Syk and Src family kinases regulate C-type lectin receptor 2 (CLEC-2)-mediated clustering of podoplanin and platelet adhesion to lymphatic endothelial cells
- PMID: 25368330
- PMCID: PMC4276840
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.584284
Syk and Src family kinases regulate C-type lectin receptor 2 (CLEC-2)-mediated clustering of podoplanin and platelet adhesion to lymphatic endothelial cells
Abstract
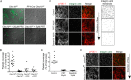
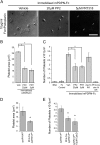
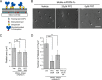
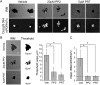
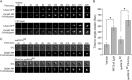
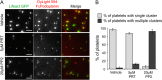
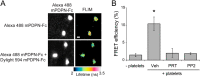
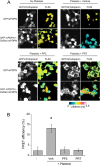
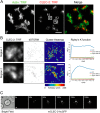
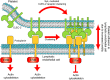
The interaction of C-type lectin receptor 2 (CLEC-2) on platelets with Podoplanin on lymphatic endothelial cells initiates platelet signaling events that are necessary for prevention of blood-lymph mixing during development. In the present study, we show that CLEC-2 signaling via Src family and Syk tyrosine kinases promotes platelet adhesion to primary mouse lymphatic endothelial cells at low shear. Using supported lipid bilayers containing mobile Podoplanin, we further show that activation of Src and Syk in platelets promotes clustering of CLEC-2 and Podoplanin. Clusters of CLEC-2-bound Podoplanin migrate rapidly to the center of the platelet to form a single structure. Fluorescence lifetime imaging demonstrates that molecules within these clusters are within 10 nm of one another and that the clusters are disrupted by inhibition of Src and Syk family kinases. CLEC-2 clusters are also seen in platelets adhered to immobilized Podoplanin using direct stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy. These findings provide mechanistic insight by which CLEC-2 signaling promotes adhesion to Podoplanin and regulation of Podoplanin signaling, thereby contributing to lymphatic vasculature development.
Keywords: CLEC-2; Endothelial Cell; ITAM; Lipid Bilayer; Platelet; Podoplanin; Receptor; Src Family Kinase; Syk; Tyrosine-Protein Kinase (Tyrosine Kinase).
© 2014 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Suzuki-Inoue K., Fuller G. L., García A., Eble J. A., Pöhlmann S., Inoue O., Gartner T. K., Hughan S. C., Pearce A. C., Laing G. D., Theakston R. D., Schweighoffer E., Zitzmann N., Morita T., Tybulewicz V. L., Ozaki Y., Watson S. P. (2006) A novel Syk-dependent mechanism of platelet activation by the C-type lectin receptor CLEC-2. Blood 107, 542–549 - PubMed
-
- Colonna M., Samaridis J., Angman L. (2000) Molecular characterization of two novel C-type lectin-like receptors, one of which is selectively expressed in human dendritic cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 30, 697–704 - PubMed
-
- Spalton J. C., Mori J., Pollitt A. Y., Hughes C. E., Eble J. A., Watson S. P. (2009) The novel Syk inhibitor R406 reveals mechanistic differences in the initiation of GPVI and CLEC-2 signaling in platelets. J. Thromb. Haemost. 7, 1192–1199 - PubMed
-
- Hughes C. E., Sinha U., Pandey A., Eble J. A., O'Callaghan C. A., Watson S. P. (2013) Critical Role for an acidic amino acid region in platelet signaling by the HemITAM (hemi-immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif) containing receptor CLEC-2 (C-type lectin receptor-2). J. Biol. Chem. 288, 5127–5135 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

