Douillard C, Defrance F, Dieudonne L, Mouton F, Lemaire C, Bertrand-Escouflaire N, Bourdelle-Hego MF, Devemy F, Evrard A, Gheerbrand D, Girardot C, Gumuche S, Hober C, Topolinski H, Lamblin B, Mycinski B, Ryndak A, Karrouz W, Duvivier E, Merlen E, Cortet C, Weill J, Lacroix D, Wémeau JL. How to diagnose a lipodystrophy syndrome. Ann. Endocrinol. 2012;73:170–189. doi: 10.1016/j.ando.2012.04.010. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

