Cationic liposomal sodium stibogluconate (SSG), a potent therapeutic tool for treatment of infection by SSG-sensitive and -resistant Leishmania donovani
- PMID: 25367907
- PMCID: PMC4291371
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.03305-14
Cationic liposomal sodium stibogluconate (SSG), a potent therapeutic tool for treatment of infection by SSG-sensitive and -resistant Leishmania donovani
Abstract
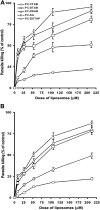
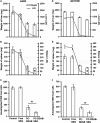
Pentavalent antimonials have been the first-line treatment for leishmaniasis for decades. However, the development of resistance to sodium stibogluconate (SSG) has limited its use, especially for treating visceral leishmaniasis (VL). The present work aims to optimize a cationic liposomal formulation of SSG for the treatment of both SSG-sensitive (AG83) and SSG-resistant (GE1F8R and CK1R) Leishmania donovani infections. Parasite killing was determined by the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay and microscopic counting of Giemsa-stained macrophages. Macrophage uptake studies were carried out by confocal microscopic imaging. Parasite-liposome interactions were visualized through transmission electron microscopy. Toxicity tests were performed using assay kits. Organ parasite burdens were determined by microscopic counting and limiting dilution assays. Cytokines were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs) and flow cytometry. Although all cationic liposomes studied demonstrated leishmanicidal activity, phosphatidylcholine (PC)-dimethyldioctadecylammonium bromide (DDAB) vesicles were most effective, followed by PC-stearylamine (SA) liposomes. Since entrapment of SSG in PC-DDAB liposomes demonstrated enhanced ultrastructural alterations in promastigotes, PC-DDAB-SSG vesicles were further investigated in vitro and in vivo. PC-DDAB-SSG could effectively alleviate SSG-sensitive and SSG-resistant L. donovani infections in the liver, spleen, and bone marrow of BALB/c mice at a dose of SSG (3 mg/kg body weight) not reported previously. The parasiticidal activity of these vesicles was attributed to better interactions with the parasite membranes, resulting in direct killing, and generation of a strong host-protective environment, necessitating a very low dose of SSG for effective cures.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Therapy with sodium stibogluconate in stearylamine-bearing liposomes confers cure against SSG-resistant Leishmania donovani in BALB/c mice.PLoS One. 2011 Mar 10;6(3):e17376. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017376. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21423750 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacies of vesicular and free sodium stibogluconate formulations against clinical isolates of Leishmania donovani.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2001 Dec;45(12):3555-9. doi: 10.1128/AAC.45.12.3555-3559.2001. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2001. PMID: 11709339 Free PMC article.
-
Refractoriness to the treatment of sodium stibogluconate in Indian kala-azar field isolates persist in in vitro and in vivo experimental models.Parasitol Res. 2005 Jun;96(4):216-23. doi: 10.1007/s00436-005-1339-1. Epub 2005 May 3. Parasitol Res. 2005. PMID: 15868188
-
Treatment outcomes of visceral leishmaniasis in Ethiopia from 2001 to 2017: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Infect Dis Poverty. 2018 Oct 19;7(1):108. doi: 10.1186/s40249-018-0491-7. Infect Dis Poverty. 2018. PMID: 30340519 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophage specific drug delivery in experimental leishmaniasis.Curr Mol Med. 2004 Sep;4(6):681-9. doi: 10.2174/1566524043360186. Curr Mol Med. 2004. PMID: 15357216 Review.
Cited by
-
Nano- and Microformulations to Advance Therapies for Visceral Leishmaniasis.ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2021 May 10;7(5):1725-1741. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.0c01132. Epub 2020 Oct 14. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2021. PMID: 33966377 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA-Seq Revealed Expression of Many Novel Genes Associated With Leishmania donovani Persistence and Clearance in the Host Macrophage.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019 Feb 5;9:17. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00017. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30805314 Free PMC article.
-
Case report: Application of metagenomic next-generation sequencing in the diagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis and its treatment evaluation.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Jan 13;9:1044043. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.1044043. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36714105 Free PMC article.
-
Exploiting knowledge on pharmacodynamics-pharmacokinetics for accelerated anti-leishmanial drug discovery/development.Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2019 Jul;15(7):595-612. doi: 10.1080/17425255.2019.1629417. Epub 2019 Jun 17. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 31174439 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cutaneous Manifestations of Human and Murine Leishmaniasis.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Jun 18;18(6):1296. doi: 10.3390/ijms18061296. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28629171 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bern C, Adler-Moore J, Berenguer J, Boelaert M, den Boer M, Davidson RN, Figueras C, Gradoni L, Kafetzis DA, Ritmeijer K, Rosenthal E, Royce C, Russo R, Sundar S, Alvar J. 2006. Liposomal amphotericin B for the treatment of visceral leishmaniasis. Clin Infect Dis 43:917–924. doi:10.1086/507530. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

